|
Djibouti Xeric Shrublands
The Djibouti xeric shrublands is an ecoregion defined by One Earth, consisting of a semi-desert strip on or near the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden coasts in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti and Somalia. This ecoregion lies mainly between sea level and 800 meters (m) elevation. There are, however, many hills and massifs, which range up to 1300 m as well as outstanding fault-induced depressions, such as the Danakil, lying as low as 155 m below sea level. This region is extremely active tectonically, experiencing many earthquakes and intermittently active volcanoes. Rainfall is very low and yearly averages range from 100 to 200 millimeters (mm), with less rain falling closer to the coast. There are many species of interest, including the endemic Archer's lark (''Heteromirafra archeri''), a species of dragon tree (''Dracaena ombet''), and a large suite of desert ungulates, including the last viable population of African wild ass (''Equus africanus somalicus''). Location and description Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awash River
The Awash (sometimes spelled Awaash; Oromo: ''Awaash'', Amharic: አዋሽ, Afar: ''We'ayot'', Somali: ''Webiga Dir'') is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of interconnected lakes that begin with Lake Gargori and end with Lake Abbe (or Abhe Bad) on the border with Djibouti, some 100 kilometres (60 or 70 miles) from the head of the Gulf of Tadjoura. It is the principal stream of an endorheic drainage basin covering parts of the Amhara, Oromia and Somali Regions, as well as the southern half of the Afar Region. The Awash Valley (and especially the Middle Awash) is internationally famous for its high density of hominin fossils, offering unparalleled insight into the early evolution of humans. " Lucy", one of the most famous early hominin fossils, was discovered in the lower Awash Valley. For its paleontological and anthropological importance, the lower valley of the Awash was inscribed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
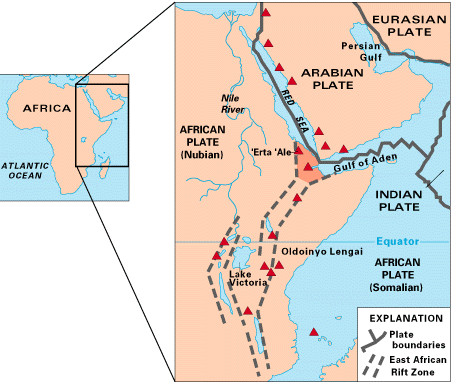
Gulf Of Aden
The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, Socotra and Somalia to the south. In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east. To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti. The ancient Greeks regarded the gulf as one of the most important parts of the Erythraean Sea. It later came to be dominated by Muslims, as the area around the gulf converted to Islam. From the late 1960s onwards, there started to be an increased Soviet naval presence in the Gulf. The importance of the Gulf of Aden declined when the Suez Canal was closed, but it was revitalized when the canal was reopened in 1975, after being deepened and widened by the Egyptian government. The waterway is part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danakil Alps
The Danakil Alps are a highland region in Ethiopia and Eritrea with peaks over 1000 metres in height and a width varying between 40 and 70 kilometres. The alps lie to the east of the Danakil Depression and separate it from the southern Red Sea. A rift escarpment facing the Red Sea forms the eastern boundary of the range. Geologically these highlands are described as a horst and are sometimes referred to as the Danakil Horst or Danakil Block. They were formed by geological faulting which has occurred since the Miocene epoch. There is Precambrian basement rock underlying the region and in coastal Eritrea Precambrian and Mesozoic rocks are exposed. The basement rock of the alps has become overlaid with flood basalt since the Oligocene epoch. About 20 million years ago the Afar rift zone opened up. This resulted in the alps breaking away from the Ethiopian plateau to which they had previously been attached and drifting to the east/northeast. The Danakil Alps contains many volcanic e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Awasa
Lake Hawassa or Awasa, is an endorheic basin in Sidama Region of Ethiopia, located in the Main Ethiopian Rift south of Addis Ababa, the capital city of the country. According to the ''Statistical Abstract of Ethiopia for 1967/68'', the lake is 16 km long and 9 km wide, with a surface area of 129 square kilometers. It has a maximum depth of 10 meters and is located at an elevation of 1,708 meters. It is located inside the Awasa Caldera. Because it is relatively accessible to scientists, Lake Hawassa is the most studied of the Rift Valley lakes in Ethiopia. According to William Taylor, a member of the African Lakes and Rivers Research Group at the University of Waterloo, Lake Hawassa is, despite its lack of an outflow, "essentially a freshwater lake (conductivity is variable, but less than 1,000) indicating that it must have a subterranean outlet." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Rift Valley, Ethiopia
The Great Rift Valley of Ethiopia, (or Main Ethiopian Rift or Ethiopian Rift Valley) is a branch of the East African Rift that runs through Ethiopia in a southwest direction from the Afar Triple Junction. In the past, it was seen as part of a "Great Rift Valley" that ran from Mozambique to Syria. Description The Great Rift Valley lies between the Ethiopian Plateau to the north and the Somalia Plateau to the south. The rift developed as the Nubian and Somali plates began to separate during the Miocene Period along the East African rift system. Rift initiation was asynchronous along the Ethiopian rift valley: deformation began around 18 million years ago at the south end, around 11 million years ago close to the Afar depression and probably around 6-8 million years ago in the central sector. The rift is extending in an ESE-WNW direction at about annually. The Ethiopian rift valley is about wide and bordered on both margins by large, discontinuous normal faults that give rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Highlands
The Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia in Northeast Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below , while the summits reach heights of up to . It is sometimes called the Roof of Africa due to its height and large area. Most of the Ethiopian Highlands are part of central and northern Ethiopia, and its northernmost portion reaches into Eritrea. History In the southern parts of the Ethiopian Highlands once was located the Kingdom of Kaffa, a medieval early modern state, whence the coffee plant was exported to the Arabian Peninsula. The land of the former kingdom is mountainous with stretches of forest. The land is very fertile, capable of three harvests a year. The term ''coffee'' derives from the ar, قهوة, italic=no ()''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "coffee, ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1891. and is traced to Kaffa. Physical geography The Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afar Triangle
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans. The Depression overlaps the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti and the entire Afar Region of Ethiopia; and it contains the lowest point in Africa, Lake Assal, Djibouti, at below sea level. The Awash River is the main waterflow into the region, but it runs dry during the annual dry season, and ends as a chain of saline lakes. The northern part of the Afar Depression is also known as the Danakil Depression. The lowlands are affected by heat, drought, and minimal air circulation, and contain the hottest places (year-round average temperatures) of anywhere on Earth. The Afar Triangle is bordered as follows (see the topo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somaliland
Somaliland,; ar, صوماليلاند ', ' officially the Republic of Somaliland,, ar, جمهورية صوماليلاند, link=no ''Jumhūrīyat Ṣūmālīlānd'' is a ''List of states with limited recognition, de facto'' sovereign state in the Horn of Africa, still considered internationally to be part of Somalia. Somaliland lies in the Horn of Africa, on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden. It is bordered by Djibouti to the northwest, Ethiopia to the south and west, and Somalia to the east.Encyclopædia Britannica, ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica'', (Encyclopædia Britannica: 2002), p.835 Its claimed territory has an area of , with approximately 5.7 million residents as of 2021. The capital and largest city is Hargeisa. The government of Somaliland regards itself as the Succession of states, successor state to British Somaliland, which, as the briefly independent State of Somaliland, united in 1960 with the Trust Territory of Somaliland (the former Italian Soma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Wild Ass
The African wild ass (''Equus africanus'') or African wild donkey is a wild member of the horse family, Equidae. This species is thought to be the ancestor of the domestic donkey (''Equus asinus''), which is sometimes placed within the same species. They live in the deserts and other arid areas of the Horn of Africa, in Eritrea, Ethiopia and Somalia. It formerly had a wider range north and west into Sudan, Egypt, and Libya. It is Critically Endangered, with about 570 individuals existing in the wild. Description The African wild ass is about tall and weighs approximately . The short, smooth coat is a light grey to fawn colour, fading quickly to white on the undersides and legs. There is a slender, dark dorsal stripe in all subspecies, while in the Nubian wild ass (''E. a. africanus''), as well as the domestic donkey, there is a stripe across the shoulder. The legs of the Somali wild ass (''E. a. somaliensis'') are horizontally striped with black, resembling those of a z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the land surface of the Earth is arid or semi-arid. This includes much of the polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks, which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter, and the resulting fragments and rubble strewn over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dracaena Ombet
''Dracaena ombet'', commonly known as Gabal Elba dragon tree, is a species of plant belonging to the Asparagaceae family, formerly included in the Ruscaceae. It is found in northeastern Africa and the western Arabian Peninsula. Description It is a tree that reaches a size of 2-8 m in height, with a forked trunk, produces a red resin. The leaves form dense rosettes at the ends of the branches, these are linear with a broad base, 40-60 x up to 3 cm, gradually tapering to the tip that is sharp, thick and rigid, with smooth margins, flat to concave in the top. The inflorescence is panicle-shaped, 0.5 m long, highly branched, glabrous or pubescent, with tiny, ovate-lanceolate bracts . Whitish tepals, 4-6 mm long, linear. Stamens somewhat shorter than tepals; flattened filaments. The fruit in the form of berries 10-12 mm in diameter. Distribution It is found at an altitude of 1000-1800 m in Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia, Sudan and Saudi A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)
