|
Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction To Ammonium
Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA), also known as nitrate/nitrite ammonification, is the result of anaerobic respiration by chemoorganoheterotrophic microbes using nitrate (NO3−) as an electron acceptor for respiration. In anaerobic conditions microbes which undertake DNRA oxidise organic matter and use nitrate (rather than oxygen) as an electron acceptor, reducing it to nitrite, and then to ammonium (NO3− → NO2− → NH4+). Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium is more common in prokaryotes but may also occur in eukaryotic microorganisms. DNRA is a component of the terrestrial and oceanic nitrogen cycle. Unlike denitrification, it acts to conserve bioavailable nitrogen in the system, producing soluble ammonium rather than unreactive nitrogen gas (). Background and process Cellular process Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium is a two step process, reducing NO3− to NO2− then NO2− to NH4+, though the reaction may begin with NO2− direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen (O2). Although oxygen is not the final electron acceptor, the process still uses a respiratory electron transport chain. In aerobic organisms undergoing respiration, electrons are shuttled to an electron transport chain, and the final electron acceptor is oxygen. Molecular oxygen is an excellent electron acceptor. Anaerobes instead use less-oxidizing substances such as nitrate (), fumarate (), sulfate (), or elemental sulfur (S). These terminal electron acceptors have smaller reduction potentials than O2. Less energy per oxidized molecule is released. Therefore, anaerobic respiration is less efficient than aerobic. As compared with fermentation Anaerobic cellular respiration and fermentation generate ATP in very different ways, and the terms should not be treated as synonyms. Cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) uses highly reduced chemical compounds such as NADH and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea and the Maldives, on the southwest by Somalia. Its total area is and its maximum depth is . The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf. Geography The Arabian Sea's surface area is about .Arabian Sea Encyclopædia Britannica The maximum width of the sea is approximately , and its maximum depth is . The biggest river flowing into the sea is the Indus River. The Arabian Sea has two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anammox
Anammox, an abbreviation for "anaerobic ammonium oxidation", is a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle that takes place in many natural environments. The bacteria mediating this process were identified in 1999, and were a great surprise for the scientific community. In the anammox reaction, nitrite and ammonium ions are converted directly into diatomic nitrogen and water. The bacteria that perform the anammox process are genera that belong to the bacterial phylum Planctomycetota. The anammox bacteria all possess one anammoxosome, a lipid bilayer membrane-bound compartment inside the cytoplasm in which the anammox process takes place. The anammoxosome membranes are rich in ladderane lipids; the presence of these lipids is so far unique in biology. "Anammox" is also the trademarked name for an anammox-based ammonium removal technology developedJetten Michael Silvester Maria, Van Loosdrecht Marinus Corneli; Technische Universiteit Delftpatent WO9807664/ref> b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoxic Waters
Anoxic waters are areas of sea water, fresh water, or groundwater that are depleted of dissolved oxygen. The US Geological Survey defines anoxic groundwater as those with dissolved oxygen concentration of less than 0.5 milligrams per litre. Anoxic waters can be contrasted with hypoxic waters, which are low (but not lacking) in dissolved oxygen. Often, hypoxia is defined as waters that have less than 2 milligrams per litre of dissolved oxygen. This condition is generally found in areas that have restricted water exchange. In most cases, oxygen is prevented from reaching the deeper levels by a physical barrier, as well as by a pronounced density stratification, in which, for instance, denser, colder or hypersaline waters rest at the bottom of a basin. Anoxic conditions will occur if the rate of oxidation of organic matter by bacteria is greater than the supply of dissolved oxygen. Anoxic waters are a natural phenomenon, and have occurred throughout geological history. The Permia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
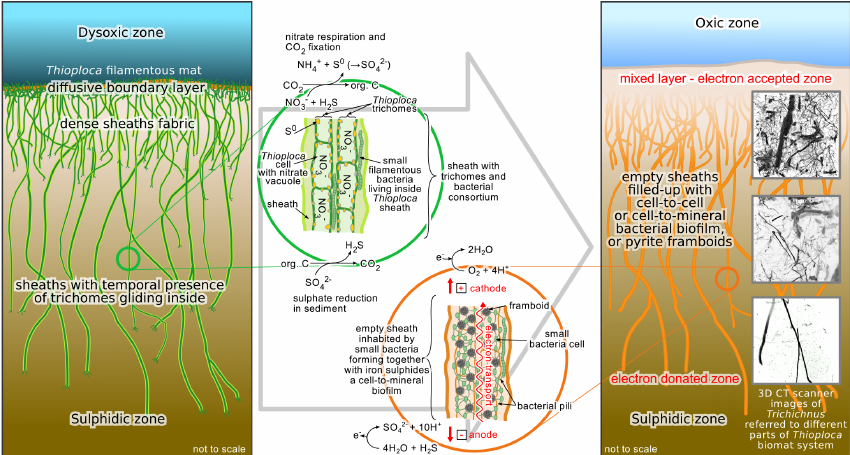
Thioploca
''Thioploca '' is a genus of filamentous sulphur-oxidizing bacteria, in the order ''Thiotrichales'' (class ''Gammaproteobacteria''). They inhabit both marine and freshwater environments, forming vast communities off the Pacific coast of South America and in other areas with a high organic matter sedimentation and bottom waters rich in nitrate and poor in oxygen. Their cells contain large vacuoles that occupy more than 80% of the cellular volume, used to store nitrate to oxidize sulphur for anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen, an important characteristic of the genus. With cell diameters ranging from 15-40 μm, they are some of the largest bacteria known. They provide an important link between the nitrogen and sulphur cycles, because they use both sulfur and nitrogen compounds. They secrete a sheath of mucus which they use as a tunnel to travel between sulphide-containing sediment and nitrate-containing sea water. Taxonomy and identification The genus ''Thioploca'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beggiatoa
''Beggiatoa'' is a genus of ''Gammaproteobacteria'' belonging to the order '' Thiotrichales'', in the ''Pseudomonadota'' phylum. These bacteria form colorless filaments composed of cells that can be up to 200 μm in diameter, and are one of the largest prokaryotes on Earth. ''Beggiatoa'' are chemolithotrophic sulfur-oxidizers, using reduced sulfur species as an energy source. They live in sulfur-rich environments such as soil, both marine and freshwater, in the deep sea hydrothermal vents, and in polluted marine environments. In association with other sulfur bacteria, e.g. '' Thiothrix'', they can form biofilms that are visible to the naked eye as mats of long white filaments; the white color is due to sulfur globules stored inside the cells. Discovery ''Beggiatoa'' was originally described as a type of blue-green algae (today known as ''Cyanobacteria'') by the botanist Vittore Trevisan in 1842, who named it in honor of the Italian doctor and botanist Francesco Secondo B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate-reducing Bacteria
Sulfate-reducing microorganisms (SRM) or sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) are a group composed of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) and sulfate-reducing archaea (SRA), both of which can perform anaerobic respiration utilizing sulfate () as terminal electron acceptor, reducing it to hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Therefore, these sulfidogenic microorganisms "breathe" sulfate rather than Allotropes of oxygen, molecular oxygen (O2), which is the terminal electron acceptor reduced to water (H2O) in Anaerobic respiration, aerobic respiration. Most sulfate-reducing microorganisms can also reduce some other oxidized inorganic sulfur Chemical compound, compounds, such as sulfite (), dithionite (), thiosulfate (), trithionate (), tetrathionate (), Allotropes of sulfur, elemental sulfur (S8), and polysulfides (). Other than sulfate reduction, some sulfate-reducing microorganisms are also capable of other reactions like disproportionation of sulfur compounds. Depending on the context, "sulfate-reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.Benthos from the Census of Antarctic Marine Life website This community lives in or near marine or freshwater sedimentary environments, from tidal pools along the , out to the continental shelf, and then down to the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolution, evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colony (biology), colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Nitrogen Cycle With The Role Of DNRA
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Minimum Zone
The oxygen minimum zone (OMZ), sometimes referred to as the shadow zone, is the zone in which oxygen saturation in seawater in the ocean is at its lowest. This zone occurs at depths of about , depending on local circumstances. OMZs are found worldwide, typically along the western coast of continents, in areas where an interplay of physical and biological processes concurrently lower the oxygen concentration (biological processes) and restrict the water from mixing with surrounding waters (physical processes), creating a "pool" of water where oxygen concentrations fall from the normal range of 4–6 mg/L to below 2 mg/L. Physical and biological processes Surface ocean waters generally have oxygen concentrations close to equilibrium with the Earth's atmosphere. In general, colder waters hold more oxygen than warmer waters. As water moves out of the mixed layer into the thermocline, it is exposed to a rain of organic matter from above. Aerobic bacteria feed on this o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |