|
Discovery Of The Americas
The human history of the Americas is thought to begin with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an ice age. These groups are generally believed to have been isolated from the people of the "Old World" until the coming of Europeans in 1492 with the voyages of Christopher Columbus. The ancestors of today's American Indigenous peoples were the Paleo-Indians; they were hunter-gatherers who migrated into North America. The most popular theory asserts that migrants came to the Americas via Beringia, the land mass now covered by the ocean waters of the Bering Strait. Small lithic stage peoples followed megafauna like bison, mammoth (now extinct), and caribou, thus gaining the modern nickname "big-game hunters." Groups of people may also have traveled into North America on shelf or sheet ice along the northern Pacific coast. Sedentary societies developed primarily in two regions: Mesoamerica and the Andean civilizations. Mesoamerican cultures include Zapotec, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
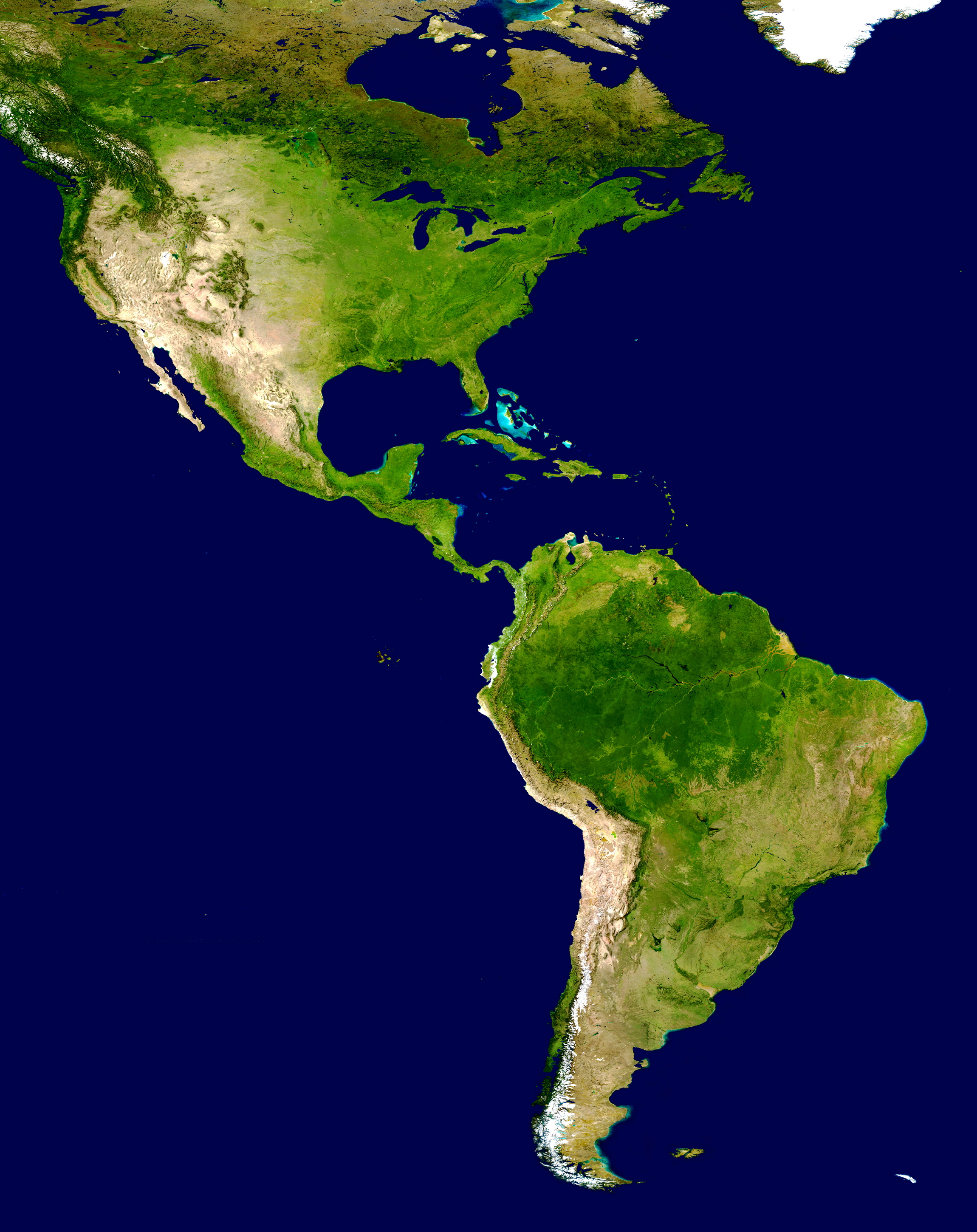
Americas Satellite Map
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a single continent, the Americas or America is the 2nd largest continent by area after Asia, and is the 3rd largest continent by population. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. Along with their Lists of islands of the Americas, associated islands, the Americas cover 8% of Earth's total surface area and 28.4% of its land area. The topography is dominated by the American Cordillera, a long chain of mountains that runs the length of the west coast. The flatter eastern side of the Americas is dominated by large river basins, such as the Amazon basin, Amazon, St. Lawrence River–Great Lakes, Mississippi River System, Mississippi, and Río de la Plata Basin, La Plata basins. Since the Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from antiquity to the early modern period. It is known by its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimor
Chimor (also Kingdom of Chimor or Chimú Empire) was the political grouping of the Chimú culture (). The culture arose about 900 CE, succeeding the Moche culture, and was later conquered by the Inca Empire, Inca emperor Topa Inca Yupanqui around 1470, fifty years before the arrival of the Spanish in the region. Chimor was the largest kingdom in the Late Intermediate Period, encompassing 1,000 kilometres (620mi) of coastline. According to Chimú oral tradition, oral history, the history of Chimor began with the arrival of :es:Taycanamo, Taycanamo in the Moche Valley from the sea on a Pre-Columbian rafts, balsa raft. From there, his descendants would conquer surrounding areas starting with his son :es:Guacricur, Guacriur. Guacricur integrated Chimú's reign over the lower valley and :es:Ñancempinco, Ñancempinco, Taycanamo's grandson would expand the kingdom by conquering the upper valley. Ñançenpinco began to further expansion both north and south of the Moche Valleys. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
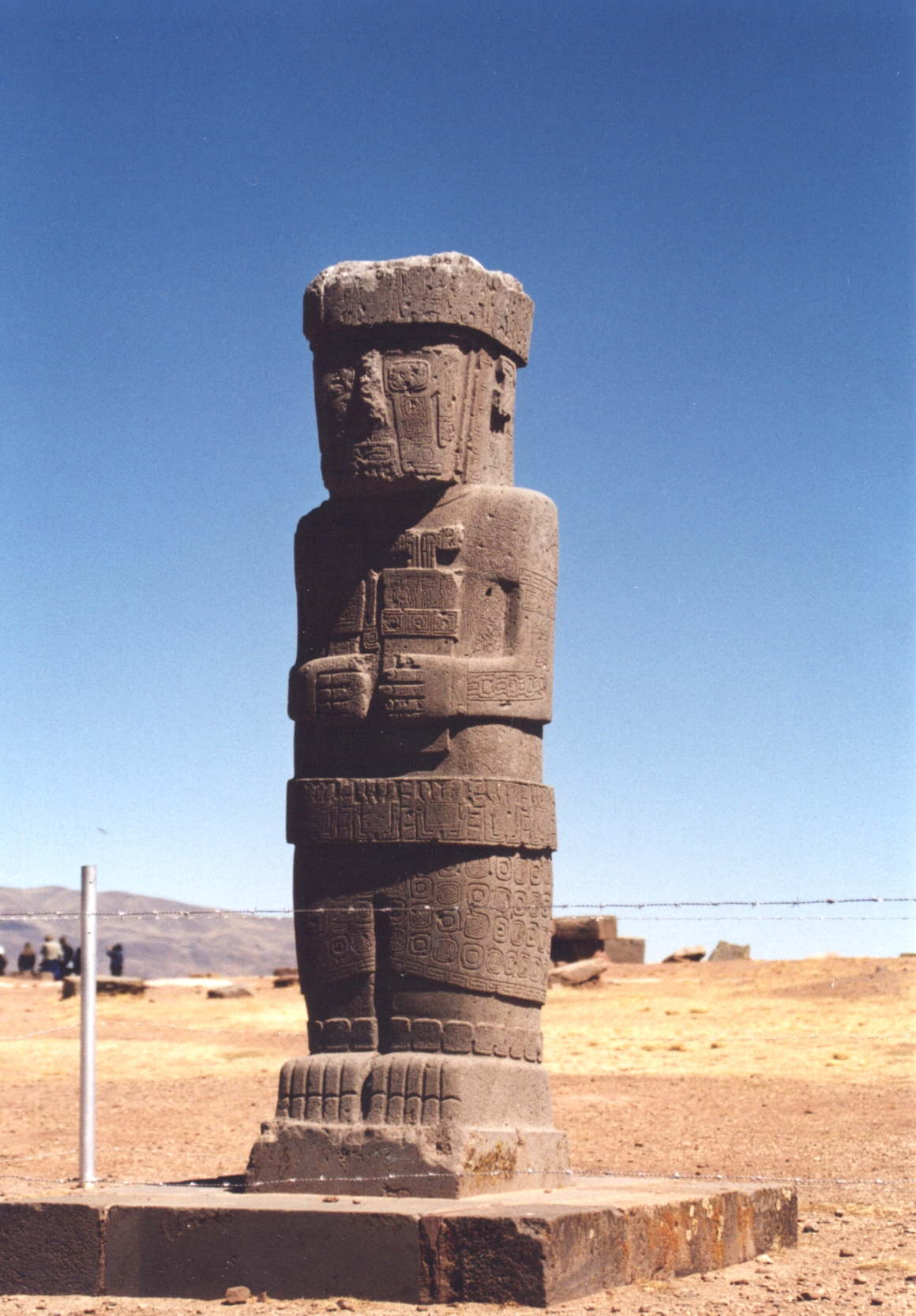
Tiwanaku
Tiwanaku ( or ) is a Pre-Columbian archaeological site in western Bolivia, near Lake Titicaca, about 70 kilometers from La Paz, and it is one of the largest sites in South America. Surface remains currently cover around 4 square kilometers and include decorated ceramics, monumental structures, and megalithic blocks. It has been conservatively estimated that the site was inhabited by 10,000 to 20,000 people in AD 800. The site was first recorded in written history in 1549 by Spanish conquistador Pedro Cieza de León while searching for the southern Inca capital of Qullasuyu. Jesuit chronicler of Peru Bernabé Cobo reported that Tiwanaku's name once was ''taypiqala'', which is Aymara meaning "stone in the center", alluding to the belief that it lay at the center of the world. The name by which Tiwanaku was known to its inhabitants may have been lost as they had no written language. Heggarty and Beresford-Jones suggest that the Puquina language is most likely to have been the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wariʼ
The Wariʼ, also known as the Pakaa Nova, are an indigenous people of Brazil, living in seven villages in the Amazon rainforest in the state of Rondônia. Their first contact with European settlers was on the shores of the Pakaa Nova River, a tributary of the Mamoré River. Many of the Wari' live within the Sagarana Indigenous Territory near the town of Rodrigues Alves (which lies between Rio Guaporé Indigenous Territory and Pacaás Novos National Park). Name Europeans at one time used the name "Pakaa Nova" to refer to the Wariʼ, because they encountered the indigenous people near the Pakaa Nova River. The people prefer to be referred to as "Wariʼ", their term in their language meaning "we, people." They are also known as the Jaru, Oro Wari, Pacaas-Novos, Pacahanovo, Pakaanova, Pakaanovas, Uari, and Uomo. Language The Wariʼ speak the Pakaásnovos language, which belongs to the Txapakura, or Chapacura-Wanham language family. Along with the Torá, the Moré (or Itenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca civilisation rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Portuguese explorer Aleixo Garcia was the first European to reach the Inca Empire in 1524. Later, in 1532, the Spanish Empire, Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire, and by 1572 Neo-Inca State, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes, Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru with what are now western Ecuador, western and south-central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and Incas in Central Chile, a large portion of modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazatec
The Mazatec are an Indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit the Sierra Mazateca in the state of Oaxaca and some communities in the adjacent states of Puebla and Veracruz. Some researchers have theorized that the Mazatec, along with Popoloca speakers, once inhabited the lowlands of the Papaloapan basin, but were driven into the adjacent highlands by the expansion of Nahuas. Language family The Mazatecan languages are part of the Popolocan family which, in turn, is part of the Otomanguean language family. Traditional religious rituals Mazatec tradition includes the cultivation of entheogens for spiritual and ritualistic use. Plants and fungi used for this purpose include psilocybin mushrooms, psychoactive morning glory seeds (from species such as ''Ipomoea tricolor'' and '' Ipomoea corymbosa''), and ''Salvia divinorum''.Valdés ''et al.'' (1983) This latter plant is known to Mazatec shamans as ''ska María Pastora'', the name containing a reference to the Virgin Mary. Notable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izapa
Izapa is a very large pre-Columbian archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Chiapas; it is best known for its occupation during the Late Formative period. The site is situated on the Izapa River, a tributary of the Suchiate River, near the base of the volcano Tacaná, the sixth tallest mountain in Mexico. History The settlement at Izapa extended over 1.4 miles, making it the largest site in Chiapas. The site reached its apogee between 850 BCE and 100 BCE; several archaeologists have theorized that Izapa may have been settled as early as 1500 BCE, making it as old as the Olmec sites of San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán and La Venta. Izapa remained occupied through the Early Postclassic period, until approximately 1200 CE. Concept of Izapan style Due to the abundance of carved Maya stelae and monuments at Izapa, the term "Izapan style" is used to describe similarly executed works throughout the Pacific foothills and highlands beyond, including some found at Takalik Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purépecha
The Purépecha ( ) are a group of Indigenous people centered in the northwestern region of Michoacán, Mexico, mainly in the area of the cities of Cherán and Pátzcuaro. They are also known by the derogatory term " Tarascan", an exonym, applied by outsiders and not one they use for themselves. The Purépecha occupied most of Michoacán but also some of the lower valleys of both Guanajuato and Jalisco. Celaya, Acambaro, Cerano, and Yurirapundaro. Now, the Purépecha live mostly in the highlands of central Michoacán, around Lakes Patzcuaro and Cuitzeo. History Prehispanic history It was one of the major empires of the Pre-Columbian era. The capital city was Tzintzuntzan. Purépecha architecture is noted for step pyramids in the shape of the letter "T". Pre-Columbian Purépecha artisans made feather mosaics that extensively used hummingbird feathers, which were highly regarded as luxury goods throughout the region. During the Pre-Colonial era, the Purépecha kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huastec People
The Huastec or Téenek (contraction of ''Te' Inik'', "people from here"; also known as Huaxtec, Wastek or Huastecos) are an Indigenous people of Mexico, living in the La Huasteca region including the Mexican state, states of Hidalgo (Mexico), Hidalgo, Veracruz, San Luis Potosí and Tamaulipas concentrated along the route of the Pánuco River and along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. There are approximately 66,000 Huastec speakers today, of which two-thirds are in San Luis Potosí and one-third in Veracruz, although their population was probably much higher, as much as half a million, when the Spanish arrived in 1529. The ancient Huastec civilization is one of the pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures. Judging from archaeological remains, they are thought to date back to approximately the 10th century BCE, although their most productive period of civilization is usually considered to be the Mesoamerican chronology, Postclassic era between the fall of Teotihuacan and the rise of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is known today as the site of many of the most architecturally significant Mesoamerican pyramids built in the pre-Columbian Americas, namely the Pyramid of the Sun and the Pyramid of the Moon. Although close to Mexico City, Teotihuacan was not a Mexica (i.e. Aztec) city, and it predates the Aztec Empire by many centuries. At its zenith, perhaps in the first half of the first millennium (1 CE to 500 CE), Teotihuacan was the largest city in the Americas, with a population of at least 25,000, but has been estimated at 125,000 or more, making it at least the sixth-largest city in the world during its epoch. The city covered and 80 to 90 percent of the total population of the valley resided in Teotihuacan. Apart from the pyramids, Teotihu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |