|
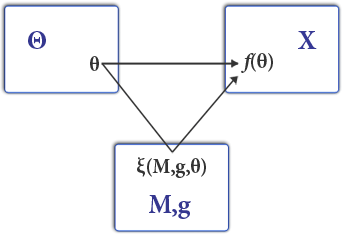
Direct-revelation Mechanism
The revelation principle is a fundamental result in mechanism design, social choice theory, and game theory which shows it is always possible to design a strategy-resistant implementation of a social decision-making mechanism (such as an electoral system or market).Gibbard, A. 1973. Manipulation of voting schemes: a general result. Econometrica 41, 587–601. It can be seen as a kind of mirror image to Gibbard's theorem. The revelation principle says that if a social choice function can be implemented with some non-honest mechanism—one where players have an incentive to lie—the same function can be implemented by an incentive-compatible (honesty-promoting) mechanism with the same equilibrium outcome (payoffs). The revelation principle shows that, while Gibbard's theorem proves it is impossible to design a system that will always be fully invulnerable to strategy (if we do not know how players will behave), it ''is'' possible to design a system that encourages honesty given a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanism Design
Mechanism design (sometimes implementation theory or institution design) is a branch of economics and game theory. It studies how to construct rules—called Game form, mechanisms or institutions—that produce good outcomes according to Social welfare function, some predefined metric, even when the designer does not know the players' true preferences or what information they have. Mechanism design thus focuses on the study of solution concepts for a class of private-information games. Mechanism design has broad applications, including traditional domains of economics such as market design, but also political science (through voting theory). It is a foundational component in the operation of the internet, being used in networked systems (such as inter-domain routing), e-commerce, and Sponsored search auction, advertisement auctions by Facebook and Google. Because it starts with the end of the game (a particular result), then works backwards to find a game that implements it, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incentive-compatible
In game theory and economics, a mechanism is called incentive-compatible (IC) if every participant can achieve their own best outcome by reporting their true preferences. For example, there is incentive compatibility if high-risk clients are better off in identifying themselves as high-risk to insurance firms, who only sell discounted insurance to high-risk clients. Likewise, they would be worse off if they pretend to be low-risk. Low-risk clients who pretend to be high-risk would also be worse off. The concept is attributed to the Russian-born American economist Leonid Hurwicz. Typology There are several different degrees of incentive-compatibility: * The stronger degree is dominant-strategy incentive-compatibility (DSIC). This means that truth-telling is a weakly-dominant strategy, i.e. you fare best or at least not worse by being truthful, regardless of what the others do. In a DSIC mechanism, strategic considerations cannot help any agent achieve better outcomes than the tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Market For Lemons
"The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism" is a widely cited seminal paper in the field of economics which explores the concept of asymmetric information in markets. The paper was written in 1970 by George Akerlof and published in the ''Quarterly Journal of Economics''. The paper's theory has since been applied to many types of markets. Akerlof examines how the quality of goods traded in a market can degrade in the presence of information asymmetry between buyers and sellers, which ultimately leaves goods that are found to be defective after purchase in the market, noted by the term 'lemon' in the title of the paper. In American slang, a lemon is a car that is found to be defective after it has been bought. Akerlof's theory of the "Market for Lemons" paper applies to markets with information asymmetry, focusing on the used car market. Information asymmetry within the market relates to the seller having more information about the quality of the car as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlated Equilibrium
In game theory, a correlated equilibrium is a solution concept that is more general than the well known Nash equilibrium. It was first discussed by mathematician Robert Aumann in 1974. The idea is that each player chooses their action according to their private observation of the value of the same public signal. A strategy assigns an action to every possible observation a player can make. If no player would want to deviate from their strategy (assuming the others also don't deviate), the distribution from which the signals are drawn is called a correlated equilibrium. Formal definition An N-player strategic game \displaystyle (N,\,\) is characterized by an action set A_i and utility function u_i for each player When player i chooses strategy a_i \in A_i and the remaining players choose a strategy profile described by the a_, then player i's utility is \displaystyle u_i(a_i,a_). A ''strategy modification'' for player i is a function \phi_i\colon A_i \to A_i. That is, \phi_i te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Myerson
Roger Bruce Myerson (born March 29, 1951) is an American economist and professor at the University of Chicago. He holds the title of the David L. Pearson Distinguished Service Professor of Global Conflict Studies at The Pearson Institute for the Study and Resolution of Global Conflicts in the Harris School of Public Policy Studies, Harris School of Public Policy, the Griffin Department of Economics, and the College of the University of Chicago. Previously, he held the title The Glen A. Lloyd Distinguished Service Professor of Economics. In 2007, he was the winner of the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel with Leonid Hurwicz and Eric Maskin for "having laid the foundations of mechanism design theory". He was elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019. Biography Roger Myerson was born in 1951 in Boston into a Jews, Jewish family. He attended Harvard University, where he received his Bachelor of Arts, A.B., ''summa cum laude'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengt Holmström
Bengt Robert Holmström (born 18 April 1949) is a Finnish economist who is currently Paul A. Samuelson Professor of Economics (Emeritus) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Together with Oliver Hart, he received the Central Bank of Sweden Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 2016. Early life and education Holmström was born in Helsinki, Finland, on 18 April 1949, and belongs to the Swedish speaking minority of Finland. He received his B.S. in mathematics and science from the University of Helsinki in 1972. He also received a Master of Science degree in operations research from Stanford University in 1975. He received his Ph.D. from the Graduate School of Business at Stanford in 1978. He moved to the United States in 1976. Career He worked as a corporate planner from 1972 until 1974, then was an assistant professor at the Hanken School of Economics from 1978 until 1979. He served as an associate professor at the Kellogg Graduate School of Management at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Maskin
Eric Stark Maskin (born December 12, 1950) is an American economist and mathematician. He was jointly awarded the 2007 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with Leonid Hurwicz and Roger Myerson "for having laid the foundations of mechanism design theory". He is the Adams University Professor and Professor of Economics and Mathematics at Harvard University. Until 2011, he was the Albert O. Hirschman Professor of Social Science at the Institute for Advanced Study, and a visiting lecturer with the rank of professor at Princeton University.Economics professor wins Nobel – The Daily Princetonian Early life and education Maskin was born in |
Bayesian Game
In game theory, a Bayesian game is a strategic decision-making model which assumes players have incomplete information. Players may hold private information relevant to the game, meaning that the payoffs are not common knowledge. Bayesian games model the outcome of player interactions using aspects of Bayesian probability. They are notable because they allowed the specification of the solutions to games with incomplete information for the first time in game theory. Hungarian economist John C. Harsanyi introduced the concept of Bayesian games in three papers from 1967 and 1968: He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for these and other contributions to game theory in 1994. Roughly speaking, Harsanyi defined Bayesian games in the following way: players are assigned a set of characteristics by nature at the start of the game. By mapping probability distributions to these characteristics and by calculating the outcome of the game using Bayesian probability, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Gibbard
Allan Fletcher Gibbard (born 1942) is an American philosopher who is the Richard B. Brandt Distinguished University Professor of Philosophy Emeritus at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Gibbard has made major contributions to contemporary ethical theory, in particular metaethics, where he has developed a contemporary version of non-cognitivism. He has also published articles in the philosophy of language, metaphysics, and social choice theory: in social choice, he first proved the result known today as Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem, which had been previously conjectured by Michael Dummett and Robin Farquharson. Life and career Allan Fletcher Gibbard was born on April 7, 1942, in Providence, Rhode Island. He received his B.A. in mathematics from Swarthmore College in 1963 with minors in physics and philosophy. After teaching mathematics and physics in Ghana with the Peace Corps (1963–1965), Gibbard studied philosophy at Harvard University, participating in the seminar on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategyproofness
In mechanism design, a strategyproof (SP) mechanism is a game form in which each player has a weakly- dominant strategy, so that no player can gain by "spying" over the other players to know what they are going to play. When the players have private information (e.g. their type or their value to some item), and the strategy space of each player consists of the possible information values (e.g. possible types or values), a truthful mechanism is a game in which revealing the true information is a weakly-dominant strategy for each player. An SP mechanism is also called dominant-strategy-incentive-compatible (DSIC), to distinguish it from other kinds of incentive compatibility. A SP mechanism is immune to manipulations by individual players (but not by coalitions). In contrast, in a group strategyproof mechanism, no group of people can collude to misreport their preferences in a way that makes every member better off. In a strong group strategyproof mechanism, no group of people can c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategic Dominance
In game theory, a strategy ''A'' dominates another strategy ''B'' if ''A'' will always produce a better result than ''B'', regardless of how any other player plays. Some very simple games (called straightforward games) can be solved using dominance. Terminology A player can compare two strategies, A and B, to determine which one is better. The result of the comparison is one of: * B strictly dominates (>) A: choosing B always gives a better outcome than choosing A, no matter what the other players do. * B weakly dominates (≥) A: choosing B always gives at least as good an outcome as choosing A, no matter what the other players do, and there is at least one set of opponents' actions for which B gives a better outcome than A. (Notice that if B strictly dominates A, then B weakly dominates A. Therefore, we can say "B dominates A" to mean "B weakly dominates A".) * B is weakly dominated by A: there is at least one set of opponents' actions for which B gives a worse outcome than A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |