|
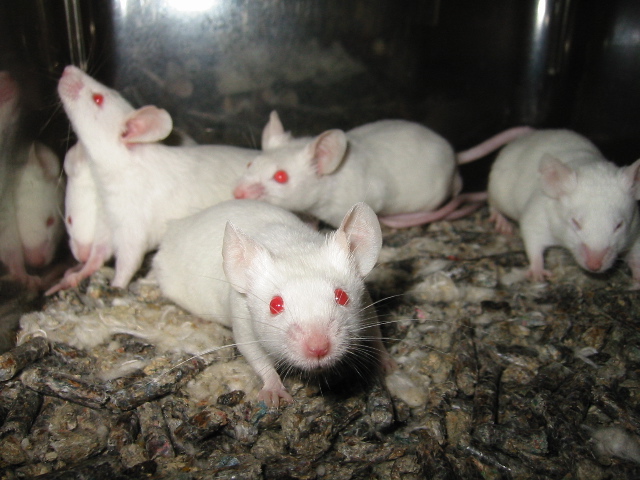
Diet-induced Obesity Model
The diet-induced obesity model (DIO model) is an Model organism, animal model used to study obesity using animals that have obesity caused by being fed high-fat or high-density diets. It is intended to mimic the most common cause of obesity in humans. Typically mice, rats, dogs, or non-human primates are used in these models. These animals can then be used to study ''in vivo'' obesity, obesity's comorbidities, and other related diseases. Users of such models must take into account the duration and type of diet (e.g. hydrated gels vs. dry pellets) as well as the Environment (biophysical), environmental conditions and age of the animals, as each may promote different bodyweights, fat percentages, or behaviors. Driven by the Epidemiology of obesity, worldwide epidemic of obesity, particularly in the Western world, the DIO model has been integral in understanding the relationship between high-fat/high-density Diet (nutrition), diets and obesity, including the discovery of Protein kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Research using animal models has been central to most of the achievements of modern medicine. It has contributed most of the basic knowledge in fields such as human physiology and biochemistry, and has played significant roles in fields such as neuroscience and infectious disease. The results have included the near- eradication of polio and the development of organ transplantation, and have benefited both humans and animals. From 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedentary Lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and/or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while engaged in an activity like socializing, Social aspects of television, watching TV, Gameplay, playing video games, reading or Problematic smartphone use, using a mobile phone or computer for much of the day. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to poor health quality, diseases as well as many preventable causes of death. Sitting time is a common measure of a sedentary lifestyle. A global review representing 47% of the global adult population found that the average person sits down for 4.7 to 6.5 hours a day with the average going up every year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC found that 25.3% of all American adults are physically inactive. Screen time is a term for the amount of time a person spends looking at a screen such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or hyposomatotropism, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood sugar or a small penis size. In adults there may be decreased muscle mass, high cholesterol levels, or poor bone density. GHD can be present at birth or develop later in life. Causes may include genetics, trauma, infections, tumors, or radiation therapy. Genes that may be involved include '' GH1'', '' GHRHR'', or '' BTK''. In a third of cases no cause is apparent. The underlying mechanism generally involves problems with the pituitary gland. Some cases are associated with a lack of other pituitary hormones, in which case it is known as combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure growth hormone levels. Treatment is by growth hormone replacement using synthetic human growth hormone. The frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
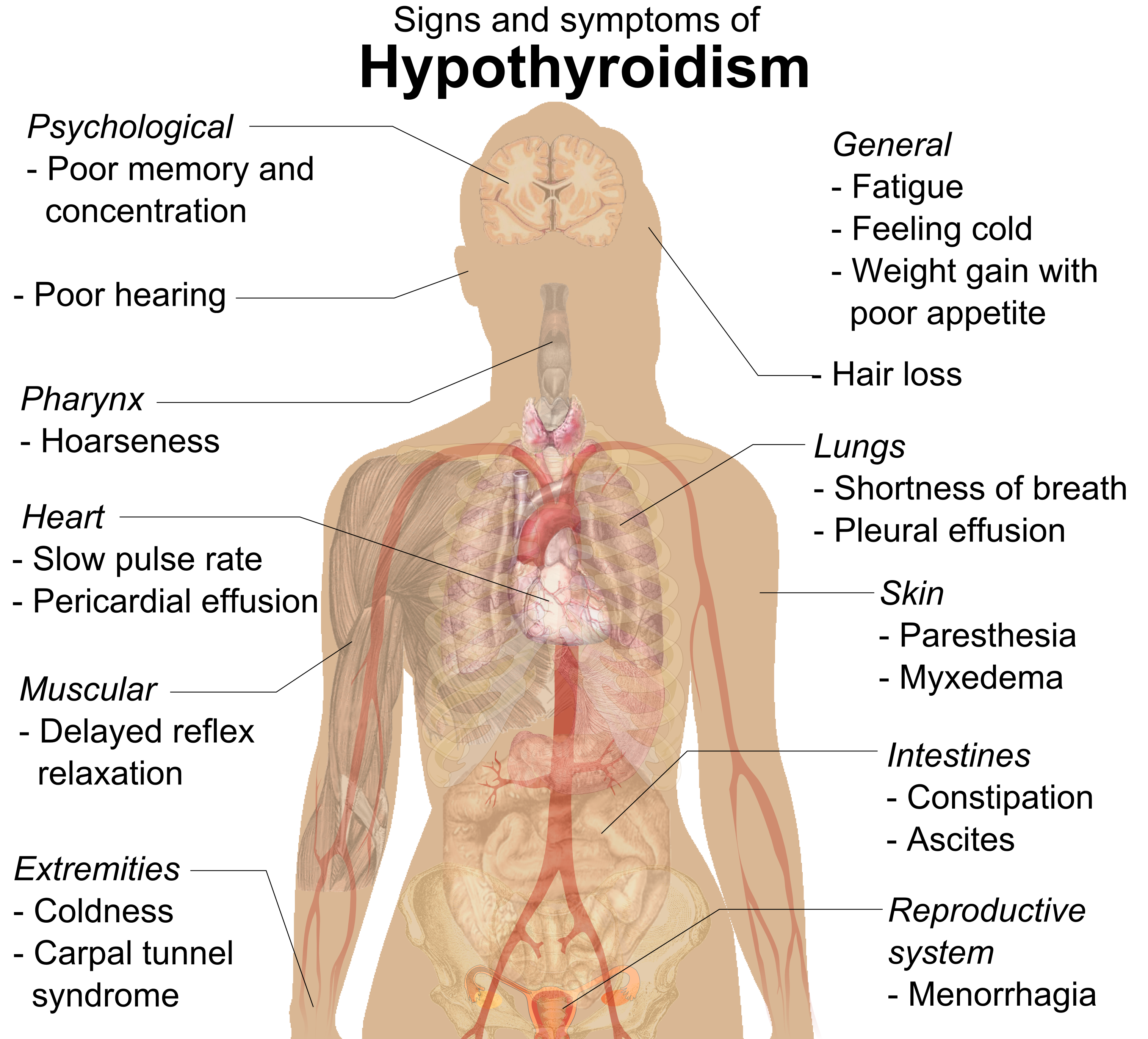
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOMO Syndrome
MOMO syndrome is an extremely rare genetic disorder which belongs to the overgrowth syndromes and has been diagnosed in only seven cases around the world, and occurs in 1 in 100 million births. The name is an acronym of the four primary aspects of the disorder: Macrosomia (excessive birth weight), Obesity, Macrocephaly (excessive head size) and Ocular abnormalities. It is unknown if it is a life-limiting condition. MOMO syndrome was first diagnosed in 1993 by Professor Danilo Moretti-Ferreira, a Brazilian researcher in the Genetic and Clinical Studies of neurodevelopmental disorders. This syndrome's acronym is an intended pun. It refers to the traditionally tall and obese king of Carnivals, Momus— Rei Momo in Portuguese. Signs and symptoms Along with the four aspects of the disorder that give it its name, there are also other common symptoms: * A downward slant of the forehead * Delayed bone maturation * Mental retardation The ocular abnormalities are generally retinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohen Syndrome
Cohen syndrome (also known as Pepper syndrome or Cervenka syndrome) is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder with varied expression, characterised by obesity, intellectual disability, distinct craniofacial abnormalities and potential ocular dysfunction. Signs and symptoms Patients with Cohen syndrome very frequently exhibit abnormal eyelash and eyelid morphology, teeth abnormalities, lingual aplasia or hypoplasia, arachnodactyly, chorioretinal dystrophy, downslanted palpebral fissures, gingival overgrowth, global developmental delay, a high and narrow palate, maxillary hypoplasia, zygomatic bone hypoplasia, hypotonia, intellectual disability, long eyelashes, low anterior hairline, microcephaly, micrognathia, myopia, neurological speech impairment, neutropenia, open mouth, prominent nasal bridge, sandal gap, short philtrum, slender toes, tapered fingers, and thick eyebrows. Some other frequently observed symptoms include abnormal skin pigmentation, cat cry, clinod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardet–Biedl Syndrome
Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a ciliopathic human genetic disorder that produces many effects and affects many body systems. It is characterized by rod/cone dystrophy, polydactyly, central obesity, hypogonadism, and kidney dysfunction in some cases. Historically, slower mental processing has also been considered a principal symptom but is now not regarded as such. Signs and symptoms Bardet–Biedl syndrome is a pleiotropic disorder with variable expressivity and a wide range of clinical variability observed both within and between families. The most common clinical features are rod–cone dystrophy, with childhood-onset night-blindness followed by increasing visual loss; postaxial polydactyly; truncal obesity that manifests during infancy and remains problematic throughout adulthood; varying degrees of learning disabilities; male hypogenitalism and complex female genitourinary malformations; and renal dysfunction, a major cause of morbidity and mortality. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prader–Willi Syndrome
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a rare genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. In newborns, symptoms include hypotonia, weak muscles, poor feeding, and slow development. Beginning in childhood, those affected become constantly hungry, which often leads to obesity and type 2 diabetes. Mild to moderate intellectual impairment and Behavioural problems, behavioral problems are also typical of the disorder. Often, affected individuals have a narrow forehead, small hands and feet, short height, and light skin and hair. Most are Infertility, unable to have children. About 74% of cases occur when part of the father's chromosome 15 is deleted. In another 25% of cases, the affected person has Uniparental disomy, two copies of the maternal chromosome 15 from the mother and lacks the paternal copy. As parts of the chromosome from the mother are turned off through Genomic imprinting, imprinting, they end up with no working copies of certain genes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Polymorphism
A gene is said to be polymorphic if more than one allele occupies that gene's locus within a population. In addition to having more than one allele at a specific locus, each allele must also occur in the population at a rate of at least 1% to generally be considered polymorphic. Gene polymorphisms can occur in any region of the genome. The majority of polymorphisms are silent, meaning they do not alter the function or expression of a gene. Some polymorphisms are visible. For example, in dogs the E locus can have any of five different alleles, known as E, Em, Eg, Eh, and e. Varying combinations of these alleles contribute to the pigmentation and patterns seen in dog coats. A polymorphic variant of a gene can lead to the abnormal expression or to the production of an abnormal form of the protein; this abnormality may cause or be associated with disease. For example, a polymorphic variant of the gene encoding the enzyme CYP4A11, in which thymidine replaces cytosine at the gene's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appetite
Appetite is the desire to eat food items, usually due to hunger. Appealing foods can stimulate appetite even when hunger is absent, although appetite can be greatly reduced by satiety. Appetite exists in all higher life-forms, and serves to regulate adequate energy intake to maintain metabolic needs. It is regulated by a close interplay between the digestive tract, adipose tissue and the brain. Appetite has a relationship with every individual's behavior. Appetitive behaviour also known as approach behaviour, and consummatory behaviour, are the only processes that involve energy intake, whereas all other behaviours affect the release of energy. When stressed, appetite levels may increase and result in an increase of food intake. Decreased desire to eat is termed anorexia, while polyphagia (or "hyperphagia") is increased eating. Dysregulation of appetite contributes to ARFID, anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, cachexia, overeating, and binge eating disorder. Role in disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |