|
Diadophis Punctatus Regalis
''Diadophis punctatus regalis'', commonly known as the regal ringneck snake, is a subspecies of ringneck snake endemic to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Description The regal ringneck snake is typically gray in color, with a dark-speckled white or cream underside, which becomes bright red or orange near and under the tail. It is distinguished by a yellow to orange ring around its neck which is typically bordered with black. However, the neck ring is frequently absent in this subspecies. The belly color extends onto one or more dorsal scale rows. They are among the larger of the ringneck snake subspecies, growing to a total length (including tail) of . Their dorsal scales are smooth. Habitat The regal ringneck snake is found in the desert, and in the mountains, unlike most snakes. Diet The regal ringneck snake, unlike other subspecies, is almost exclusively ophiophagous, having a diet that consists primarily of other snakes, such as the earth snakes (gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spencer Fullerton Baird
Spencer Fullerton Baird (; February 3, 1823 – August 19, 1887) was an American naturalist, ornithologist, ichthyologist, herpetologist, and museum curator. Baird was the first curator to be named at the Smithsonian Institution. He eventually served as assistant Secretary of the Smithsonian from 1850 to 1878, and as Secretary from 1878 until 1887. He was dedicated to expanding the natural history collections of the Smithsonian which he increased from 6,000 specimens in 1850 to over 2 million by the time of his death. He published over 1,000 works during his lifetime. Early life and education Spencer Fullerton Baird was born in Reading, Pennsylvania in 1823. His mother was a member of the prominent Philadelphia Biddle family; he was a nephew of Speaker of the Pennsylvania Senate Charles B. Penrose and a first cousin, once removed, of U.S. Senator Boies Penrose and his distinguished brothers, Richard, Spencer, and Charles. He became a self-trained naturalist as a young man, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiophagy
Ophiophagy (Greek "snake eating") is a specialized form of feeding or alimentary behavior of animals which hunt and eat snakes. There are ophiophagous mammals (such as the skunks and the mongooses), birds (such as snake eagles, the secretarybird, and some hawks), lizards (such as the common collared lizard), and even other snakes, such as the Central and South American mussuranas and the North American common kingsnake. The genus of the venomous king cobra (''Ophiophagus hannah'') is named for this habit. Ophiophagy in myth and legend :''The mythic associations of snakes are discussed at Serpent (symbolism).'' A snake-eating bird of prey appears in a legend of the Mexican people, who gave rise to the Aztec empire, and it is represented in the Mexican flag: The Mexicas, guided by their god Huitzilopochtli, sought a place where the bird landed on a prickly pear cactus, devouring a snake. They found the sign on an island in Lake Texcoco, where they erected the city of Tenoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Hazen Wright
Albert Hazen Wright (August 15, 1879 – July 5, 1970) was an American herpetologist and professor at Cornell University. He was also an honorary member of the International Ornithological Congress. He did a great deal of study of the Okefenokee Swamp. In 1955 he won the Eminent Ecologist Award. Biography Albert Hazen Wright was born on August 15, 1879, in Hilton, New York, to parents Delos C. Wright and Emily Hazen. His parents also had a younger daughter named Mabel. On June 25, 1910, Wright married his wife, Anna Maria Allen, whom he met at Cornell University. Wright died on July 5, 1970, in Ithaca, New York, at the age of ninety. Education and career Wright attended Hilton High School and Brockport Normal School, and upon graduating high school, enrolled at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, where he studied herpetology. He earned his PhD from Cornell in vertebrate zoology in 1908. Both Wright and his wife were interested in studying amphibians; as such, they would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, and a few mammals ( monotremes, tenrecs, golden moles, and marsupial moles), have this orifice, from which they excrete both urine and feces; this is in contrast to most placental mammals, which have two or three separate orifices for evacuation. Excretory openings with analogous purpose in some invertebrates are also sometimes referred to as cloacae. Mating through the cloaca is known as cloacal copulation, commonly referred to as cloacal kiss. The cloacal region is also often associated with a secretory organ, the cloacal gland, which has been implicated in the scent-marking behavior of some reptiles, marsupials, amphibians, and monotremes. Etymology The word is from the Latin verb ''cluo'', "(I) cleanse", thus the noun ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musk
Musk ( Persian: مشک, ''Mushk'') is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial substances with similar odors. ''Musk'' was a name originally given to a substance with a strong odor obtained from a gland of the musk deer. The substance has been used as a popular perfume fixative since ancient times and is one of the most expensive animal products in the world. The name originates from the Late Greek μόσχος 'moskhos', from Persian 'mushk', similar to Sanskrit मुष्क muṣka ("testicle"), derived from Proto-Indo-European noun ''múh₂s'' meaning "mouse". The deer gland was thought to resemble a scrotum. It is applied to various plants and animals of similar smell (e.g. muskox) and has come to encompass a wide variety of aromatic substances with similar odors, despite their often differing chemical str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corkscrew
A corkscrew is a tool for drawing corks from wine bottles and other household bottles that may be sealed with corks. In its traditional form, a corkscrew simply consists of a pointed metallic helix (often called the "worm") attached to a handle, which the user screws into the cork and pulls to extract it. Corkscrews are necessary because corks themselves, being small and smooth, are difficult to grip and remove, particularly when inserted fully into an inflexible glass bottle. More recent styles of corkscrew incorporate various systems of levers that further increase the amount of force that can be applied outwards upon the cork, making easier the extraction of difficult corks. History Its design may have derived from the gun worm which was a device used by men to remove unspent charges from a musket's barrel in a similar fashion, from at least the early 1630s.winepros.com.au. The corkscrew is possibly an English invention, due to the tradition of beer and cider, and ''Treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal Animal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as cats and ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsiers and some owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as ''Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intense sunlight. Diurnal animals, including squirrels and songbirds, are act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venom (poison)
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a stinger, in a process called envenomation. Venom is often distinguished from poison, which is a toxin that is passively delivered by being ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, and toxungen, which is actively transferred to the external surface of another animal via a physical delivery mechanism. Venom has evolved in terrestrial and marine environments and in a wide variety of animals: both predators and prey, and both vertebrates and invertebrates. Venoms kill through the action of at least four major classes of toxin, namely necrotoxins and cytotoxins, which kill cells; neurotoxins, which affect nervous systems; myotoxins, which damage muscles; and haemotoxins, which disrupt blood clotting. Venomous animals cause tens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
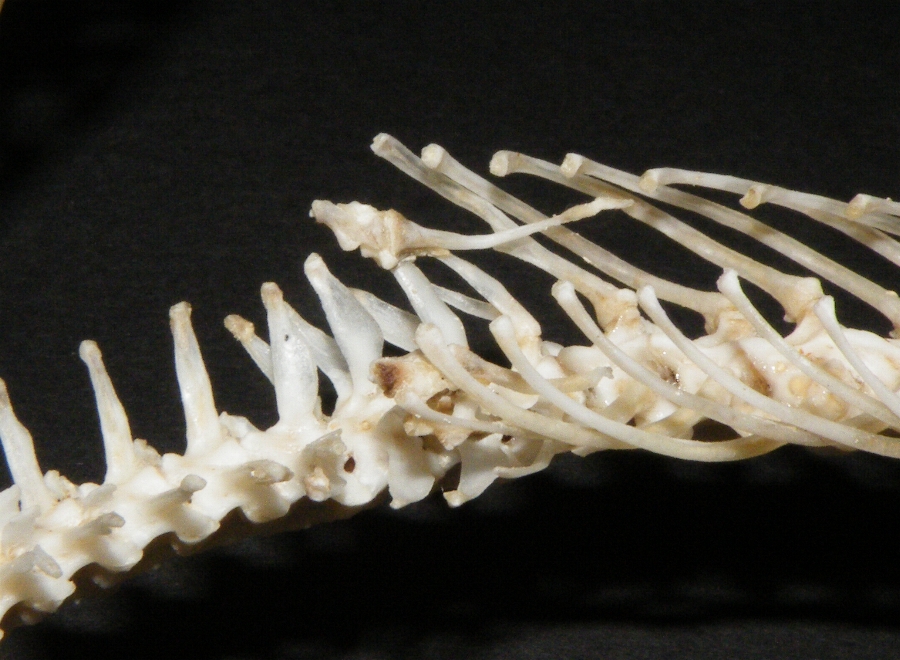
Opisthoglypha
A snake skeleton consists primarily of the skull, vertebrae, and ribs, with only vestigial remnants of the limbs. Skull The skull of a snake is a very complex structure, with numerous joints to allow the snake to swallow prey far larger than its head. The typical snake skull has a solidly ossified braincase, with the separate frontal bones and the united parietal bones extending downward to the basisphenoid, which is large and extends forward into a rostrum extending to the ethmoidal region. The nose is less ossified, and the paired nasal bones are often attached only at their base. The occipital condyle is either trilobate and formed by the basioccipital and the exoccipitals, or a simple knob formed by the basioccipital; the supraoccipital is excluded from the foramen magnum. The basioccipital may bear a curved ventral process or hypapophysis in the vipers. The prefrontal bone is situated, on each side, between the frontal bone and the maxilla, and may or may not be in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantilla
''Tantilla'' is a large genus of harmless New World snakes in the family Colubridae. The genus includes 66 species, which are commonly known as centipede snakes, blackhead snakes, and flathead snakes.Wilson, Larry David. 1982. Tantilla.' Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles. Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles. 303:1-4.Wilson, Larry David, and Vicente Mata-Silva. 2015. A checklist and key to the snakes of the Tantilla clade (Squamata: Colubridae), with comments on taxonomy, distribution, and conservation.' Mesoamerican Herpetology 2: 418–498. Description ''Tantilla'' are small snakes, rarely exceeding 20 cm (8 inches) in total length (including tail). They are generally varying shades of brown, red or black in color. Some species have a brown body with a black head. Behavior ''Tantilla'' are nocturnal, secretive snakes. They spend most of their time buried in the moist leaf litter of semi-forested regions or under rocks and debris. Diet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



.jpg)