|
Dermatoglyphics
Dermatoglyphics (from Ancient Greek ''derma'', "skin", and ''glyph'', "carving") is the scientific study of fingerprints, lines, mounts and shapes of hands, as distinct from the superficially similar pseudoscience of palmistry. Dermatoglyphics also refers to the making of naturally occurring ridges on certain body parts, namely palms, fingers, soles, and toes. These are areas where hair usually does not grow, and these ridges allow for increased leverage when picking up objects or walking barefoot. In a 2009 report, the scientific basis underlying dermatoglyphics was questioned by the National Academy of Sciences, for the discipline's reliance on subjective comparisons instead of conclusions drawn from the scientific method. History 1823 marks the beginning of the scientific study of Dermis#Dermal papillae, papillary ridges of the hands and feet, with the work of Jan Evangelista Purkyně. By 1858, Sir William Herschel, 2nd Baronet, while in India, became the first European to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmistry
Palmistry is the pseudoscientific practice of fortune-telling through the study of the palm. Also known as palm reading, chiromancy, chirology or cheirology, the practice is found all over the world, with numerous cultural variations. Those who practice palmistry are generally called ''palmists'', ''hand readers'', ''hand analysts'', or ''chirologists''. There are many—and often conflicting—interpretations of various lines and palmar features across various teachings of palmistry. Palmistry is widely viewed as a pseudoscience due to various contradictions between different interpretations and the lack of evidence for palmistry's predictions. History Ancient palmistry Palmistry is a practice common to many different places on the Eurasian landmass; it has been practiced in the cultures of Sumer, Babylonia, Arabia, Canaan, Persia, India, Nepal, Tibet and China. The acupuncturist Yoshiaki Omura describes its roots in Hindu astrology (known in Sanskrit as '' jyotish''), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Cummins
Harold Cummins (May 28, 1893 – May 12, 1976) was an anatomist and dermatoglyphics specialist. He is considered to be the founder of dermatoglyphics. Early life and education A native of Markleville, Indiana, Cummins attended the University of Michigan, receiving his BA in 1916. While attending the University of Michigan, he was inducted into two academic honor societies: Sigma Xi and Phi Beta Kappa. Cummins completed his PhD in anatomy at Tulane University in 1925. Career In his multiple positions as an educator, Cummins taught over 5000 students. Cummins worked at Vanderbilt University as a Histology instructor (1916-1917) and as an assistant professor of Microscopic Anatomy from 1917 through 1919. In 1919, Cummins joined the faculty at Tulane University where he remained for the rest of his educational career, nearly five decades, serving in a variety of positions. His positions at Tulane University included: *Chairman of the Department of Anatomy (1933–1960) *Chairma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or dead and thus unab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) leading to the complete or partial deletion of the pseudoautosomal regions (PAR1, PAR2) in the affected X chromosome. Typically, people have two sex chromosomes (XX for females or XY for males). The chromosomal abnormality is often present in just some cells, in which case it is known as Turner syndrome with mosaicism. 45,X0 with mosaicism can occur in males or females, but Turner syndrome without mosaicism only occurs in females. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected but often include additional skin folds on the neck, arched palate, low-set ears, low hairline at the nape of the neck, short stature, and lymphedema of the hands and feet. Those affected do not normally develop menstrual periods or mammary glands without hormone trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
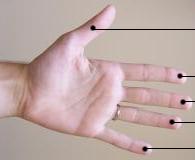
Single Transverse Palmar Crease
In humans, a single transverse palmar crease is a single crease that extends across the palm of the hand, formed by the fusion of the two palmar creases. Although it is found more frequently in persons with several abnormal medical conditions, it is not predictive of any of these conditions since it is also found in persons with no abnormal medical conditions. This crease is estimated to occur in 1.5-3% of the general population, although it is more common in East Asian and Native American populations. Former name Because it resembles the usual condition of non-human simians, it was, in the past, called the simian crease or simian line. These terms have widely fallen out of favor due to their pejorative connotation. Medical significance This crease is found in 45% of people with down syndrome. The presence of a single transverse palmar has been associated with several abnormal medical conditions—that is, it is found at a higher than 1.5% frequency, but in all of these condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guide To Finger-print Identification (electronic Resource) (1905) (14597875770)
A guide is a person who leads travelers, sportspeople, or tourists through unknown or unfamiliar locations. The term can also be applied to a person who leads others to more abstract goals such as knowledge or wisdom. Travel and recreation Explorers in the past venturing into territory unknown by their own people invariably hired guides. Military explorers Lewis and Clark were hired by the United States Congress to explore the Pacific Northwest. They in turn hired the better qualified Native American Sacagawea to help them. Wilfred Thesiger hired guides in the deserts that he ventured into, such as Kuri on his journey to the Tibesti Mountains in 1938. Tour guide Tour guides lead visitors through tourist attractions and give information about the attractions' natural and cultural significance. Often, they also act as interpreters for travelers who do not speak the local language. Automated systems like audio tours are sometimes substituted for human tour guides. Tour operato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digit (anatomy)
A digit is one of several most distal parts of a limb, such as fingers or toes, present in many vertebrates. Names Some languages have different names for hand and foot digits (English: respectively "finger" and " toe", German: "Finger" and "Zeh", French: "doigt" and "orteil"). In other languages, e.g. Arabic, Russian, Polish, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Czech, Tagalog, Turkish, Bulgarian, and Persian, there are no specific one-word names for fingers and toes; these are called "digit of the hand" or "digit of the foot" instead. In Japanese, yubi (指) can mean either, depending on context. Human digits Humans normally have five digits on each extremity. Each digit is formed by several bones called phalanges, surrounded by soft tissue. Human fingers normally have a nail at the distal phalanx. The phenomenon of polydactyly occurs when extra digits are present; fewer digits than normal are also possible, for instance in ectrodactyly. Whether such a mutation can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cri Du Chat
Cri du chat syndrome is a rare genetic disorder due to a partial chromosome deletion on chromosome 5. Its name is a French term ("cat-cry" or " call of the cat") referring to the characteristic cat-like cry of affected children. It was first described by Jérôme Lejeune in 1963. The condition affects an estimated 1 in 50,000 live births across all ethnicities and is more common in females by a 4:3 ratio. Signs and symptoms The syndrome gets its name from the characteristic cry of affected infants, which is similar to that of a meowing kitten, due to problems with the larynx and nervous system. About one third of children lose the cry by age of 2 years. Other symptoms of cri du chat syndrome may include: * feeding problems because of difficulty in swallowing and sucking; * mutism; * low birth weight and poor growth; * severe cognitive, speech and motor disabilities; * behavioural problems such as hyperactivity, aggression, outbursts and repetitive movements; * unusual f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn Syndrome
Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS), also known as chromatophore nevus of Naegeli and Naegeli syndrome, is a rare autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia, characterized by reticular skin pigmentation, diminished function of the sweat glands, the absence of teeth and hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles. One of the most striking features is the absence of fingerprint lines on the fingers. Naegeli syndrome is similar to dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis, both of which are caused by a specific defect in the keratin 14 protein. Cause NFJS is caused by mutations in the keratin 14 (KRT14) gene, located on chromosome 17q12-21. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 17 is an autosome), and only one copy of the defective gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder. Diagnosis In most cases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archives Of Disease In Childhood
''Archives of Disease in Childhood'' is a peer review, peer-reviewed medical journal published by the BMJ Group and covering the field of paediatrics. It is the official journal of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health. Scope ''Archives of Disease in Childhood'' focuses on all aspects of pediatric nursing, child health and child disease, disease from the perinatal period through to adolescence. It includes original research reports, commentaries, reviews of clinical and policy issues, and evidence reports. Other sections include: guidelines updates, international health, and a column written by patients about their experience with the health care system. Douglas Gairdner served as editor from 1964 to 1979 and because of his creative editing, he was awarded the Dawson-Williams prize of the British Medical Association. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed on MEDLINE/Index Medicus, Web of Science, and EMBASE, Excerpta Medica. According to the ''Journal Cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Impairment
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks, including reading and walking. The terms ''low vision'' and ''blindness'' are often used for levels of impairment which are difficult or impossible to correct and significantly impact daily life. In addition to the various permanent conditions, fleeting temporary vision impairment, amaurosis fugax, may occur, and may indicate serious medical problems. The most common causes of visual impairment globally are uncorrected refractive errors (43%), cataracts (33%), and glaucoma (2%). Refractive errors include near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism (eye), astigmatism. Cataracts are the most common cause of blindness. Other disorders that may cause visual problems include age-related macular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |