|
Derby Racecourse Roman Settlement
The Derby Racecourse Roman settlement was the third settlement in Derby or Derventio which was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. It lies 600m east of Derventio fort in Little Chester, on the outskirts of Derby, in the English county of Derbyshire. The Roman road from Derventio to Sawley on the River Trent passes the settlement. It is a scheduled National Monument. Description The first Roman fort in the area was built on the opposite bank of the River Derwent at Strutt's Park. It was replaced about AD 80 by a fort at Little Chester, but this only lasted about forty years, then decommissioned. The fort was later re-occupied and re-used for a further twenty five years then unoccupied until the late 3rd century when a stone wall was built around the town. There is evidence of extensive Roman activity in Little Chester. Derby Racecourse Roman settlement site was founded around AD 90. It is considered by English Heritage to be an import example of a fort-vicus. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. It borders Greater Manchester, West Yorkshire, and South Yorkshire to the north, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the south and west, and Cheshire to the west. Derby is the largest settlement, and Matlock is the county town. The county has an area of and a population of 1,053,316. The east of the county is more densely populated than the west, and contains the county's largest settlements: Derby (261,400), Chesterfield (88,483), and Swadlincote (45,000). For local government purposes Derbyshire comprises a non-metropolitan county, with eight districts, and the Derby unitary authority area. The East Midlands Combined County Authority includes Derbyshire County Council and Derby City Council. The north and centre of Derbyshire are hilly and contain the southern end of the Pennines, most of which are part of the Peak District National Park. They include Kinde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
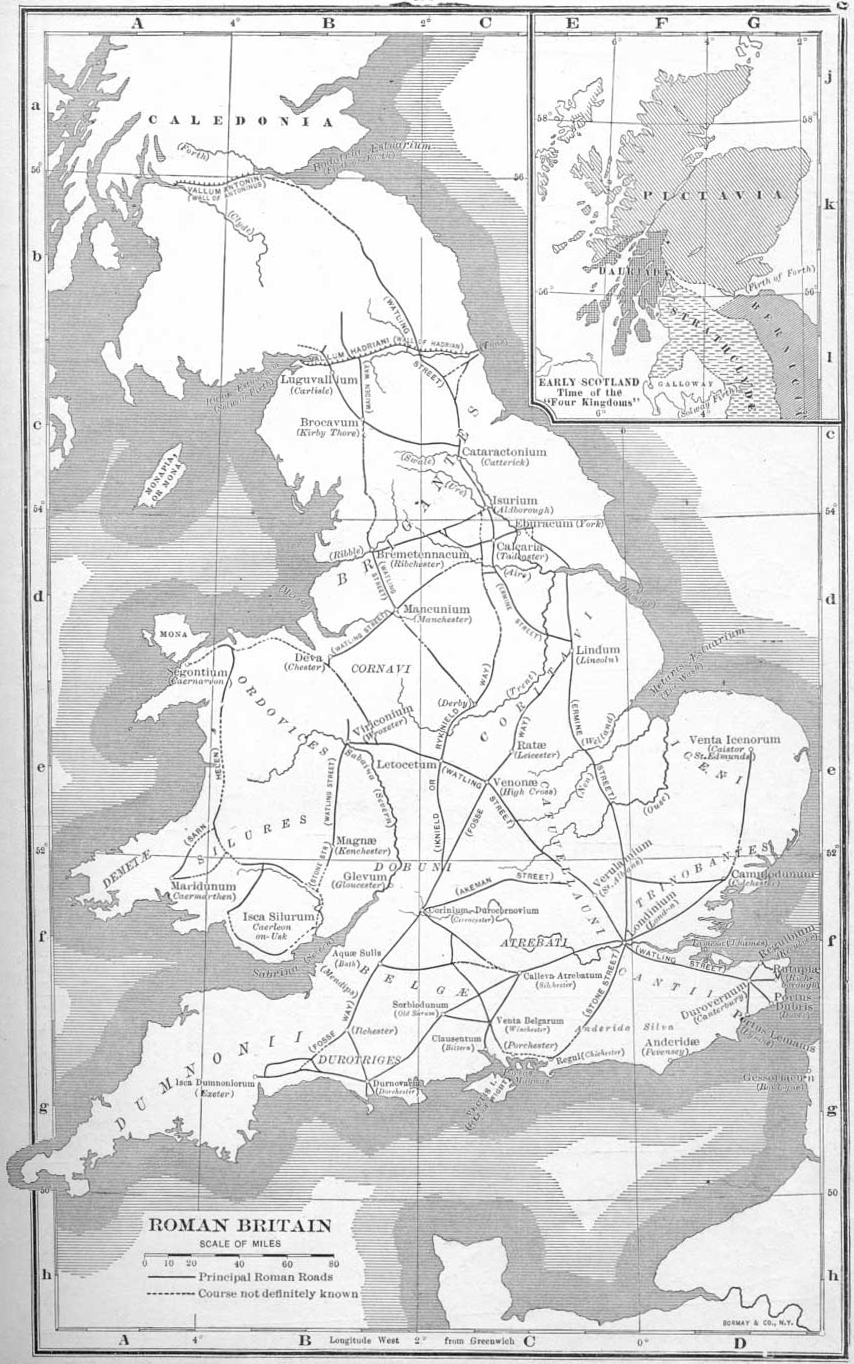
Cornovii (Midlands)
The Cornovīī (Common Brittonic: *''Cornowī'') were a Celtic people of the Iron Age and Roman Britain, who lived principally in the modern English counties of Cheshire, Shropshire, north Staffordshire, north Herefordshire and eastern parts of the Welsh counties of Flintshire, Powys and Wrexham. Their capital in pre-Roman times was probably a hillfort on the Wrekin. Ptolemy's 2nd-century ''Geography'' names two of their towns: Deva Victrix (Chester) and Viroconium Cornoviorum ( Wroxeter), which became their capital under Roman rule. Their territory was bordered by the Brigantes to the North, the Corieltauvi to the East, the Dobunni to the South, and the Deceangli and Ordovices to the West. The people who inhabited the very north of the British mainland (modern Caithness), and Cornwall were also known by the same name, but according to mainstream or academic opinion were quite separate and unrelated peoples. (see list of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes). Nomenclatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geographer Ptolemy named the Brigantes as a people in Ireland also, where they could be found around what is now counties Wexford, Kilkenny and Waterford, while another people named '' Brigantii'' is mentioned by Strabo as a sub-tribe of the Vindelici in the region of the Alps. Within Britain, the territory which the Brigantes inhabited was bordered by that of four other peoples: the Carvetii in the northwest, the Parisii to the east and, to the south, the Corieltauvi and the Cornovii. To the north was the territory of the Votadini, which straddled the present day border between England and Scotland. Etymology The name ( in Ancient Greek) shares the same Proto-Celtic root as the goddess Brigantia, meaning 'high, elevated', and it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' (Latin: ) and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ), originally formed a continuous narrative of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the end of Domitian’s reign (96 AD). The surviving portions of the Annals focus on the reigns of Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see ), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricolae''). Tacitus's ''Histories'' offers insights into Roman attitudes towards Jews, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnaeus Julius Agricola
Gnaeus Julius Agricola (; 13 June 40 – 23 August 93) was a Roman general and politician responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Born to a political family of senatorial rank, Agricola began his military career as a military tribune under governor Gaius Suetonius Paulinus. In his subsequent career, he served in a variety of political positions in Rome. In 64, he was appointed quaestor in Asia province. Two years later, he was appointed Plebeian Tribune, and in 68, he was made praetor. During the Year of the Four Emperors in 69, he supported Vespasian, general of the Syrian army, in his bid for the throne. When Vespasian became emperor, Agricola was made a patrician and appointed governor of Gallia Aquitania. In 77, he was made consul and governor of Britannia. As governor, he completed the conquest of what is today Wales and northern England, and led his army to the far north of Scotland, establishing forts across much of the lowlands. In 85, Agricola was rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartimandua
Cartimandua or Cartismandua (reigned ) was a 1st-century queen of the Brigantes, a Celtic people living in what is now northern England. She is known through the writings of Roman historian Tacitus. She came to power during the time period that Rome was campaigning against Britain. She was widely influential during her reign. As ruler of the Brigantes, she united various British tribes that eventually surrendered their loyalty to Rome. Cartimandua is portrayed notoriously in Tacitus's account of her. She is recorded betraying the Celtic chieftain Caratacus, insincerely offering him sanctuary, but instead turning him in to the Romans in exchange for wealth. She also is recorded as having divorced her consort and replacing him with a common military man. She subsequently was engaged in extended military conflict with her ex-consort as he staged revolts against her multiple times, and she eventually lost to him. History Although Cartimandua is first mentioned by Tacitus in AD 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus (fl. AD 40–69) was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated Boudica and her army during the Boudican revolt. Early life Little is known of Suetonius' family, but it likely came from Pisaurum (modern Pesaro), a town on the Adriatic coast of Italy. Mauretanian campaign Having served as ''praetor'' in 40 AD, Suetonius was appointed governor of Mauretania (modern northern Morocco) the following year. In collaboration with Gnaeus Hosidius Geta, he suppressed the revolt led by Aedemon in the mountainous province that arose from the execution of the local ruler by Caligula. In 41 AD Suetonius was the first Roman commander to lead troops across the Atlas Mountains, and Pliny the Elder quotes his description of the area in his ''Natural History''. Governor of Britain In 58 AD, before being consul,A. R. Birley, "Suetonius Paullinus, Gaius (fl. c.AD 40–69)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Veranius
Quintus Veranius (died AD 57) was a Roman general around the mid-first century CE. He was ''III vir monetalis'', tribune of Legio IV ''Scythica'' and quaestor under Tiberius. He was appointed tribune of the plebs Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune () was the first office of the Roman Republic, Roman state that was open to the plebs, plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the pow ... in 41 and praetor in 42. In 43, the Emperor Claudius constituted the new province of Lycia, and appointed Veranius as its governor. He governed the province until 48, and during this period put down the rebellion of Cilicia (Roman province), Cilicia Trachea. He served as Roman consul, consul in 49, and was elevated to Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician status by Claudius, who also appointed him as an augur. __NOTOC__ Veranius became governor of Roman Britain, Britain in 57, replacing Aulus Didius Gallus. He reversed Didius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunni; and to the west by the Demetae. Origins According to Tacitus's biography of Agricola, the Silures usually had a dark complexion and curly hair. Due to their appearance, Tacitus believed they had crossed over from Spain at an earlier date.The dark complexion of the Silures, their usually curly hair, and the fact that Spain is the opposite shore to them, are an evidence that Iberians of a former date crossed over and occupied these parts. Jordanes, in his Origins and Deeds of the Goths, describes the Silures. The Silures have swarthy features and are usually born with curly black hair, but the inhabitants of Caledonia have reddish hair and large loose-jointed bodies. They are like the Gauls or the Spaniards. The Iron Age hillfort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossington
Rossington is a civil parish and former mining village in the City of Doncaster, South Yorkshire, England and is surrounded by countryside and the market towns of Bawtry and Tickhill. Geography Historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, it has a population of 13,255, increasing to 13,557 at the 2011 Census. Robin Hood Airport Doncaster Sheffield is around two miles to the east. The village is demarcated to the north and west by a line of 400 kV pylons, as seen from the M18, to the north. The Finningley and Rossington Relief Road Scheme – from Junction 3 of the M18 to Parrot's Corner (junction of the A638 and the B6463 roads) – is proposed to allow access to the airport. Construction was due to start in late summer 2012 though initial site clearance work only commenced in early 2013. To the north-west, the village borders Loversall, with the boundary following the River Torne, passing directly next to the western edge of the former Rossington Main Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wroxeter
Wroxeter ( ) is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Wroxeter and Uppington, in the Shropshire district, in the ceremonial county of Shropshire, England. It is beside the River Severn, south-east of Shrewsbury. In 1961 the parish had a population of 657. '' Viroconium Cornoviorum'', the fourth largest city in Roman Britain, was sited here, and is gradually being excavated. In 2024, archaeologists uncovered a 2,000 year old mosaic depicting dolphins and fish. The village contains one of Shropshire's commercial vineyards. History Roman Wroxeter, near the end of the Watling Street Roman road that ran across Romanised Celtic Britain from '' Dubris'' (Dover), was a key frontier position lying on the bank of the River Severn whose valley penetrated deep into what later became known as Wales, and also on a route south leading to the Wye valley. Archaeology has shown that the site of the later city first was established about AD 55 as a frontier post fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheshire Plain
The Cheshire Plain is a relatively flat expanse of lowland within the county of Cheshire in North West England but extending south into Shropshire. It extends from the Mersey Valley in the north to the Shropshire Hills in the south, bounded by the hills of North Wales to the west and the foothills of the Pennines to the north-east. The Wirral Peninsula lies to the north-west whilst the plain merges with the West Lancashire Coastal Plain, South Lancashire Plain in the embayment occupied by Manchester to the north. In detail, the plain comprises two areas with distinct characters, the one to the west of the Mid Cheshire Ridge and the other, larger part, to its east. The plain is the surface expression of the Cheshire Basin, a deep sedimentary basin that extends north into Lancashire and south into Shropshire. It assumed its current form as the ice-sheets of the last glacial period melted away between 20,000 and 15,000 years ago leaving behind a thick cover of glacial till and exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |