|
Depth Of Focus (tectonics)
In seismology, the depth of focus or focal depth is the depth at which an earthquake occurs. Earthquakes occurring at a depth of less than are classified as shallow-focus earthquakes, while those with a focal depth between and are commonly termed mid-focus or intermediate-depth earthquakes. In subduction zones, where older and colder oceanic crust sinks under another tectonic plate, deep-focus earthquakes may occur at much greater depths in the mantle, ranging from up to . The cause of deep-focus earthquakes is still not entirely understood since subducted lithosphere at that pressure and temperature regime should not exhibit brittle behavior. A possible mechanism for the generation of deep-focus earthquakes is faulting caused by olivine undergoing a phase transition into a spinel structure, with which they are believed to be associated. Earthquakes at this depth of focus typically occur at oceanic-continental convergent boundaries, along Wadati–Benioff zones. Discovery The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through planetary bodies. It also includes studies of the environmental effects of earthquakes such as tsunamis; other seismic sources such as volcanoes, plate tectonics, glaciers, rivers, oceanic microseisms, and the atmosphere; and artificial processes such as explosions. Paleoseismology is a related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes. A recording of Earth's motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who works in basic or applied seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
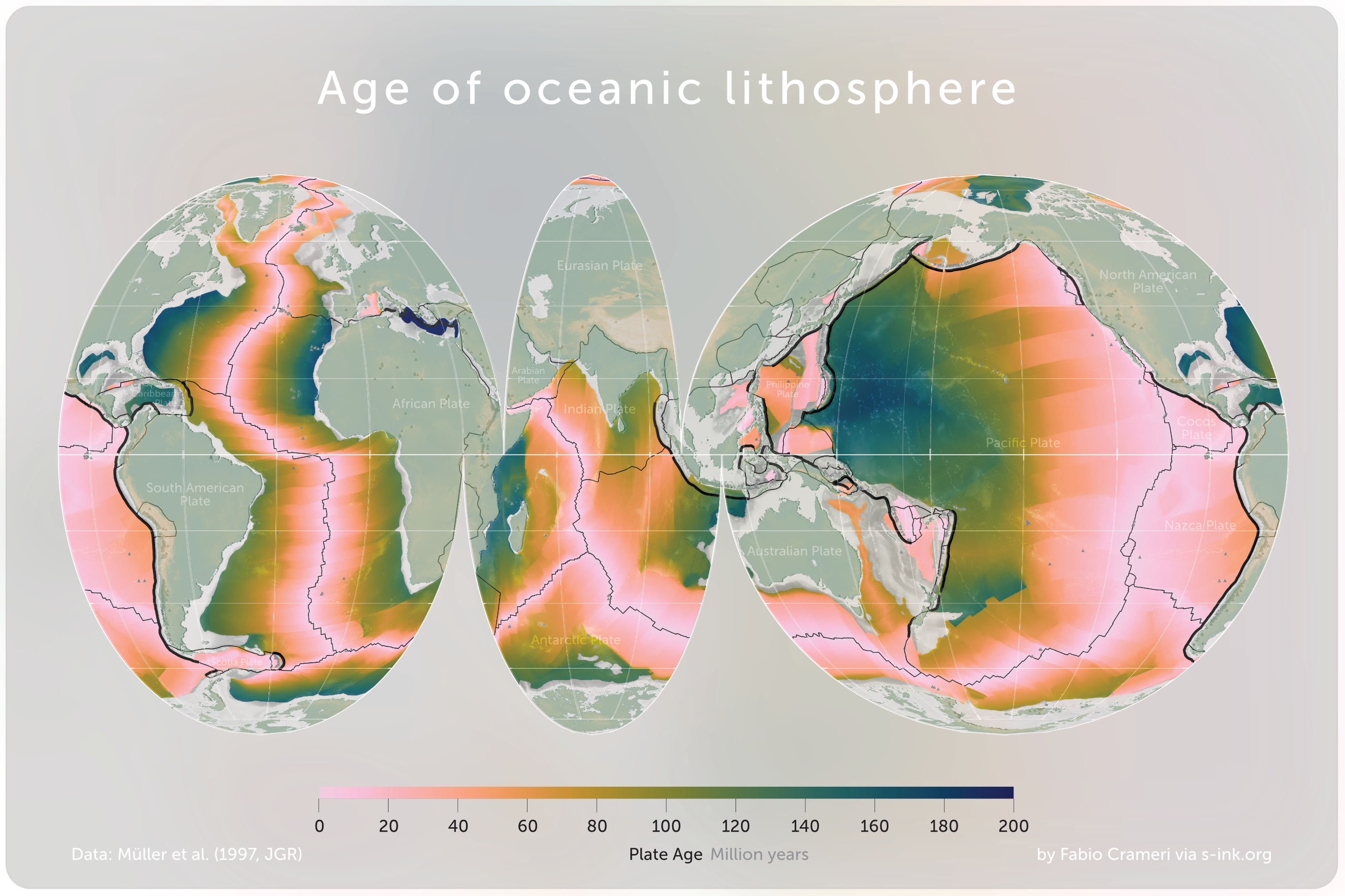
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust lies above the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep-focus Earthquake
A deep-focus earthquake in seismology (also called a plutonic earthquake) is an earthquake with a hypocenter depth exceeding 300 km. They occur almost exclusively at convergent boundaries in association with subducted oceanic lithosphere. They occur along a dipping tabular zone beneath the subduction zone known as the Wadati–Benioff zone. Discovery Preliminary evidence for the existence of deep-focus earthquakes was first brought to the attention of the scientific community in 1922 by Herbert Hall Turner. In 1928, Kiyoo Wadati proved the existence of earthquakes occurring well beneath the lithosphere, dispelling the notion that earthquakes occur only with shallow focal depths. Seismic characteristics Deep-focus earthquakes give rise to minimal surface waves. Their focal depth causes the earthquakes to be less likely to produce seismic wave motion with energy concentrated at the surface. The path of deep-focus earthquake seismic waves from focus to recording statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Earthquake Information Center
The National Earthquake Information Center (abbreviated NEIC) is part of the United States Geological Survey (USGS) located on the campus of the Colorado School of Mines in Golden, Colorado. The NEIC has three main missions: * First, the NEIC determines, as rapidly and as accurately as possible, the location and size of all significant earthquakes that occur worldwide. The NEIC disseminates this information immediately to concerned national and international agencies, scientists, critical facilities, and the general public. * Second, the NEIC collects and provides to scientists and to the public an extensive seismic database that serves as a solid foundation for scientific research, principally through the operation of modern digital national and global seismograph networks and through cooperative international agreements. The NEIC is the U.S. national data center and archive for earthquake information. * Third, the NEIC pursues an active research program to improve its abilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the lithospheric mantle (or mantle lithosphere), the uppermost part of the mantle that is not convecting. The layer below the lithosphere is called the asthenosphere, which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle that is able to convect. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron Silicate minerals, silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of Nesosilicates, nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. Olivine has many uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmember (mineralogy), endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as Mole (unit), molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and/or fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30, or just Fo70 with Fa30 implied). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while fayalite's is much lower – about . Melting temperature varies smoothly between the two end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic State of matter, states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma (physics), plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical property, physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition States of matter Phase transitions commonly refer to when a substance tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinel
Spinel () is the magnesium/aluminium member of the larger spinel group of minerals. It has the formula in the cubic crystal system. Its name comes from the Latin word , a diminutive form of ''spine,'' in reference to its pointed crystals. Properties Spinel crystallizes in the isometric system; common crystal forms are octahedron, octahedra, usually Crystal twinning, twinned. It has no true Cleavage (crystal), cleavage, but shows an octahedral Parting (crystal), parting and a conchoidal fracture. Its Mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness is 8, its specific gravity is 3.5–4.1, and it is transparent to opaque with a vitreous to dull Lustre (mineralogy), luster. It may be colorless, but is usually various shades of red, lavender (color), lavender, blue, green, brown, black, or yellow. Chromium(III) causes the red color in spinel from Burma. Some spinels are among the most famous gemstones; among them are the Black Prince's Ruby and the "Timur ruby" in the British Crown Jewels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surface to the mantle. These convection cells bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadati–Benioff Zone
A Wadati–Benioff zone (also Benioff–Wadati zone or Benioff zone or Benioff seismic zone) is a planar zone of seismicity corresponding with the down-going slab in a subduction zone. Differential motion along the zone produces numerous earthquakes, the foci of which may be as deep as about . The term was named for the two seismologists, Hugo Benioff of the California Institute of Technology and Kiyoo Wadati of the Japan Meteorological Agency, who independently discovered the zones. Wadati–Benioff zone earthquakes develop beneath volcanic island arcs and continental margins above active subduction zones. They can be produced by slip along the subduction thrust fault or slip on faults within the downgoing plate, as a result of bending and extension as the plate is pulled into the mantle. The deep-focus earthquakes along the zone allow seismologists to map the three-dimensional surface of a subducting slab of oceanic crust and mantle. Discovery In 1949, Hugo Benioff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |