|
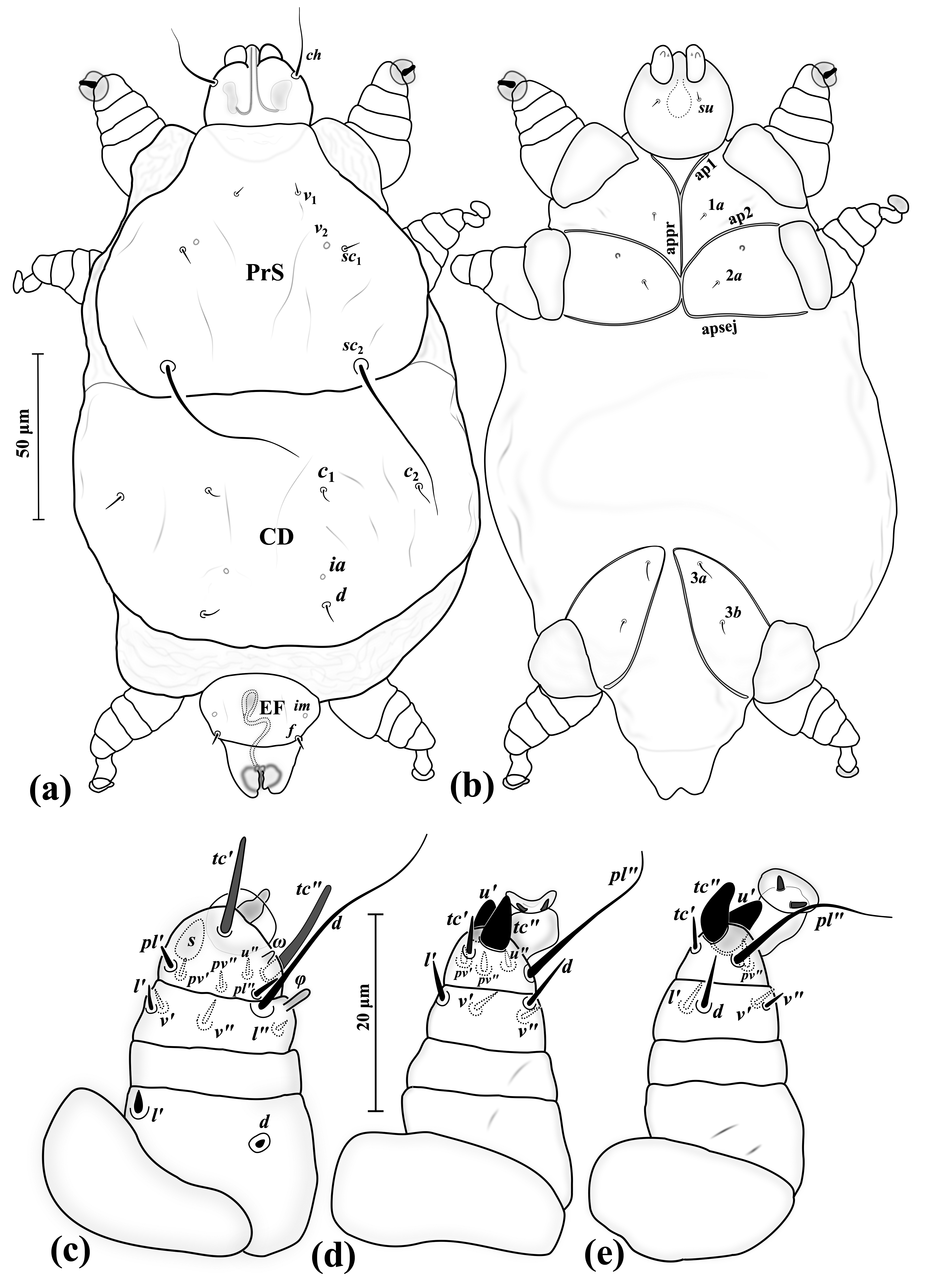
Demodex Injai
''Demodex injai'' is a hair follicle mite in the domestic dog The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers .... References Trombidiformes Animals described in 2003 Dog diseases {{Trombidiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair Follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between hormones, neuropeptides, and immune cells. This complex interaction induces the hair follicle to produce different types of hair as seen on different parts of the body. For example, terminal hairs grow on the scalp and lanugo hairs are seen covering the bodies of fetuses in the uterus and in some newborn babies. The process of hair growth occurs in distinct sequential stages: ''anagen'' is the active growth phase, ''catagen'' is the regression of the hair follicle phase, ''telogen'' is the resting stage, ''exogen'' is the active shedding of hair phase and ''kenogen'' is the phase between the empty hair follicle and the growth of new hair. The function of hair in humans has long been a subject of interest and continues to be an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group invalid as a clade. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are Predation, predators or Parasitism, parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy Mites are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Dog
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the gray wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it was selectively bred from a population of wolves during the Late Pleistocene by hunter-gatherers. The dog was the first species to be domesticated by humans, over 14,000 years ago and before the development of agriculture. Due to their long association with humans, dogs have gained the ability to thrive on a starch-rich diet that would be inadequate for other canids. Dogs have been bred for desired behaviors, sensory capabilities, and physical attributes. Dog breeds vary widely in shape, size, and color. They have the same number of bones (with the exception of the tail), powerful jaws that house around 42 teeth, and well-developed senses of smell, hearing, and sight. Compared to humans, dogs possess a superior sense of smell and hearing, but inferior visual acuity. Dogs perform many roles for humans, such as hunting, herding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Medical Entomology
The ''Journal of Medical Entomology'' is a peer-reviewed bimonthly scientific journal published by Oxford University Press for the Entomological Society of America. The journal publishes reports on all aspects of medical entomology and medical acarology. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'' the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 1.953. References External links * Academic journals established in 1964 Entomology journals and magazines Bimonthly journals English-language journals Academic journals published by learned and professional societies of the United States Oxford University Press academic journals Entomological Society of America academic journals {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes
Trombidiformes is a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as ''Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera and 25,821 species, and there were another 10 species with 24 species that present only as fossils. These 151 famili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animals Described In 2003
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozoa, Cni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |