|
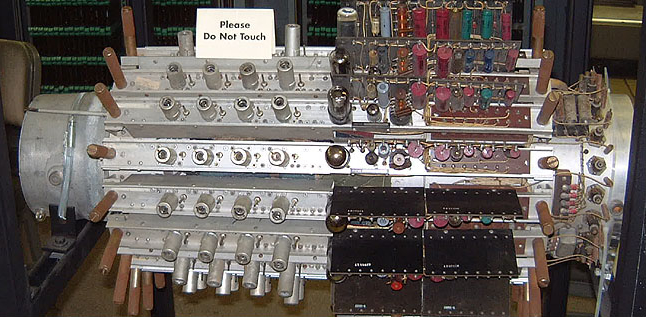
Delay-line Memory
Delay-line memory is a form of computer memory, mostly obsolete, that was used on some of the earliest Digital data, digital computers, and is reappearing in the form of #Optical_delay_lines, optical delay lines. Like many modern forms of electronic computer memory, delay-line memory was a memory refresh, refreshable memory, but as opposed to modern random-access memory, delay-line memory was Sequential access, sequential-access. Analog delay line technology had been used since the 1920s to delay the propagation of analog signals. When a delay line is used as a memory device, an amplifier and a pulse shaping, pulse shaper are connected between the output of the delay line and the input. These devices recirculate the signals from the output back into the input, creating a loop that maintains the signal as long as power is applied. The shaper ensures the pulses remain well-formed, removing any degradation due to losses in the medium. The memory capacity equals the time to transmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ''core'' (for magnetic core memory) and ''store''. Main memory operates at a high speed compared to mass storage which is slower but less expensive per bit and higher in capacity. Besides storing opened programs and data being actively processed, computer memory serves as a Page cache, mass storage cache and write buffer to improve both reading and writing performance. Operating systems borrow RAM capacity for caching so long as it is not needed by running software. If needed, contents of the computer memory can be transferred to storage; a common way of doing this is through a memory management technique called ''virtual memory''. Modern computer memory is implemented as semiconductor memory, where data is stored within memory cell (com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostrictive
Magnetostriction is a property of magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron. Magnetostriction applies to magnetic fields, while electrostriction applies to electric fields. Magnetostriction causes energy loss due to frictional heating in susceptible ferromagnetic cores, and is also responsible for the low-pitched humming sound that can be heard coming from transformers, where alternating currents produce a changing magnetic field. Explanation Internally, ferromagnetic materials have a structure that is divided into '' domains'', each of which is a region of uniform magnetization. When a magnetic field is applied, the boundaries between the domains shift and the domains rotat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piezoelectricity
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The piezoelectric effect results from the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and electrical states in crystalline materials with no inversion symmetry. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process: materials exhibiting the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect, the internal generation of a mechanical strain resulting from an applied electric field. For example, lead zirconate titanate crystals will generate measurable piezoelectricity when their static structure is deformed by about 0.1% of the original dimension. Conversely, those same crystals will change about 0.1% of their static dimension when an external electric field is applied. The inverse piezoelectric effect is used in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore School Of Electrical Engineering
The Moore School of Electrical Engineering was a school at the University of Pennsylvania. The school was integrated into the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science. The Moore School came into existence as a result of an endowment from Alfred Fitler Moore on June 4, 1923. It was granted to Penn's School of Electrical Engineering, located in the Towne Building. The first dean of the Moore School was Harold Pender. The Moore School is particularly famed as the birthplace of the computer industry: * It was here that the first general-purpose Turing complete digital electronic computer, the ENIAC, was built between 1943 and 1946. * Preliminary design work on the ENIAC's successor machine the EDVAC resulted in the stored program concept used in all computers today, the logical design having been promulgated in John von Neumann's ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC'', a set of notes synthesized from meetings he attended at the Moore School. * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of founder and first president Benjamin Franklin, who had advocated for an educational institution that trained leaders in academia, commerce, and public service. The university has four undergraduate schools and 12 graduate and professional schools. Schools enrolling undergraduates include the College of Arts and Sciences, the University of Pennsylvania School of Engineering and Applied Science, School of Engineering and Applied Science, the Wharton School, and the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing, School of Nursing. Among its graduate schools are its University of Pennsylvania Law School, law school, whose first professor, James Wilson (Founding Father), James Wilson, helped write the Constitution of the United States, U.S. Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raytheon
Raytheon is a business unit of RTX Corporation and is a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. Founded in 1922, it merged in 2020 with United Technologies Corporation to form Raytheon Technologies, which changed its name to RTX Corporation in July 2023. Raytheon was established in 1922, reincorporated in 1928, and adopted the Raytheon Company name in 1959. More than 90% of Raytheon's revenues were obtained from military contracts and, as of 2012, it was the fifth-largest military contractor in the world. , it was the third-largest defense contractor in the United States by defense revenue. It was the world's largest producer of guided missiles, and was involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft until early 2007. In 2018, the company had around 67,000 employees worldwide and annual revenues of about US$25.35 billion. Over the years, Raytheon shifted its headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. Located in Washington, DC, it was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological development and prototyping. The laboratory's specialties include plasma physics, space physics, materials science, and tactical electronic warfare. NRL is one of the first US government scientific R&D laboratories, having opened in 1923 at the instigation of Thomas Edison, and is currently under the Office of Naval Research. As of 2016, NRL was a Navy Working Capital Fund activity, which means it is not a line-item in the US Federal Budget. Instead of direct funding from Congress, all costs, including overhead, were recovered through sponsor-funded research projects. NRL's research expenditures were approximately $1 billion per year. Research The Naval Research Laboratory conducts a wide variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Wave
In physics, a surface wave is a mechanical wave that propagates along the Interface (chemistry), interface between differing media. A common example is gravity waves along the surface of liquids, such as ocean waves. Gravity waves can also occur within liquids, at the interface between two fluids with different densities. Elastic surface waves can travel along the surface of solids, such as ''Rayleigh wave, Rayleigh'' or ''Love wave, Love'' waves. Electromagnetic waves can also propagate as "surface waves" in that they can be guided along with a refractive index gradient or along an interface between two media having different dielectric constants. In radio transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a ''ground wave'' is a guided wave that propagates close to the surface of the Earth. Mechanical waves In seismology, several types of surface waves are encountered. Surface waves, in this mechanical sense, are commonly known as either ''Love waves'' (L waves) or ''Rayleigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an Acoustical engineering, acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing (sense), Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Repetition Frequency
The pulse-repetition frequency (PRF) is the number of pulses of a repeating signal in a specific time unit. The term is used within a number of technical disciplines, notably radar. In radar, a radio signal of a particular carrier frequency is turned on and off; the term "frequency" refers to the carrier, while the PRF refers to the number of switches. Both are measured in terms of cycle per second, or hertz. The PRF is normally much lower than the frequency. For instance, a typical World War II radar like the Type 7 GCI radar had a basic carrier frequency of 209 MHz (209 million cycles per second) and a PRF of 300 or 500 pulses per second. A related measure is the pulse width, the amount of time the transmitter is turned on during each pulse. After producing a brief pulse of radio signal, the transmitter is turned off in order for the receiver units to detect the reflections of that signal off distant targets. Since the radio signal has to travel out to the target and back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Display
A radar display is an electronic device that presents radar data to the operator. The radar system transmits pulses or continuous waves of electromagnetic radiation, a small portion of which backscatter off targets (intended or otherwise) and return to the radar system. The receiver converts all received electromagnetic radiation into a continuous electronic analog signal of varying (or oscillating) voltage that can be converted then to a screen display. Modern systems typically use some sort of raster graphics, raster scan display to produce a map-like image. Early in radar development, however, numerous circumstances made such displays difficult to produce. People developed several different display types. Oscilloscopes Early radar displays used adapted oscilloscopes with various inputs. An oscilloscope generally receives three ''channels'' of varying (or oscillating) voltage as input and displays this information on a cathode ray tube. The oscilloscope amplifies the input vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |