|
Deep-sky Object
A deep-sky object (DSO) is any astronomical object that is not an individual star or Solar System object (such as Sun, Moon, planet, comet, etc.). The classification is used for the most part by amateur astronomers to denote visually observed faint naked eye and Optical telescope, telescopic objects such as star clusters, nebulae and galaxy, galaxies. This distinction is practical and technical, implying a variety of instruments and techniques appropriate to observation, and does not distinguish the nature of the object itself. Origins and classification Classifying non-stellar astronomical objects began soon after the invention of the telescope. One of the earliest comprehensive lists was Charles Messier's 1774 Messier catalog, which included 103 "nebulae" and other faint fuzzy objects he considered a nuisance since they could be mistaken for comets, the objects he was actually searching for. As telescopes improved these faint nebulae would be broken into more descriptive scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion 3008 Huge (detail)
Orion may refer to: Common meanings * Orion (constellation), named after the mythical hunter * Orion (mythology), a hunter in Greek mythology Arts and media Fictional entities Characters and species * Orion (character), a DC Comics character * Orion (Star Trek), Orion (''Star Trek''), a sentient alien species * Orion, code name of Stephen J. Bartowski on the television show ''Chuck'' * Orion, in the fighting game ''Brawlhalla'' * Orions, a race in the ''Starfire (board wargame), Starfire'' board game and book series * Orion, a List of Power Rangers Megaforce characters, character from ''Power Rangers Super Megaforce'' * Captain Orion, in the Japanese series ''X-Bomber'' * Orion Pax, the former name of Optimus Prime. Orion Black, the father of Sirius Black and Regulus Black, in the Harry Potter Series Vessels * ''Orion'', a spaceplane in the film 2001: A Space Odyssey (film), ''2001: A Space Odyssey'' * ''Orion'', a spaceship in ''Raumpatrouille Orion'' (''Space Patrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
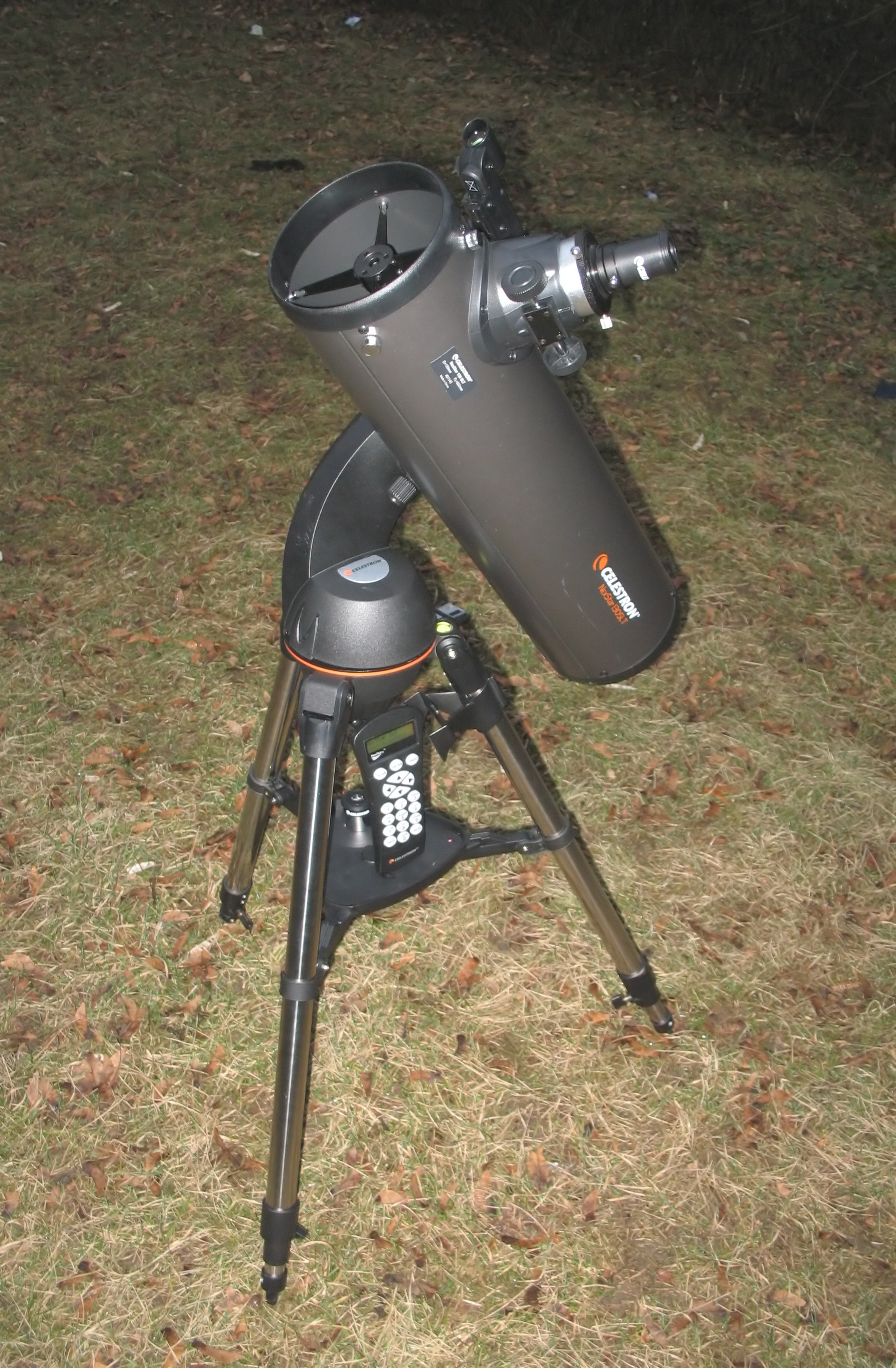
GoTo (telescopes)
In amateur astronomy, "GoTo" refers to a type of telescope mount and related software that can automatically point a telescope at astronomical objects that the user selects. Both axes of a GoTo mount are driven by a motor and controlled by a computer. It may be either a microprocessor-based integrated controller or an external personal computer. This differs from the single-axis semi-automated tracking of a traditional clock-drive equatorial mount. The user can command the mount to point the telescope to the celestial coordinates that the user inputs, or to objects in a pre-programmed database including ones from the Messier catalogue, the New General Catalogue, and even major Solar System bodies (the Sun, Moon, and planets). Like a standard equatorial mount, equatorial GoTo mounts can track the night sky by driving the right ascension axis. Since both axes are computer controlled, GoTo technology also allows telescope manufacturers to add equatorial tracking to mechanica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
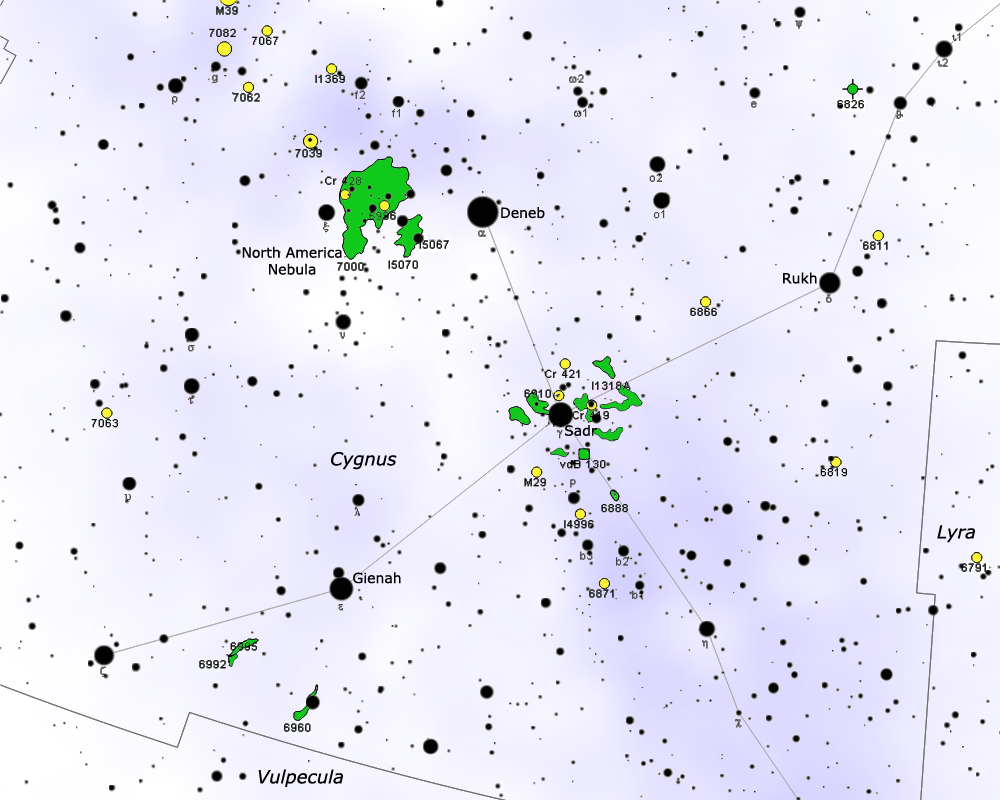
Reflection Nebula
In astronomy, reflection nebulae are interstellar cloud, clouds of Cosmic dust, interstellar dust which might reflect the light of a nearby star or stars. The energy from the nearby stars is insufficient to Ionization, ionize the gas of the nebula to create an emission nebula, but is enough to give sufficient scattering to make the dust visible. Thus, the frequency spectrum shown by reflection nebulae is similar to that of the illuminating stars. Among the microscopic particles responsible for the scattering are carbon compounds (e. g. diamond dust) and compounds of other elements such as iron and nickel. The latter two are often aligned with the Galaxy#Magnetic fields, galactic magnetic field and cause the scattered light to be slightly Polarization (waves), polarized. Discovery Analyzing the spectrum of the nebula associated with the star Merope (star), Merope in the Pleiades, Vesto Slipher concluded in 1912 that the source of its light is most likely the star itself, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emission Nebula
An emission nebula is a nebula formed of ionized gases that emit light of various wavelengths. The most common source of ionization is high-energy ultraviolet photons emitted from a nearby hot star. Among the several different types of emission nebulae are H II regions, in which star formation is taking place and young, massive stars are the source of the ionizing photons; and planetary nebulae, in which a dying star has thrown off its outer layers, with the exposed hot core then ionizing them.Nebulae< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
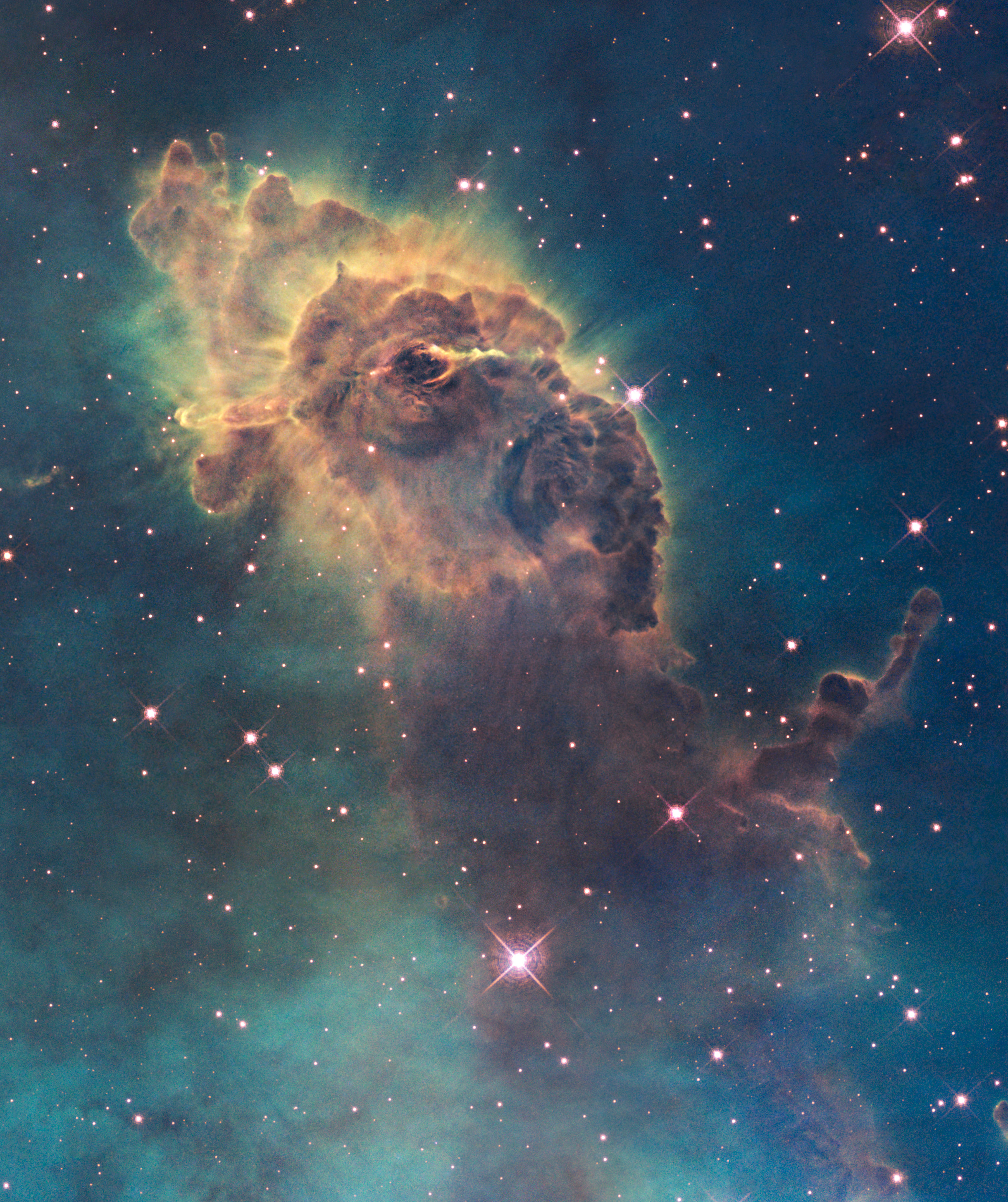
Bright Nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dense tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Galactic Nucleus
An active galactic nucleus (AGN) is a compact region at the center of a galaxy that emits a significant amount of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum, with characteristics indicating that this luminosity is not produced by the stars. Such excess, non-stellar emissions have been observed in the radio waves, radio, microwave, infrared, visible spectrum, optical, ultra-violet, X-ray and gamma ray wavebands. A galaxy hosting an AGN is called an active galaxy. The non-stellar radiation from an AGN is theorized to result from the accretion (astrophysics), accretion of matter by a supermassive black hole at the center of its host galaxy. Active galactic nuclei are the most luminous persistent sources of electromagnetic radiation in the universe and, as such, can be used as a means of discovering distant objects; their evolution as a function of cosmic time also puts constraints on cosmology, models of the cosmos. The observed characteristics of an AGN depend on several properties s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. The boundary (topology), boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. A black hole has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, but has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with thermal radiation, the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the Orders of magnitude (temperature), order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
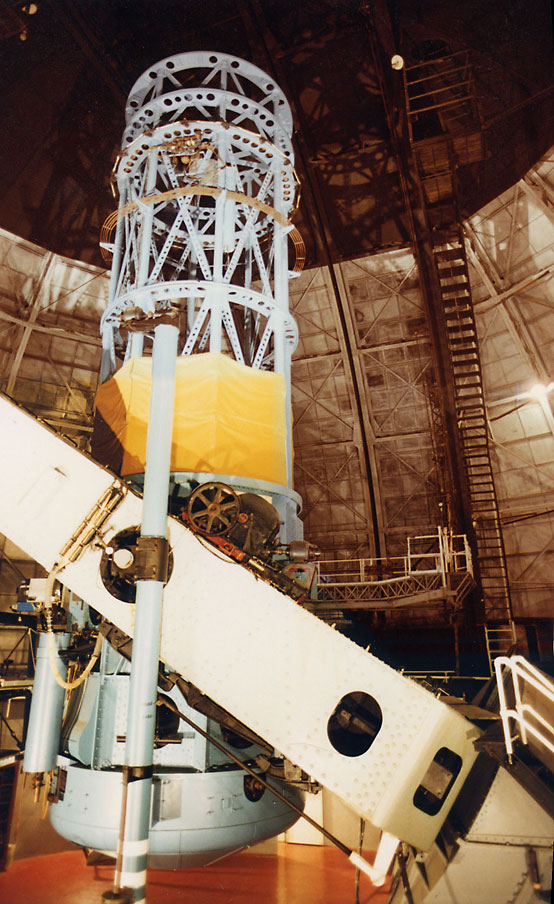
Telescopes
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herschel 400 Catalogue
The Herschel 400 catalogue is a subset of William Herschel, William Herschel's original ''Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'', selected by Brenda F. Guzman (Branchett), Lydel Guzman, Paul Jones, James Morris, Peggy Taylor and Sara Saey of the Ancient City Astronomy Club in St. Augustine, Florida, United States 1980. They decided to generate the list after reading a letter published in Sky and telescope, ''Sky & Telescope'' by James Mullaney of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. In this letter Mr. Mullaney suggested that William Herschel's original catalogue of 2,500 objects would be an excellent basis for deep sky object selection for amateur astronomers looking for a challenge after completing the Messier Catalogue. The Herschel 400 is a subset of John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters'' published in 1864 of 5,000 objects, and hence also of the ''New General Catalogue''. The catalogue forms the basis of thAstronomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier Marathon
A Messier marathon is an attempt, usually organized by amateur astronomers, to find as many Messier objects as possible during one night. The Messier catalogue was compiled by French astronomer Charles Messier during the late 18th century and consists of 110 relatively bright deep-sky objects (galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters). When and where a marathon is possible The number of Messier objects visible in any one night varies depending on a few factors, including the location of the observer, the duration of daylight and nighttime, and the season (the positions of the Messier objects relative to the Sun varies with the season, as does the length of the night). Location Because Messier compiled his catalog from a northern latitude, not all of the Messier objects are visible from the southern hemisphere. In particular, M81, M82, M52, and M103 make southern-hemisphere Messier marathons difficult, because they are all located at a declination of 60° north or greater. Altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Filter
An astronomical filter is a telescope accessory consisting of an optical filter used by amateur astronomers to improve the details and contrast of celestial objects, either for viewing or for photography. Research astronomers, on the other hand, use various band-pass filters for photometry on telescopes, in order to obtain measurements which reveal objects' astrophysical properties, such as stellar classification and placement of a celestial body on its Wien curve. Most astronomical filters work by blocking a specific part of the color spectrum above and below a ''bandpass'', significantly increasing the signal-to-noise ratio of the interesting wavelengths, and so making the object gain detail and contrast. While the color filters transmit certain colors from the spectrum and are usually used for observation of the planets and the Moon, the polarizing filters work by adjusting the brightness, and are usually used for the Moon. The broad-band and narrow-band filters transmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |