|
Declarative Procedural Model Of Language
Declarative may refer to: * Declarative learning, acquiring information that one can speak about * Declarative memory, one of two types of long term human memory * Declarative programming, a computer programming paradigm * Declarative sentence, a type of sentence that makes a statement * Declarative mood A realis mood ( abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact; in other words, to express what the speaker considers to be a known state of affairs, as in declarative sentences. Mo ..., a grammatical verb form used in declarative sentences See also * Declaration (other) {{disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Declarative Learning
Declarative learning is acquiring information that one can speak about (contrast with motor learning). The capital of a state is a declarative piece of information, while knowing how to ride a bike is not. Episodic memory and semantic memory are a further division of declarative information. Overview There are two ways to learn a telephone number: memorize it using your declarative memory, or use it many times to create a habit. Habit learning is called procedural memory. Declarative memory uses your medial temporal lobe and enables you to recall the telephone number at will. Procedural memory activates the telephone number only when you are at the telephone, and uses your right-hemisphere's skill, pattern recognition. Research indicates declarative and habit memory compete with each other during distraction. When in doubt, the brain chooses habit memory because it is automatic. Several researchers at the UCLA tested the hypothesis that distraction can change the way a ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
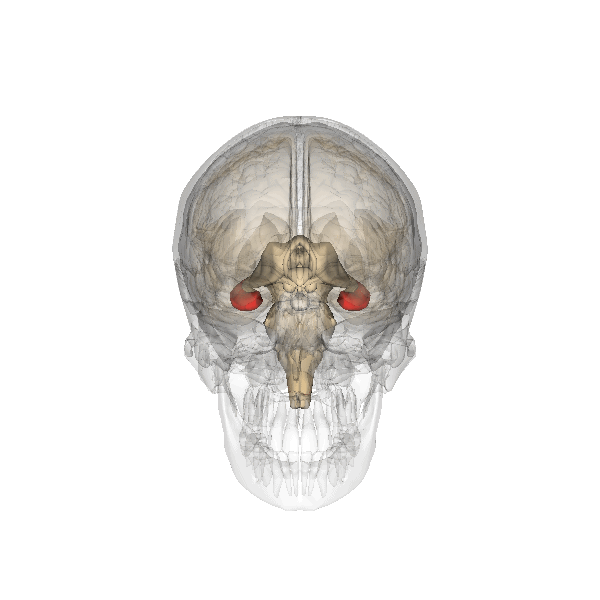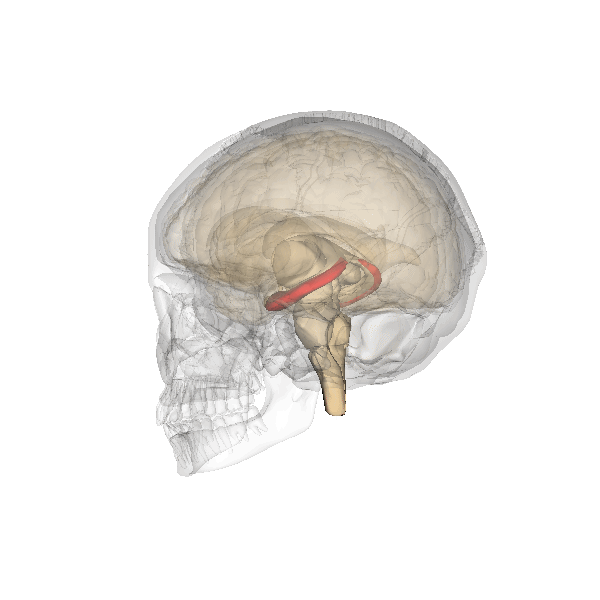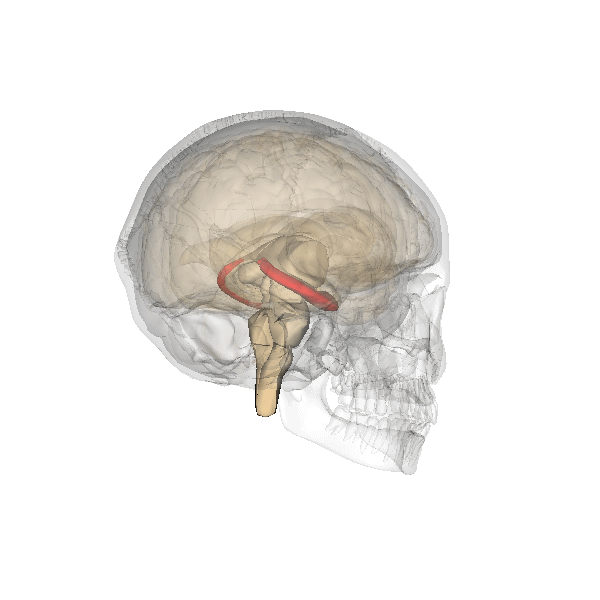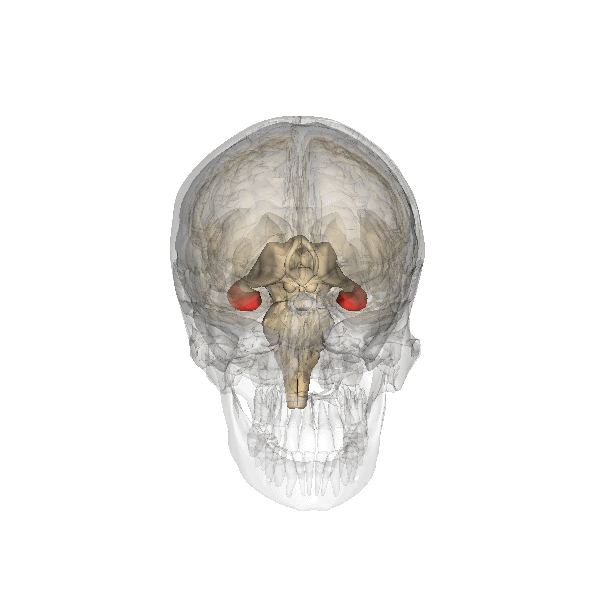 |
Declarative Memory
Explicit memory (or declarative memory) is one of the two main types of Long-term memory, long-term human memory, the other of which is implicit memory. Explicit memory is the Consciousness, conscious, intentional Recall (memory), recollection of factual information, previous experiences, and concepts. This type of memory is dependent upon three processes: acquisition, Memory Consolidation, consolidation, and retrieval. Explicit memory can be divided into two categories: episodic memory, which stores specific Experience, personal experiences, and semantic memory, which stores factual information.Tulving E. 1972. Episodic and semantic memory. In Organization of Memory, ed. E Tulving, W Donaldson, pp. 381–403. New York: Academic Explicit memory requires gradual learning, with multiple presentations of a Stimulus (psychology), stimulus and response. The type of knowledge that is stored in explicit memory is called declarative knowledge. Its counterpart, known as implicit memory, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Declarative Programming
In computer science, declarative programming is a programming paradigm—a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs—that expresses the logic of a computation without describing its control flow. Many languages that apply this style attempt to minimize or eliminate side effects by describing ''what'' the program must accomplish in terms of the problem domain, rather than describing ''how'' to accomplish it as a sequence of the programming language primitives (the ''how'' being left up to the language's implementation). This is in contrast with imperative programming, which implements algorithms in explicit steps. Declarative programming often considers programs as theories of a formal logic, and computations as deductions in that logic space. Declarative programming may greatly simplify writing parallel programs. Common declarative languages include those of database query languages (e.g., SQL, XQuery), regular expressions, logic programming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Declarative Sentence
Declarative may refer to: * Declarative learning, acquiring information that one can speak about * Declarative memory, one of two types of long term human memory * Declarative programming In computer science, declarative programming is a programming paradigm—a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs—that expresses the logic of a computation without describing its control flow. Many languages that ap ..., a computer programming paradigm * Declarative sentence, a type of sentence that makes a statement * Declarative mood, a grammatical verb form used in declarative sentences See also * Declaration (other) {{disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Declarative Mood
A realis mood ( abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact; in other words, to express what the speaker considers to be a known state of affairs, as in declarative sentences. Most languages have a single realis mood called the indicative mood, although some languages have additional realis moods, for example to express different levels of certainty. By contrast, an irrealis mood is used to express something that is not known to be the case in reality. An example of the contrast between realis and irrealis moods is seen in the English sentences "He works" and "It is necessary that he work". In the first sentence, ''works'' is a present indicative (realis) form of the verb, and is used to make a direct assertion about the real world. In the second sentence, ''work'' is in the subjunctive mood, which is an irrealis mood – here ''that he work'' does not necessarily express a fact about the real world (he could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |