|
Debate On The Chineseness Of The Yuan And Qing Dynasties
The debate on the "Chineseness" of the Yuan and Qing dynasties is concerned with whether the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) and the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1644–1912) can be considered "Chinese dynasties", and whether they were representative of "China" during their respective historical periods. The debate, although historiographical in nature, has political implications. Mainstream academia and successive governments of China, including the imperial governments of the Yuan and Qing dynasties, have maintained the view that they were "Chinese" and representative of "China".葉碧苓《九一八事變後中國史學界對日本「滿蒙論」之駁斥—以〈東北史綱〉第一卷為中心之探討》,〈國史館學術集刊〉第11期,2007-03-01,第105-142頁方修琦,萧凌波,魏柱灯《8~19世纪之交华北平原气候转冷的社会影响及其发生机制》,〈中国科学〉第43卷第5期,2013年 The debate stemmed from differing opinions on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinational State
A multinational state or a multinational union is a sovereign entity that comprises two or more nations or states. This contrasts with a nation state, where a single nation accounts for the bulk of the population. Depending on the definition of "nation" (which touches on ethnicity, language, and political identity), a multinational state is usually multicultural or multilingual, and is geographically composed of more than one country, such as the countries of the United Kingdom. Historical multinational states that have since split into multiple states include the Ottoman Empire, British India, Qing Empire, Czechoslovakia, the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia, the United Arab Republic and Austria-Hungary (a dual monarchy of two multinational states). Some analysts have described the European Union as a multinational state or a potential one.Kelemen, R. Daniel. (2007). In ''Making History: State of the European Union'', Vol. 8, edited by Sophie Meunier and Kate McNamara, Oxford Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanji Ishiwara
was a general in the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II. He and Seishirō Itagaki were the men primarily responsible for the Mukden Incident that took place in Manchuria in 1931. Early life Ishiwara was born in Tsuruoka City, Yamagata Prefecture, into a ''samurai'' class family. His father was a police officer, but as his clan had supported the Tokugawa bakufu and then the Northern Alliance during the Boshin War of the Meiji Restoration, its members were shut out of higher government positions. At 13, Ishiwara was enrolled in a military preparatory school. He was subsequently accepted at the 21st class of the Imperial Japanese Army Academy and graduated in 1909. He served in the IJA 65th Infantry Regiment in Korea after its annexation by Japan in 1910, and in 1915, he passed the exams for admittance to the 30th class of the Army Staff College. He graduated second in his class in 1918. Ishiwara spent several years in various staff assignments and then was selected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Binglin
Zhang Binglin (January 12, 1869 – June 14, 1936), also known by his art name Zhang Taiyan, was a Chinese philologist, textual critic, philosopher, and revolutionary. His philological works include ''Wen Shi'' (文始 "The Origin of Writing"), the first systematic work of Chinese etymology. He also made contributions to historical Chinese phonology, proposing that "the ''niang'' (娘) and ''ri'' (日) syllable onset, initials [in Middle Chinese] come from the ''ni'' (泥) initial [in Old Chinese]" (known as ''niang ri gui ni'' 娘日歸泥). He developed a system of shorthand based on the seal script, called ''jiyin zimu'' (記音字母), later adopted as the basis of zhuyin. Though innovative in many ways, he was skeptical of new archaeological findings, regarding the oracle bones as forgery. An activist as well as a scholar, he produced many political works. Because of his outspoken character, he was jailed for three years by the Qing dynasty, Qing Empire and put under house a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored Imperial House of Japan, imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ruling emperors before the Meiji Restoration, the events restored practical power to, and consolidated the political system under, the Emperor of Japan. The Restoration led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure and spanned both the late Edo period (often called the Bakumatsu) and the beginning of the Meiji era, during which time Japan rapidly Industrialization, industrialised and adopted Western culture, Western ideas and production methods. The origins of the Restoration lay in economic and political difficulties faced by the Tokugawa shogunate. These problems were compounded by the encroachment of foreign powers in the region which challenged the Tokugawa policy of , specifically the arrival of the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
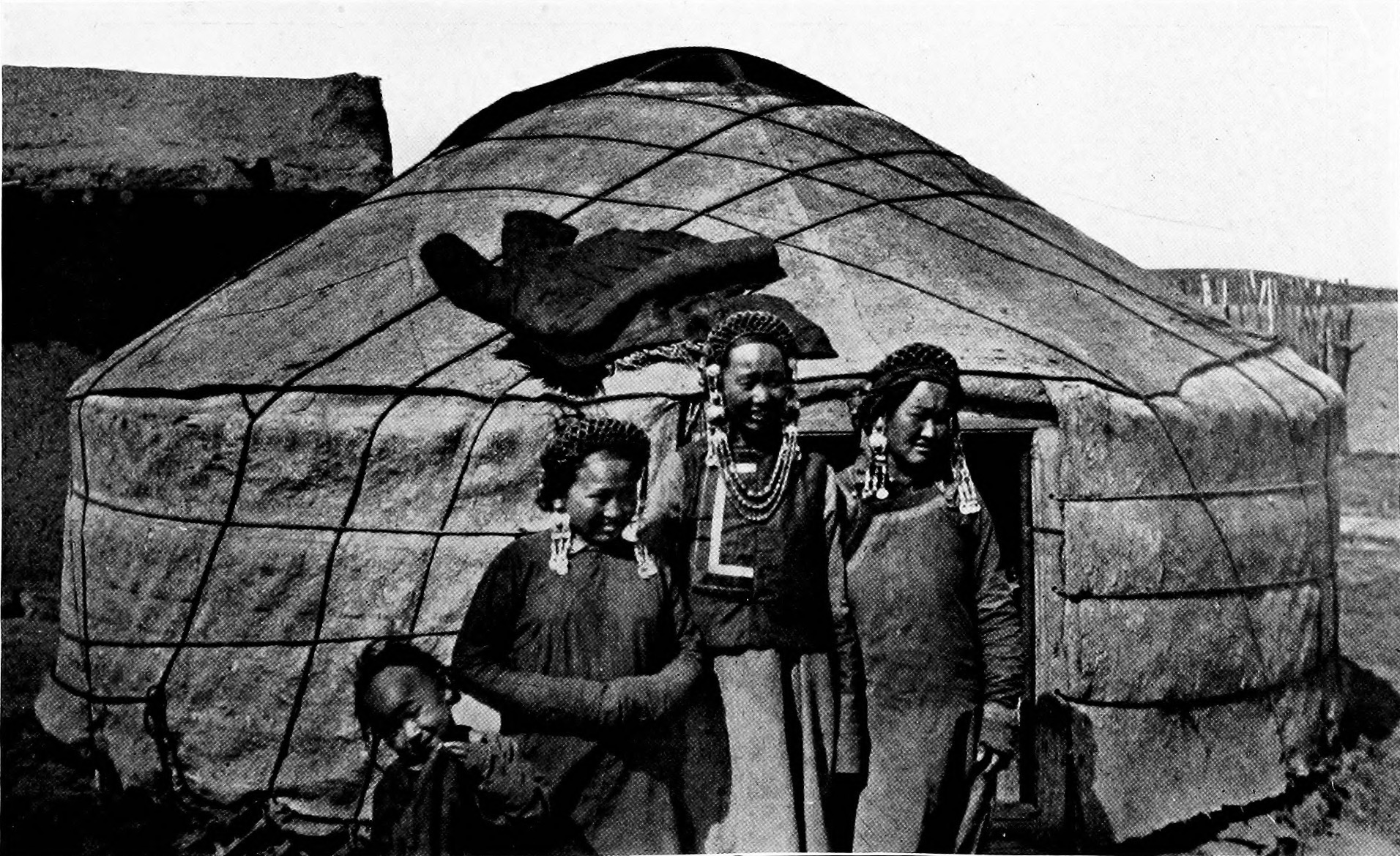
Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and Qing (1636–1912) dynasties of China were established and ruled by the Manchus, who are descended from the Jurchen people who earlier established the Jin dynasty (1115–1234) in northern China. Manchus form the largest branch of the Tungusic peoples and are distributed throughout China, forming the fourth largest ethnic group in the country. They are found in 31 Chinese provincial regions. Among them, Liaoning has the largest population and Hebei, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Inner Mongolia and Beijing have over 100,000 Manchu residents. About half of the population live in Liaoning and one-fifth in Hebei. There are a number of Manchu autonomous counties in China, such as Xinbin, Xiuyan, Qinglong, Fengning, Yitong, Qingyuan, Weichang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols In China
Mongols in China, also known as Mongolian Chinese or Chinese Mongols, are ethnic Mongols who live in China. They are one of the List of ethnic groups in China#Ethnic groups recognized by the People's Republic of China, 56 ethnic groups recognized by the Chinese government. As of 2020, there are 6,290,204 Mongols in China, a 0.45% increase from the 2010 national census. Most of them live in Inner Mongolia, Northeast China, Xinjiang and Qinghai. The Mongol population in China is nearly twice as much as that of the sovereign state of Mongolia. Distribution The Mongols in China are divided between autonomous regions and provinces as follows: * 68.72%: Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region * 11.52%: Liaoning Province * 2.96%: Jilin Province * 2.92%: Hebei Province * 2.58%: Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region * 2.43%: Heilongjiang Province * 1.48%: Qinghai Province * 1.41%: Henan Province * 5.98%: Rest of PRC Besides the Inner Mongolia autonomous region, there are other Mongol autonomo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Nationality Law
Chinese nationality law details the conditions by which a person holds nationality of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The primary law governing these requirements is the Nationality Law of the People's Republic of China, which came into force on September 10, 1980. Foreign nationals may naturalize if they are permanent residents in any part of China or they have immediate family members who are Chinese citizens. Residents of the Taiwan Area are also considered Chinese citizens, due to the PRC's extant claim over areas controlled by the Republic of China (ROC). Although mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau are all administered by the PRC, Chinese citizens do not have automatic residence rights in all three jurisdictions; each territory maintains a separate immigration policy. Voting rights and freedom of movement are tied to the region in which a Chinese citizen is domiciled, determined by ''hukou'' in mainland China and right of abode in the two special administrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplomacy
Diplomacy is the communication by representatives of State (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, non-governmental institutions intended to influence events in the international system.Ronald Peter Barston, ''Modern Diplomacy'', Pearson Education, 2006, p. 1 Diplomacy is the main instrument of foreign policy which represents the broader goals and strategies that guide a state's interactions with the rest of the world. International Treaty, treaties, Executive agreement, agreements, alliances, and other manifestations of international relations are usually the result of diplomatic negotiations and processes. Diplomats may also help shape a state by advising government officials. Modern diplomatic methods, practices, and principles originated largely from 17th-century European customs. Beginning in the early 20th century, diplomacy became professionalized; the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, ratified by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention, pact, or exchange of letters, among other terms; however, only documents that are legally binding on the parties are considered treaties under international law. Treaties may be bilateral (between two countries) or multilateral (involving more than two countries). Treaties are among the earliest manifestations of international relations; the first known example is a border agreement between the Sumer, Sumerian city-states of Lagash and Umma around 3100 BC. International agreements were used in some form by most major civilizations and became increasingly common and more sophisticated during the Early modern period, early modern era. The early 19th century saw developments in diplomacy, foreign policy, and international law reflected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Community
The international community is a term used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world. Usage Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is typically used to imply the existence of a common point of view towards such matters as specific issues of human rights. It is sometimes used in calling for action to be taken against an enemy, e.g., action against perceived political repression in a target country. The term is also commonly used to imply legitimacy and consensus for a point of view on a disputed issue, e.g., to enhance the credibility of a majority vote in the United Nations General Assembly. Criticism Several prominent legal figures and authors have argued that the term is more often used to describe a small minority of states, and not literally all nations or states in the world. According to International Criminal Court jurist Victor P. Tsilonis, it refers to "the interests of the most pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
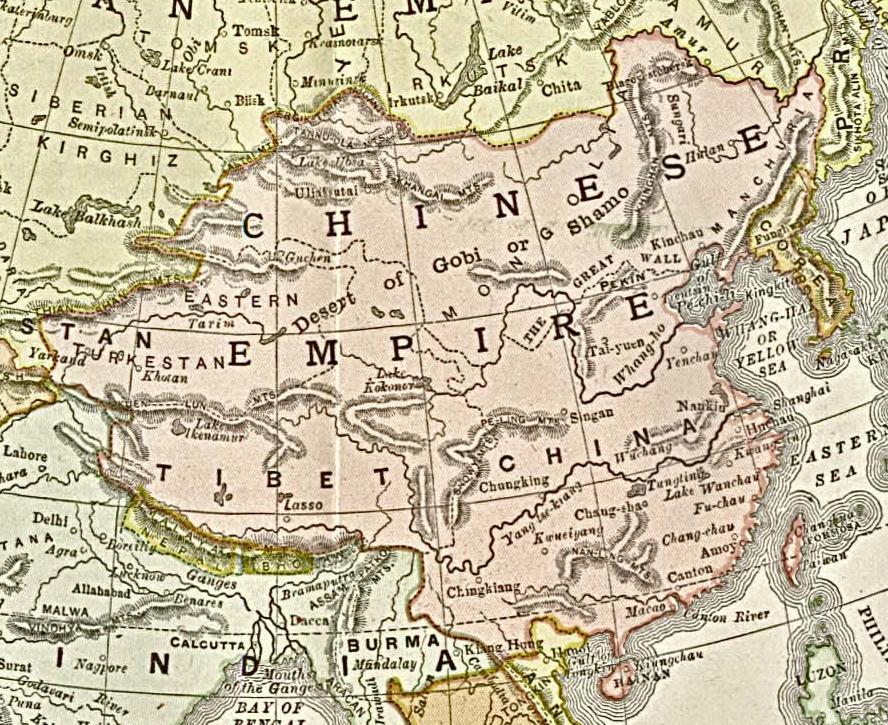
Chinese Empire
Chinese Empire (), or Empire of China, refers to the realm ruled by the Emperor of China during the era of Imperial China. It was coined by western scholars to describe the Ming dynasty, Ming and Qing dynasty, Qing dynasties (or imperial Dynasties of China, Chinese dynasties in general). Another term was the "Celestial Empire", in reference to the status of the emperor as the Son of Heaven. In 221 BC, China was unified under an emperor for the first time, and various imperial dynasties ruled China for a total of two millennia since then, including the Qin dynasty, Qin, Han dynasty, Han, Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin, Sui dynasty, Sui, Tang dynasty, Tang, Song dynasty, Song, Yuan dynasty, Yuan, Ming, and Qing, among others. Etymology and usage The word "China" has been used in English since the 16th century. China was previously known to Europeans as Cathay, as used in Marco Polo's book on The Travels of Marco Polo, his travels in the 13th century (during the Yuan dynasty), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |