|
Death Deity
The mythology or religion of most cultures incorporate a god of death or, more frequently, a divine being closely associated with death, an afterlife, or an underworld. They are often amongst the most powerful and important entities in a given tradition, reflecting the fact that death, like birth, is central to the human experience. In religions where a single god is the primary object of worship, the representation of death is usually that god's antagonist, and the struggle between the two is central to the folklore of the culture. In such dualistic models, the primary deity usually represents good, and the death god embodies evil. Similarly, death worship is used as a derogatory term to accuse certain groups of morally abhorrent practices which set no value on human life. In monotheistic religions, death is commonly personified by an angel or demon standing in opposition to the god. Occurrence In polytheistic religions which have a complex system of deities governing various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
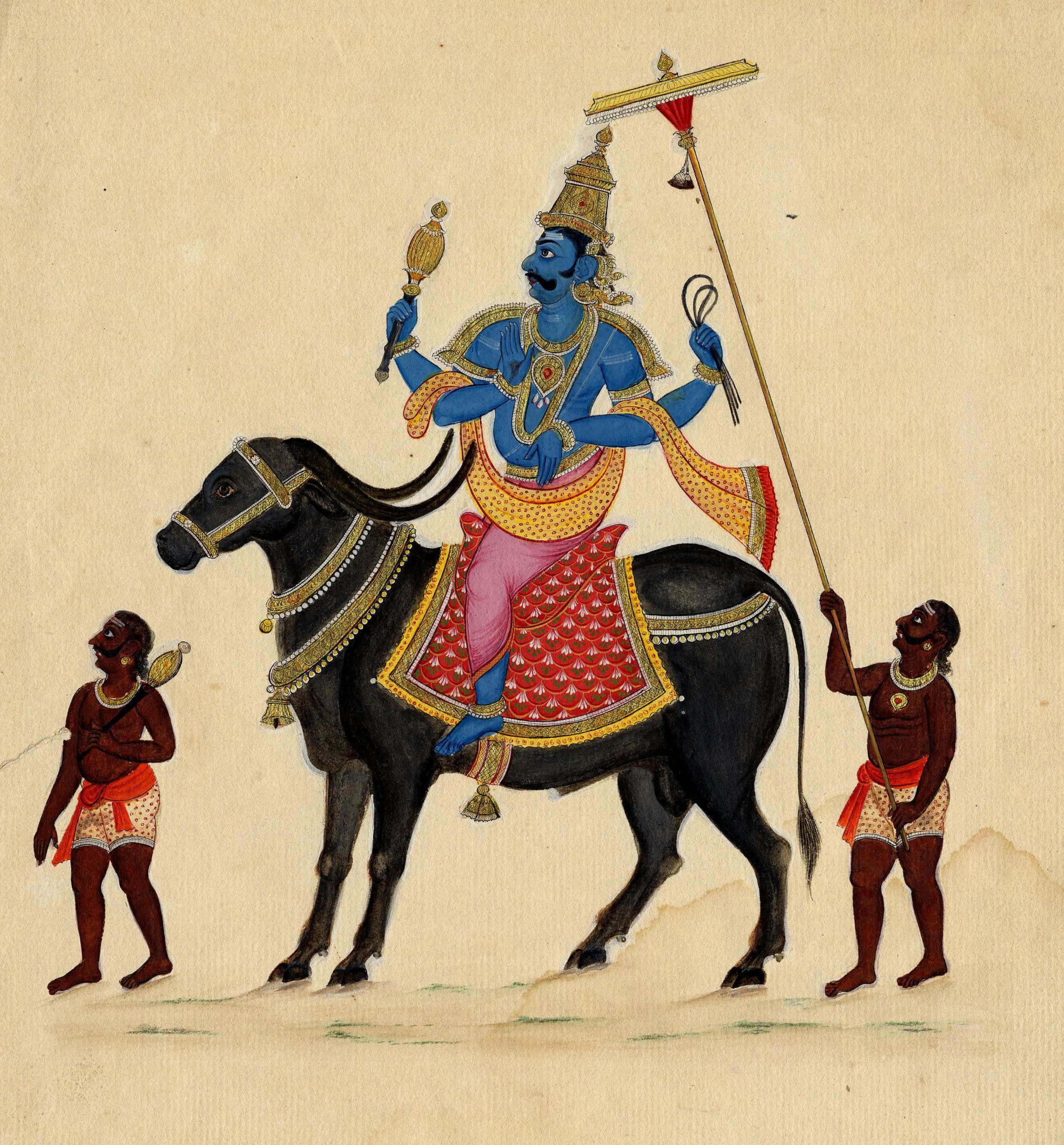
Yama On Buffalo
Yama (), also known as Kāla and Dharmarāja, is the Hindu god of death and justice, responsible for the dispensation of ṛta, law and punishment of sinners in his abode, Naraka (Hinduism), Naraka. He is often identified with #Identification with Dharmadeva, Dharmadeva, the personification of ''Dharma'', though the two deities have different origins and myths. In Vedic tradition, Yama was considered the first mortal who died and espied the way to the celestial abodes; as a result, he became the ruler of the departed. His role, characteristics, and abode have been expounded in texts such as the ''Upanishads'', the ''Ramayana'', the ''Mahabharata'', and the ''Puranas''. Yama is described as the twin of the goddess Yami, and the son of the god Surya (sun) (in earlier traditions Vivasvat) and Sanjna. He judges the souls of the dead and, depending on their deeds, assigns them to the realm of the Pitris (forefathers), Naraka (hell), or to be reborn on the earth. Yama is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Religion
The Yorùbá religion (Yoruba language, Yoruba: Ìṣẹ̀ṣe), West African Orisa (Òrìṣà), or Isese (Ìṣẹ̀ṣe), comprises the traditional religious and spiritual concepts and practice of the Yoruba people. Its homeland is in present-day Southwestern Nigeria and Southern Benin, which comprises the majority of the States of Nigeria, states of; Oyo State, Oyo, Ogun State, Ogun, Osun State, Osun, Ondo State, Ondo, Ekiti State, Ekiti, Kwara State, Kwara, Lagos State, Lagos and parts of Kogi State, Kogi in Nigeria, the Departments of Benin, Departments of; Collines Department, Collines, Ouémé Department, Oueme, Plateau Department, Plateau in Benin, and the adjoining parts of central Togo, commonly known as Yorubaland (). It has become the largest indigenous African tradition / belief system in the world with several million adherents worldwide. It shares some parallels with the Vodun practised by the neighbouring Fon people, Fon and Ewe people, Ewe peoples to its west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqen
Aqen was a rarely mentioned ancient Egyptian deity of the underworld. He is first mentioned in the famous Book of the Dead. There, he guided the sun god Ra as the "protector of Ra's celestial bark" by "bringing the ''shen''-ring to his majesty". He was also described as the "mouth of the time", from which the gods and demons pulled the "rope of time", as described in the tomb of king Seti I Menmaatre Seti I (or Sethos I in Greek language, Greek) was the second pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom period, ruling or 1290 BC to 1279 BC. He was the son of Ramesses I and Sitre, and th ....Erik Hornung, Marsha Hill: ''The tomb of Pharaoh Seti I''. Artemis Verlag, 1991, , pp. 19. See also * Kherty * Charon * Duat References Egyptian death gods Underworld gods Egyptian underworld {{Egyptian-myth-stub Time and fate gods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of Polytheism, polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with Ancient Egyptian deities, many deities believed to be present and in control of the world. About 1,500 deities are known. Rituals such as prayer and offerings were provided to the gods to gain their favor. Formal religious practice centered on the pharaohs, the rulers of Egypt, believed to possess divine powers by virtue of their positions. They acted as intermediaries between their people and the gods, and were obligated to sustain the gods through rituals and offerings so that they could maintain Ma'at, the order of the cosmos, and repel Isfet (Egyptian mythology), Isfet, which was chaos. The state dedicated enormous resources to religious rituals and to the construction of Egyptian temple, temples. Individuals could interact with the gods for their own purposes, appealing for hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anubis
Anubis (; ), also known as Inpu, Inpw, Jnpw, or Anpu in Ancient Egyptian (), is the god of funerary rites, protector of graves, and guide to the underworld in ancient Egyptian religion, usually depicted as a canine or a man with a canine head. Like many ancient Egyptian deities, Anubis assumed different roles in various contexts. Depicted as a protector of graves as early as the First Dynasty (), Anubis was also an embalmer. By the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BC) he was replaced by Osiris in his role as lord of the underworld. One of his prominent roles was as a god who ushered souls into the afterlife. He attended the weighing scale during the "Weighing of the Heart", in which it was determined whether a soul would be allowed to enter the realm of the dead. Anubis is one of the most frequently depicted and mentioned gods in the Egyptian pantheon; however, few major myths involved him. Anubis was depicted in black, a color that symbolized regeneration, life, the soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andjety
Andjety (meaning "He of Andjet") is a local ancient Egyptian deity of the ninth nome, centered at Andjet, which was known as Busiris to the Greeks. This deity is also known by the alternative names Anezti ''or'' Anedjti. Andjety is considered one of the earliest Egyptian gods, possibly with roots in prehistoric Egypt. Andjety is thought to have been a precursor of Osiris. Like Osiris, he is depicted holding the crook and flail and has a crown similar to Osiris's Atef crown. Pharaoh Sneferu of the Fourth Dynasty, builder of the first true pyramid, is shown wearing the crown of Andjety. In the Pyramid Texts the deceased pharaoh is identified with Andjety. In the temple of Seti I, the pharaoh is shown offering incense to Osiris-Andjety who is accompanied by Isis. He also is shown to have fertility aspects, being known by the epithet "bull of vultures". His name is sometimes written with a substitution of a stylized uterus for the feather in the hieroglyphs. Writings mentioning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Mythology
Egyptian mythology is the collection of myths from ancient Egypt, which describe the actions of the Egyptian pantheon, Egyptian gods as a means of understanding the world around them. The beliefs that these myths express are an important part of ancient Egyptian religion. Myths appear frequently in Egyptian Ancient Egyptian literature, writings and Art of ancient Egypt, art, particularly in short stories and in religious material such as hymns, ritual texts, Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, funerary texts, and Egyptian temple, temple decoration. These sources rarely contain a complete account of a myth and often describe only brief fragments. Inspired by the cycles of nature, the Egyptians saw time in the present as a series of recurring patterns, whereas the earliest periods of time were linear. Myths are set in these earliest times, and myth sets the pattern for the cycles of the present. Present events repeat the events of myth, and in doing so renew ''maat'', the fundament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aker (god)
Aker was an ancient Egyptian personification of the horizon, and an earth and underworld god, believed to guard the eastern (Bakhu) and western (Land of Manu, Manu) horizons. Description Aker was first depicted as the torso of a recumbent lion with a widely opened mouth. Later, he was depicted as two recumbent lion torsos merged with each other and still looking away from each other.Christian Leitz: ''Lexikon der ägyptischen Götter und Götterbezeichnungen (LGG)'' (= ''Orientalia Lovaniensia Analecta'', vol. 6). Peeters Publishers, Leuven 2002, , pp. 83 - 85. From Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom onwards Aker appears as a pair of twin lions, one named ''Duaj'' (meaning "tomorrow") and the other ''Sefe'' (meaning "yesterday"). Aker was thus often titled "He who's looking forward and behind". When depicted as a lion pair, a hieroglyphic sign for "Akhet (hieroglyph), horizon" (two merged mountains) and a sun disc was put between the lions; the lions were sitting back-on- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mot (Semitic God)
Mot ( ''mūt'', ''māweṯ'', ) was the Canaanite god of death and the Underworld. He was also known to the people of Ugarit and in Phoenicia, where Canaanite religion was widespread. The main source of information about Mot in Canaanite mythology comes from the texts discovered at Ugarit, but he is also mentioned in the surviving fragments of Philo of Byblos's Greek translation of the writings of the Phoenician Sanchuniathon. Forms of the name In Ugaritic myth, Mot (spelled ''mt'') is a personification of death. The word belongs to a set of cognates meaning 'death' in other Semitic and Afro-Asiatic languages: Arabic موت ''mawt''; Hebrew מות (''mot'' or ''mavet''; ancient Hebrew ''muth'' or ''maveth''/''maweth''); Maltese ''mewt''; Syriac ܡܰܘܬܳܐ (''mautā''); Ge'ez ሞት (''mot''); Canaanite, Egyptian, Berber, Aramaic, Nabataean, and Palmyrene מות (''mwt''); Jewish Aramaic, Christian Palestinian Aramaic, and Samaritan מותא (''mwt’''); Mandaean ''mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horus
Horus (), also known as Heru, Har, Her, or Hor () in Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as the god of kingship, healing, protection, the sun, and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Egypt (Roman province), Roman Egypt. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history, and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptology, Egyptologists."The Oxford Guide: Essential Guide to Egyptian Mythology", Edited by Donald B. Redford, Horus: by Edmund S. Meltzer, pp. 164–168, Berkley, 2003, . These various forms may be different manifestations of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or Syncretism, syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality. He was most often depicted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan Religion
Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom. Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups (including the Fanti, Ashanti, the Akuapem, the Wassa, the Abron, the Anyi, and the Baoulé, among others), so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans. Anansi the spider is a folk hero who is prominent in Ashanti folktales where he is depicted as a wise trickster. In other aspects of Akan spirituality, Anansi is also sometimes considered both a trickster and a deity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are creatures, spirits, angels, demons, or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afterlife. Their role is not to judge the deceased, but simply to guide them. Appearing frequently on funerary art, psychopomps have been depicted at different times and in different cultures as anthropomorphic entities, horses, deer, dogs, whip-poor-wills, ravens, crows, vultures, owls, sparrows, and cuckoos. In the case of birds, these are often seen in huge masses, waiting outside the home of the dying. Overview Ancient religion Classical examples of a psychopomp are the ancient Egyptian god Anubis, the deity Pushan in Hinduism, the Greek ferryman Charon, the goddess Hecate, and god Hermes,RADULOVI, IFIGENIJA; VUKADINOVI, SNEŽANA; SMIRNOVBRKI, ALEKSANDRA – Hermes the Transformer Ágora. Estudos Clássicos em debate, núm. 17, 2015, pp. 45–62 Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |