|
David Of Ashby
David of Ashby (fl. 1260 – 1275) was an English-born Dominican friar who was sent from the Holy Land city of Acre to the Mongol ruler Hulagu in 1260, by the Papal legate . He stayed around 15 years among the Mongols, and only returned from Iran in 1274. David of Ashby was a member of the Mongol embassy to the Second Council of Lyon in 1274, sent by Abaqa. The embassy arrived on 5 July 1274. David was accompanied by the clerk Rychaldus, in the service of the Mongols, and 14 Mongol dignitaries. The leader of the Mongols underwent baptism on this occasion, on 16 July. David of Ashby wrote a book ''Les fais des Tatars'' ("The facts about the Tartars") describing the culture of the Mongols, mainly in Iran under Abaqa Khan, and their remarkable military organization and discipline. A manuscript remained, but it disappeared in the fire of the Turin National Library in 1904. Its only remains are in the ''Notice et extraits'' of Auguste Scheler in 1867.C. Brunel, p. 39. See also *Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' ( ; usually abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for 'flourished') denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are Will (law), wills Attestation clause, attested by John Jones in 1204 and 1229, as well as a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)", even though Jones was born before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats and the Buryats are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or as subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity, descending from the Proto-Mongols. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The contiguous geographical area in which the Mongols primarily live is referred to as the Mongol heartland, especially in discussions of the Mongols' history under the Mongol Empire. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyks and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Arkhorchin, Asud, Baarins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century English People
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258) and the destruction of the House of Wisdom. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The earliest Islamic states in Southeast Asia formed during this century, most notably Samudera Pasai. The Kingdoms of Sukhothai and Hanthawaddy would emerge and go on to dominate their surrounding territories. Europe entered the apex of the High Middle Ages, characterized by rapid legal, cultural, and religious ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franco-Mongol Alliance
Several attempts at a military alliance between the Franks#Crusaders and other Western Europeans as "Franks", Frankish Crusaders and the Mongol Empire against the Islamic caliphates, their common enemy, were made by various leaders among them during the 13th century. Such an alliance might have seemed an obvious choice: the Mongols were already sympathetic to Christianity, given the presence of many influential Nestorian Christians in the Mongol court. The Franks—Western Europeans, and those in the Levantine Crusader states—were open to the idea of support from the East, in part owing to the long-running legend of the mythical Prester John, an Eastern king in an Eastern kingdom who many believed would one day come to the assistance of the Crusaders in the Holy Land.Jackson. ''Mongols and the West''. p. 4. "The failure of Ilkhanid-Western negotiations, and the reasons for it, are of particular importance in view of the widespread belief in the past that they might well have succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste Scheler
Jean Auguste Ulric Scheler (1819–1890), also styled Auguste Scheler was a Belgian philologist. Biography He was born at Ebnat, Switzerland. His father, a German, was chaplain to King Leopold I of Belgium, and Jean Scheler, after studying at Bonn and Munich, became King's librarian, and professor at the Universite Libre de Bruxelles. His investigations in Romance philology earned him a wide reputation. He died at Ixelles (French language, French, ) or (Dutch language, Dutch, ) is one of the List of municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region, Belgium. Located to the south-east of Pentagon (Brussels), Brusse ..., Belgium, in 1890. Works The most important of his numerous philological works are: *''Mémoire sur la conjugaison française considérée sous le rapport étymologique'' (Brussels, 1847) *''Dictionnaire d'étymologie française d'après les résultats de la science moderne'' (Brussels, 1862) *''Étude sur la t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin National University Library
The National University Library (), located in Turin, Italy, is one of the country's main libraries. It was founded in 1720 as the Royal University Library by Victor Amadeus II, who unified collections from the library of the University of Turin and that of the Dukes of Savoy. It was renamed as the National Library in 1872, after Italian unification. In 1904 a fire destroyed thousands of books and manuscripts from the library. () Expertise gained from recovering from the fire was used to train restorers such as Erminia Caudana. It was also bombed in December 1942. At present time, the library owns over 763,833 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abaqa Khan
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, , "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler ('' Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hulagu Khan and Lady Yesünčin and the grandson of Tolui, he reigned from 1265 to 1282 and was succeeded by his brother Ahmed Tekuder. Much of Abaqa's reign was consumed with civil wars in the Mongol Empire, such as those between the Ilkhanate and the northern khanate of the Golden Horde, and the Chagatai Khanate in Central Asia. Abaqa also engaged in unsuccessful attempts at invading Syria under the Mamluk Sultanate, which included the Second Battle of Homs. Life Abaqa was born in Mongolia on 27 February 1234, son of Ilkhanate founder Hulagu Khan. Abaqa was a Buddhist. A favoured son of Hulagu, he was made governor of Turkestan.Runciman, p. 320. Hulagu died from illness in 1265. Before his death, he had been negotiating with the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos to add a daughter of the Byzantine imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the northeast, Afghanistan to the east, Pakistan to the southeast, and the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. With a Ethnicities in Iran, multi-ethnic population of over 92 million in an area of , Iran ranks 17th globally in both List of countries and dependencies by area, geographic size and List of countries and dependencies by population, population. It is the List of Asian countries by area, sixth-largest country entirely in Asia and one of the world's List of mountains in Iran, most mountainous countries. Officially an Islamic republic, Iran is divided into Regions of Iran, five regions with Provinces of Iran, 31 provinces. Tehran is the nation's Capital city, capital, List of cities in Iran by province, largest city and financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
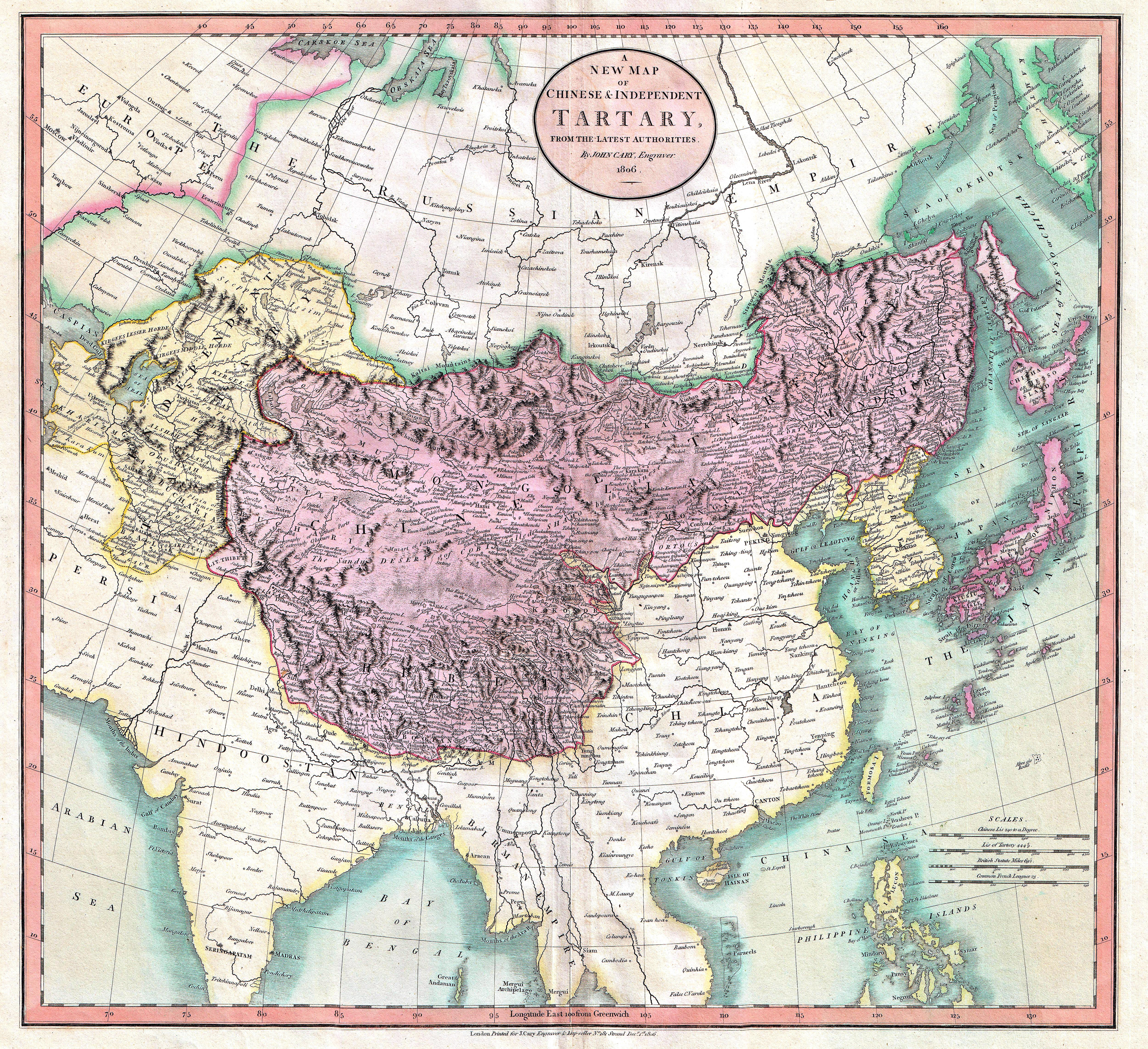
Tartars
Tartary (Latin: ''Tartaria''; ; ; ) or Tatary () was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounded by the Caspian Sea, the Ural Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the northern borders of China, India, and Persia, at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers. The active use of the toponym (place name) can be traced from the 13th to the 19th centuries. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner Asia or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main nomadic population of which in the past was engaged in animal husbandry. Ignorance surrounding Tartary's use as a place name has spaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers (, abbreviated OP), commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic Church, Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilians, Castilian priest named Saint Dominic, Dominic de Guzmán. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as Dominicans, generally display the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for , meaning 'of the Order of Preachers'. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, Religious sister (Catholic), active sisters, and Laity, lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as Third Order of Saint Dominic, tertiaries). More recently, there have been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the The gospel, gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed it at the forefront of the intellectual life of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rychaldus
Rychaldus, Richaldus or Richardus (13th century) was a clerk and translator (''notarius...ac interpreters Latinorum'')Jackson, p.173 for the Mongol Ilkhanate rulers Hulagu Khan, and then Hulagu's son Abaqa Khan. He was best known for delivering a report on behalf of the Mongols at the 1274 Second Council of Lyon. Biography Little is known of Rychaldus, except that he was a part of some Mongol embassies to European rulers. There are different mentions of a "Richaldus" in the Mongol court, and it is generally assumed by modern historians that they refer to the same individual, but it is not certain. In 1262, a Rychaldus was known to have been accompanying an aborted Mongol embassy sent by Hulagu, which was intercepted by an ally of the Egyptian Mamluks, King Manfred of Sicily. Manfred was in conflict with Pope Urban IV, and Rychaldus was returned to the Mongols by ship. Another mention was made of Richardus, a Latin secretary in the Ilkhan's court, in 1267. The reference there sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abaqa
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, , "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler ('' Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hulagu Khan and Lady Yesünčin and the grandson of Tolui, he reigned from 1265 to 1282 and was succeeded by his brother Ahmed Tekuder. Much of Abaqa's reign was consumed with civil wars in the Mongol Empire, such as those between the Ilkhanate and the northern khanate of the Golden Horde, and the Chagatai Khanate in Central Asia. Abaqa also engaged in unsuccessful attempts at invading Syria under the Mamluk Sultanate, which included the Second Battle of Homs. Life Abaqa was born in Mongolia on 27 February 1234, son of Ilkhanate founder Hulagu Khan. Abaqa was a Buddhist. A favoured son of Hulagu, he was made governor of Turkestan.Runciman, p. 320. Hulagu died from illness in 1265. Before his death, he had been negotiating with the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos to add a daughter of the Byzantine imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |