|
Danakil Microplate
The Danakil microplate (also called Arrata microplate) is a small tectonic plate, (called a microplate) situated in the horn of Africa, spanning over Eritrea and Ethiopia. The Danakil microplate is surrounded by the Nubian plate and the Arabian plate, and is adjacent to the Somalian plate. The extension velocities relative to the Nubian plate vary between 0 mm/yr in the north and 18 mm/yr in the south. Extension velocities relative to the Arabian plate vary from 0 mm/yr in the south to 15 mm/yr in the north. Theses variations imply that the Danakil microplate is rotating counterclockwise. This also implies that the Afar rift in propagating towards the north and the Red Sea rift is propagating towards the south, forming a large-scale relay structure. The Danakil microplate comprises a continental part, forming the Danakil Alps and parts of coastal areas of Eritrea, and an oceanic part, forming the southernmost part of the Red Sea. The movement of the Danakil microplate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
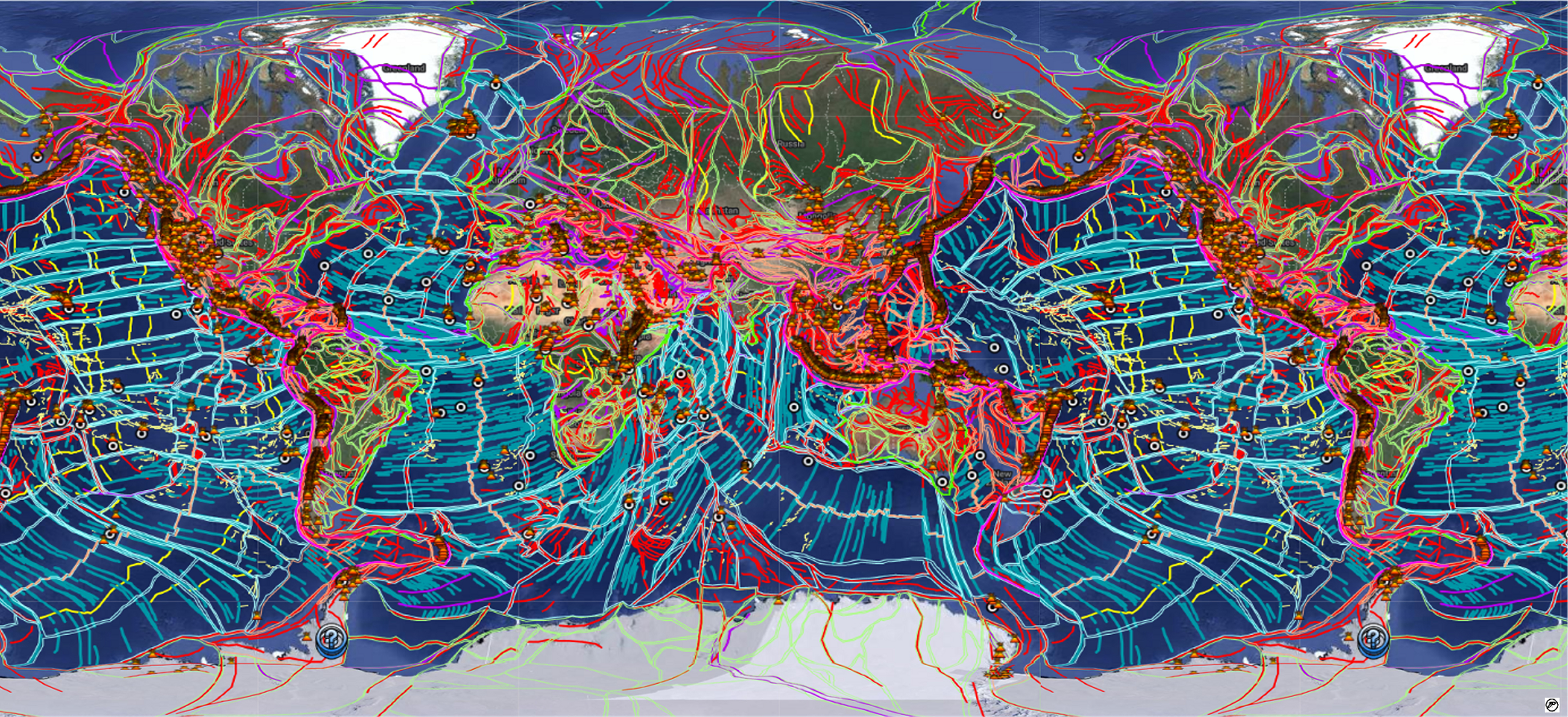
List Of Tectonic Plates
This is a list of tectonic plates on Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. Plate tectonics, Tectonic plates are pieces of Earth's crust and uppermost mantle (geology), mantle, together referred to as the lithosphere. The plates are around thick and consist of two principal types of material: oceanic crust (also called ''Sima (geology), sima'' from silicon and magnesium) and continental crust (''sial'' from silicon and aluminium). The composition of the two types of crust differs markedly, with mafic basaltic rocks dominating oceanic crust, while continental crust consists principally of lower-density felsic granite, granitic rocks. Current plates Geologists generally agree that the following tectonic plates currently exist on Earth#Surface, Earth's surface with roughly definable boundaries. Tectonic plates are sometimes subdivided into three fairly arbitrary categories: ''major'' (or ''primary'') ''plates'', ''minor'' (or ''secondary'') ''plates'', and ''microplates'' (or ''tertiary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
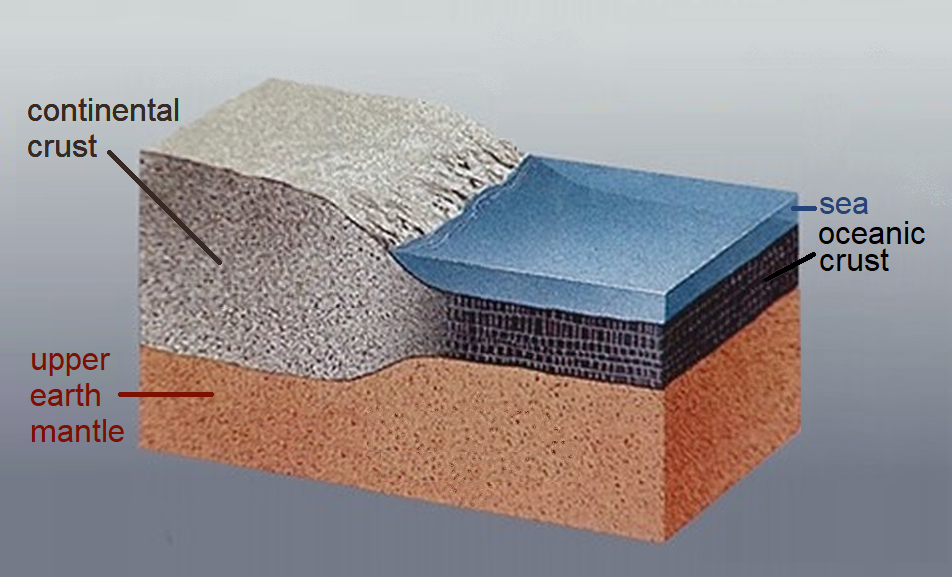
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. Most continental crust is dry land above sea level. However, 94% of the Zealandia continental crust region is submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean, with New Zealand constituting 93% of the above-water portion. Thickness and density The continental crust consists of various layers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Tadjoura
The Gulf of Tadjoura (; ) is a gulf or basin of the Indian Ocean in the Horn of Africa. It lies south of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, or the entrance to the Red Sea, at . The gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive coral reefs, and abundant pearl oysters. Most of its coastline is the territory of Djibouti, except for a short stretch on the southern shore, which is part of the territory of Somaliland. The Gulf’s other marine habitats include sea grass beds, salt pans and mangroves. History In August 1840, the conclusion of a treaty of friendship and commerce between the Sultan Mohammed bin Mohammed of Tadjoura and Commander Robert Moresby of the Indian Navy is tracking the sale of Moucha Island to Great Britain for ten sacks of rice. The sale will however follow any occupation. In 1887, Britain cedes sovereignty of the island to France at the same time it recognizes the French sphere of influence in the Gulf of Tadjoura, in exchange for the abandonment by France of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buri Peninsula
The Buri Peninsula extends from central Eritrea north into the Red Sea. Geography The Buri Peninsula is an area of land in the Ghela'elo subregion of Eritrea, that juts out into the Red Sea. To its west lies the Gulf of Zula, also known as Annesley Bay, with the village of Arafali at its head. To the north of the peninsula is the Massawa Channel and a group of islands, the Dahlak Archipelago, the largest and closest to the mainland being Dahlak Kebir. To the east of the peninsula lies Howakil Bay, a broad bay, scattered with islands, the largest of which is Howakil Island, and to the south lies a ridge of low hills. The peninsula is generally low and undulating, composed of lava flows at the southern end and granite at the north. It is about long and wide, with a constriction wide in the middle. Further inland to the south are volcanic hills, some conical and others located on ridges, with small sandy plains between them. The highest mountains on the peninsula is Mount A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Fragment
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin. Causes Continental fragments and microcontinent crustal compositions are very similar to those of regular continental crust. The rifting process that caused the continental fragments to form most likely impacts their layers and overall thickness along with the addition of mafic intrusions to the crust. Studies have determined that the average crustal thickness of continental fragments is approximately . The sedimentary layer of continental fragments can be up to thick and can overlay two to three crustal layers. Continental fragments have an average crustal density of which is very similar to that of typical continental crust. Strike-slip fault zones cause the fragmentation of microcontinents. The zones link the extensional zones where co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's figure of the Earth, shape; its gravitational, Earth's magnetic field, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its structure of the Earth, internal structure and Earth#Chemical composition, composition; its geodynamics, dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; geophysical fluid dynamics, fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; atmospheric electricity, electricity and magnetism in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler Pole
:''This article describes techniques; for a history of the movement of tectonic plates, see Geological history of Earth.'' Plate reconstruction is the process of reconstructing the positions of tectonic plates relative to each other (relative motion) or to other reference frames, such as the Earth's magnetic field or groups of hotspots, in the geological past. This helps determine the shape and make-up of ancient supercontinents and provides a basis for paleogeographic reconstructions. Defining plate boundaries An important part of reconstructing past plate configurations is to define the edges of areas of the lithosphere that have acted independently at some time in the past. Present plate boundaries Most present plate boundaries are easily identifiable from the pattern of recent seismicity. This is now backed up by the use of geodetic data, such as GPS/GNSS, to confirm the presence of significant relative movement between plates. Past plate boundaries Identifying past (but now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
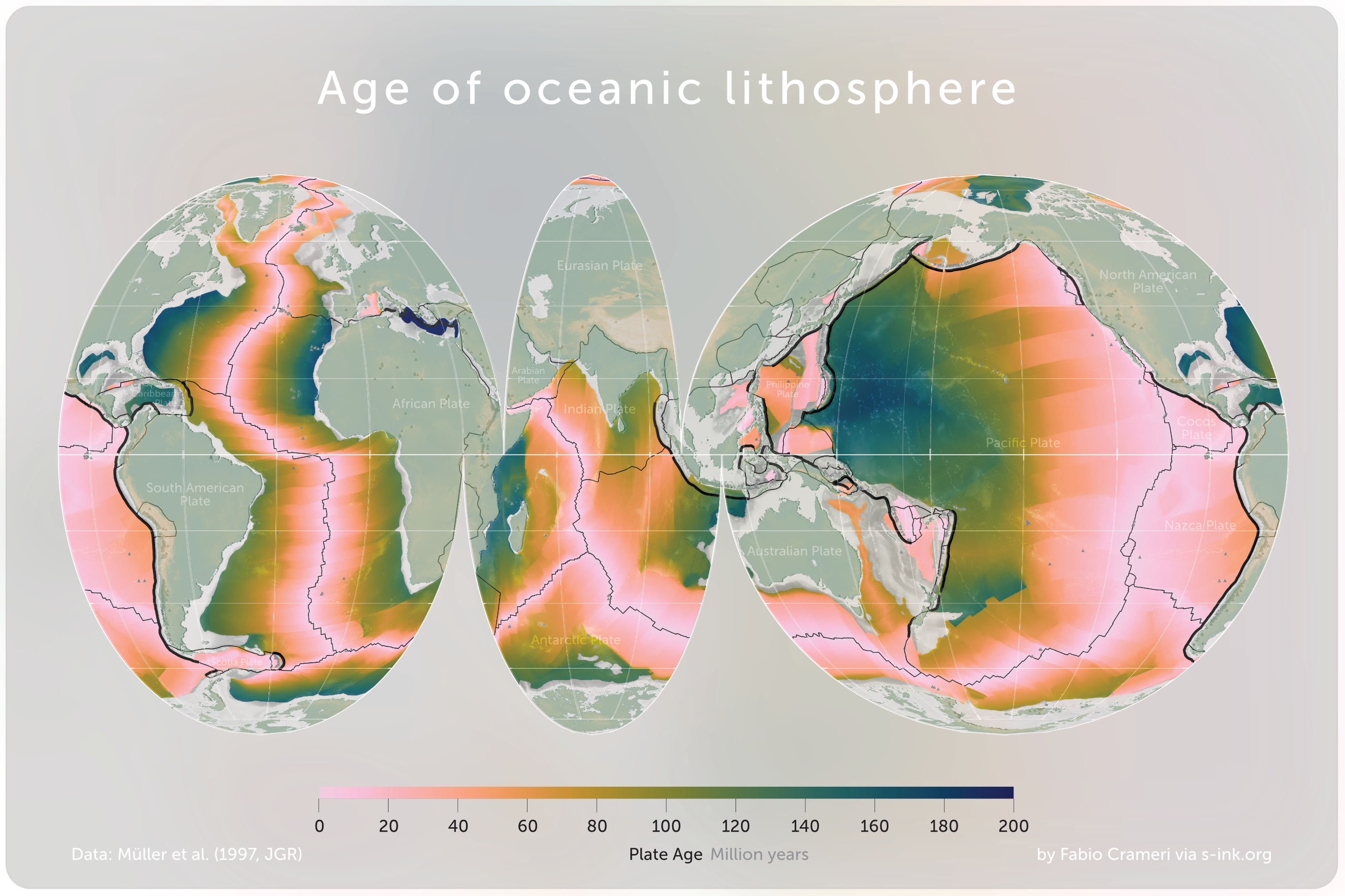
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a Divergent boundary, divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from Mantle (geology), mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab-el-Mandeb
The Bab-el-Mandeb (), the Gate of Grief or the Gate of Tears, is a strait between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula and Djibouti and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden and by extension the Indian Ocean. Etymology In "Bab-el-Mandeb", "Bab" means "gate" while "Mandeb" means "lamentation" or "grief". The strait derives its name from the dangers attending its navigation or, according to an Arab legend, from the numbers who were drowned by an earthquake that separated the Arabian Peninsula from the Horn of Africa. History Paleo-environmental and tectonic events in the Miocene epoch created the Danakil Isthmus, a land bridge forming a broad connection between Yemen and Ethiopia. During the last 100,000 years, eustatic sea level fluctuations have led to alternate opening and closing of the straits. According to the recent single origin hypothesis, the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb were probably witness to the earliest migrations of modern humans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez—leading to the Suez Canal. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley. The Red Sea has a surface area of roughly , is about long, and wide at its widest point. It has an average depth of , and in the central Suakin Trough, it reaches its maximum depth of . Approximately 40% of the Red Sea is quite shallow at less than deep and about 25% is less than deep. The extensive shallow shelves are noted for their marine life and corals. More than 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral live in the sea. The Red Sea is the world's northernmost tropical sea and has been designated a Global 200 ecoregion. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumulates. The crust lies above the rigid uppermost layer of the mantle. The crust and the rigid upper mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium. It is thinner than continental crust, or sial, generally less than 10 kilometers thick; however, it is denser, having a mean density of about 3.0 grams per cubic centimeter as opposed to continental crust which has a density of about 2.7 grams per cubic centimeter. The crust uppermost is the result of the cooling of magma derived from mantle material below the plate. The magma is injected into the spreading center, which consists mainly of a partly solidified crystal mush derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danakil Alps
The Danakil Alps are a highland region in Ethiopia and Eritrea with peaks over 1000 metres in height and a width varying between 40 and 70 kilometres. The area is known in the Afar language as Arrata. The alps lie along the southern Red Sea to the east of the Danakil Depression and separate it from the sea. The alps are asymmetric in cross-section with a comparatively gentle rift escarpment facing the Red Sea and intense normal faulting on the inland side. In the northern part of the alps the basement rock is less elevated and there are many volcanic edifices, such as those forming the Nabro Volcanic Range. The largest of the Nabro Volcanic Range edifices are the Mallahle, Nabro, and Dubbi. The volcanic range extends northwestward to the Red Sea, ending with the Kod Ali volcano offshore. The Danakil Alps have been cut off from the sea since the late Pleistocene. Composition Geologically these highlands are described as a horst and are sometimes referred to as the Danakil H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |