|
DNxHR Codec
Avid DNxHR, which stands for "Digital Nonlinear Extensible High Resolution", is a lossy UHDTV post-production codec engineered for multi-generation compositing with reduced storage and bandwidth requirements. The codec was specifically developed for resolutions considered above FHD/1080p, including 2K, 4K and 8K resolution. DNxHD will continue to be used for HD resolutions. On September 12, 2014, Avid Technology, Inc. announced the DNxHR codec as part of a broader "Avid Resolution Independence" announcement at their Fall 2014 Avid Connect event, which was held during the IBC 2014 conference in Amsterdam, Netherlands. On December 22, 2014, Avid released Media Composer 8.3 which included support for 4K project formats and the DNxHR codec. Further details for the DNxHR codec were outlined in the "Avid High-Resolution Workflows Guide - December 2014". Uses It is used in both hardware and software. For example, some camera monitor A camera monitor (or external monitor) is a mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size for storing, handling, and transmitting content. The different versions of the photo of the cat on this page show how higher degrees of approximation create coarser images as more details are removed. This is opposed to lossless data compression (reversible data compression) which does not degrade the data. The amount of data reduction possible using lossy compression is much higher than using lossless techniques. Well-designed lossy compression technology often reduces file sizes significantly before degradation is noticed by the end-user. Even when noticeable by the user, further data reduction may be desirable (e.g., for real-time communication or to reduce transmission times or storage needs). The most widely used lossy compression al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
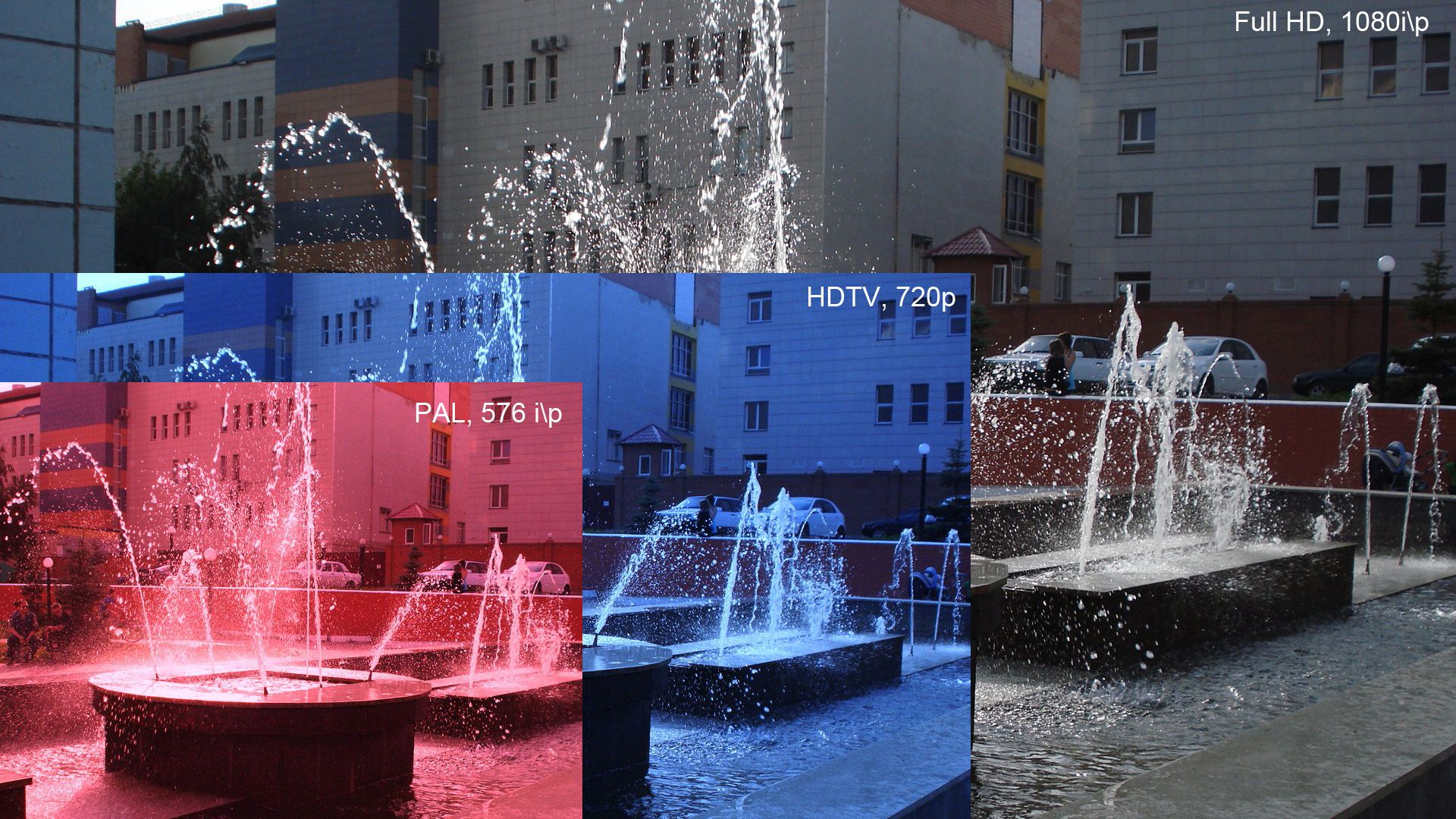
Ultra-high-definition Television
Ultra-high-definition television (also known as Ultra HD television, Ultra HD, UHDTV, UHD and Super Hi-Vision) today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed by NHK Science & Technology Research Laboratories and later defined and approved by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The Consumer Electronics Association announced on October 17, 2012, that "Ultra High Definition", or "Ultra HD", would be used for displays that have an aspect ratio of 16:9 or wider and at least one digital input capable of carrying and presenting native video at a minimum resolution of . In 2015, the Ultra HD Forum was created to bring together the end-to-end video production ecosystem to ensure interoperability and produce industry guidelines so that adoption of ultra-high-definition television could accelerate. From just 30 in Q3 2015, the forum published a list up to 55 commercial services available arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-production
Post-production is part of the process of filmmaking, video production, audio production, and photography. Post-production includes all stages of production occurring after principal photography or recording individual program segments. The first part of the post-production process is the traditional non-linear (analog) film editing at the outset of post-production has mostly been replaced by digital or video editing software that operates as a non-linear editing (NLE) system. The advantage of being able to have this non-linear capacity is in the flexibility for editing scenes out of order, making creative changes at will, carefully shaping the film in a thoughtful, meaningful way for emotional effect. Once the production team is satisfied with the picture editing, the picture editing is said to be "locked." At this point begins the turnover process, where the picture is prepared for lab and color finishing and the sound is "spotted" and turnover to the composer and sound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codec
A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. ''Codec'' is a portmanteau of coder/decoder. In electronic communications, an endec is a device that acts as both an encoder and a decoder on a signal or data stream, and hence is a type of codec. ''Endec'' is a portmanteau of encoder/decoder. A coder or encoder encodes a data stream or a signal for transmission or storage, possibly in encrypted form, and the decoder function reverses the encoding for playback or editing. Codecs are used in videoconferencing, streaming media, and video editing applications. History In the mid-20th century, a codec was a device that coded analog signals into digital form using pulse-code modulation (PCM). Later, the name was also applied to software for converting between digital signal formats, including companding functions. Examples An audio codec converts analog audio signals into digital signals for transmission or encodes them for storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositing
Compositing is the process or technique of combining visual elements from separate sources into single images, often to create the illusion that all those elements are parts of the same scene. Live-action shooting for compositing is variously called " chroma key", "blue screen", "green screen" and other names. Today, most, though not all, compositing is achieved through digital image manipulation. Pre-digital compositing techniques, however, go back as far as the trick films of Georges Méliès in the late 19th century, and some are still in use. Basic procedure All compositing involves the replacement of selected parts of an image with other material, usually, but not always, from another image. In the digital method of compositing, software commands designate a narrowly defined color as the part of an image to be replaced. Then the software (e.g. Natron) replaces every pixel within the designated color range with a pixel from another image, aligned to appear as part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2K Resolution
2K resolution is a generic term for display devices or content having horizontal resolution of approximately 2,000 pixels. In the movie projection industry, Digital Cinema Initiatives is the dominant standard for 2K output and defines 2K resolution as . For television and consumer media, is the most common 2K resolution, but this is normally referred to as 1080p. Resolutions Standards and terminology In the cinematography industry, 2K resolution traditionally refers to a digital scan of 35mm film with a resolution around 2000 pixels wide. Typically this is done at , but the exact dimensions vary based on the aspect ratio and size of the scan area. Another common 2K resolution in cinema is . This is the resolution of the 2K container format standardized by DCI in their Digital Cinema System Specification in 2005. The resolution of the encapsulated video content follows the SMPTE 428-1 standard, which establishes the following resolutions for a 2K distribution: * (full f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 40962160 (DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically during 2014 and 2015. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3840×2160 pixels equal approximately 8.3 megapixels, which is not considered to be es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8K Resolution
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 (UHDTV) standard. 8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manufacturers pushed to make 4K a new standard by 2017. At CES 2019, the first 8K TVs were unveiled. The feasibility of a fast transition to this new standard is questionable in view of the absence of broadcasting resources. It is predicted (2018 forecast by Strategy Analytics) that 8K-ready devices will still only account for 3% of UHD TVs by 2023 with global sales of 11 million units a year. However, TV manufacturers remain optimistic as the 4K market grew much faster than expected, with actual sales exceeding projections nearly six-fold in 2016. In 2013, a transmission network's capability to carry HDTV resolution was limited by internet speeds and relied on satellite broadcast to transmit the high data rates. The demand is expected to driv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNxHD
Avid DNxHD ("Digital Nonlinear Extensible High Definition") is a lossy high-definition video post-production codec developed by Avid for multi-generation compositing with reduced storage and bandwidth requirements. It is an implementation of SMPTE VC-3 standard. Overview DNxHD is a video codec intended to be usable as both an intermediate format suitable for use while editing and as a presentation format. DNxHD data is typically stored in an MXF container, although it can also be stored in a QuickTime container. On February 13, 2008, Avid reported that DNxHD was approved as compliant with the SMPTE VC-3 standard. DNxHD is intended to be an open standard, but as of March 2008, has remained effectively a proprietary Avid format. The source code for the Avid DNxHD codec is freely available from Avid for internal evaluation and review, although commercial use requires Avid licensing approval. It has been commercially licensed to a number of companies including Ikegami, FilmLight, Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-definition Video
High-definition video (HD video) is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for ''high-definition'', generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical scan lines (North America) or 576 vertical lines (Europe) is considered high-definition. 480 scan lines is generally the minimum even though the majority of systems greatly exceed that. Images of standard resolution captured at rates faster than normal (60 frames/second North America, 50 fps Europe), by a high-speed camera may be considered high-definition in some contexts. Some television series shot on high-definition video are made to look as if they have been shot on film, a technique which is often known as filmizing. History The first electronic scanning format, 405 lines, was the first ''high definition'' television system, since the mechanical systems it replaced had far fewer. From 1939, Europe and the US tried 605 and 441 lines until, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avid Technology
Avid Technology is an American technology and multimedia company based in Burlington, Massachusetts, and founded in August 1987 by Bill Warner. It specialises in audio and video; specifically, digital non-linear editing (NLE) systems, video editing software, audio editing software, music notation software, management and distribution services. Avid products are now used in the television and video industry to create television shows, feature films, and commercials. Media Composer, a professional non-linear editing system, is Avid's flagship product. History Avid was founded by Bill Warner, a former marketing manager from Apollo Computer. A prototype of their first non-linear editing system, the Avid/1 Media Composer, was shown at the National Association of Broadcasters (NAB) convention in April 1988. The Avid/1 was based on an Apple Macintosh II computer, with special hardware and software of Avid's own design installed. The Avid/1 was "the biggest shake-up in editing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)