|
DNA Sequencing Theory
DNA sequencing theory is the broad body of work that attempts to lay analytical foundations for determining the order of specific nucleotides in a sequence of DNA, otherwise known as DNA sequencing. The practical aspects revolve around designing and optimizing sequencing projects (known as "strategic genomics"), predicting project performance, troubleshooting experimental results, characterizing factors such as sequence bias and the effects of software processing algorithms, and comparing various sequencing methods to one another. In this sense, it could be considered a branch of systems engineering or operations research. The permanent archive of work is primarily mathematical, although numerical calculations are often conducted for particular problems too. DNA sequencing theory addresses ''physical processes'' related to sequencing DNA and should not be confused with theories of analyzing resultant DNA sequences, e.g. sequence alignment. Publications sometimes do not make a careful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all Life, life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common Nutrient, nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a pentose, five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Eric Lander
Eric Steven Lander (born February 3, 1957) is an American mathematician and geneticist who is a professor of biology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and a professor of systems biology at Harvard Medical School. Eric Lander is founding director emeritus of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. Lander served as the 11th director of the Office of Science and Technology Policy and Science Advisor to the President in Joe Biden's Cabinet of the United States, presidential Cabinet. In response to allegations that he had engaged in bullying and abusive conduct, Lander apologized and resigned from the Biden Administration effective February 18, 2022. Early life and education Lander was born in Brooklyn, New York City, to American Jews, Jewish parents, the son of Rhoda G. Lander, a social studies teacher, and Harold Lander, an attorney. He was captain of the math team at Stuyvesant High School, graduating in 1974 as valedictorian and an International Mathematical Oly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
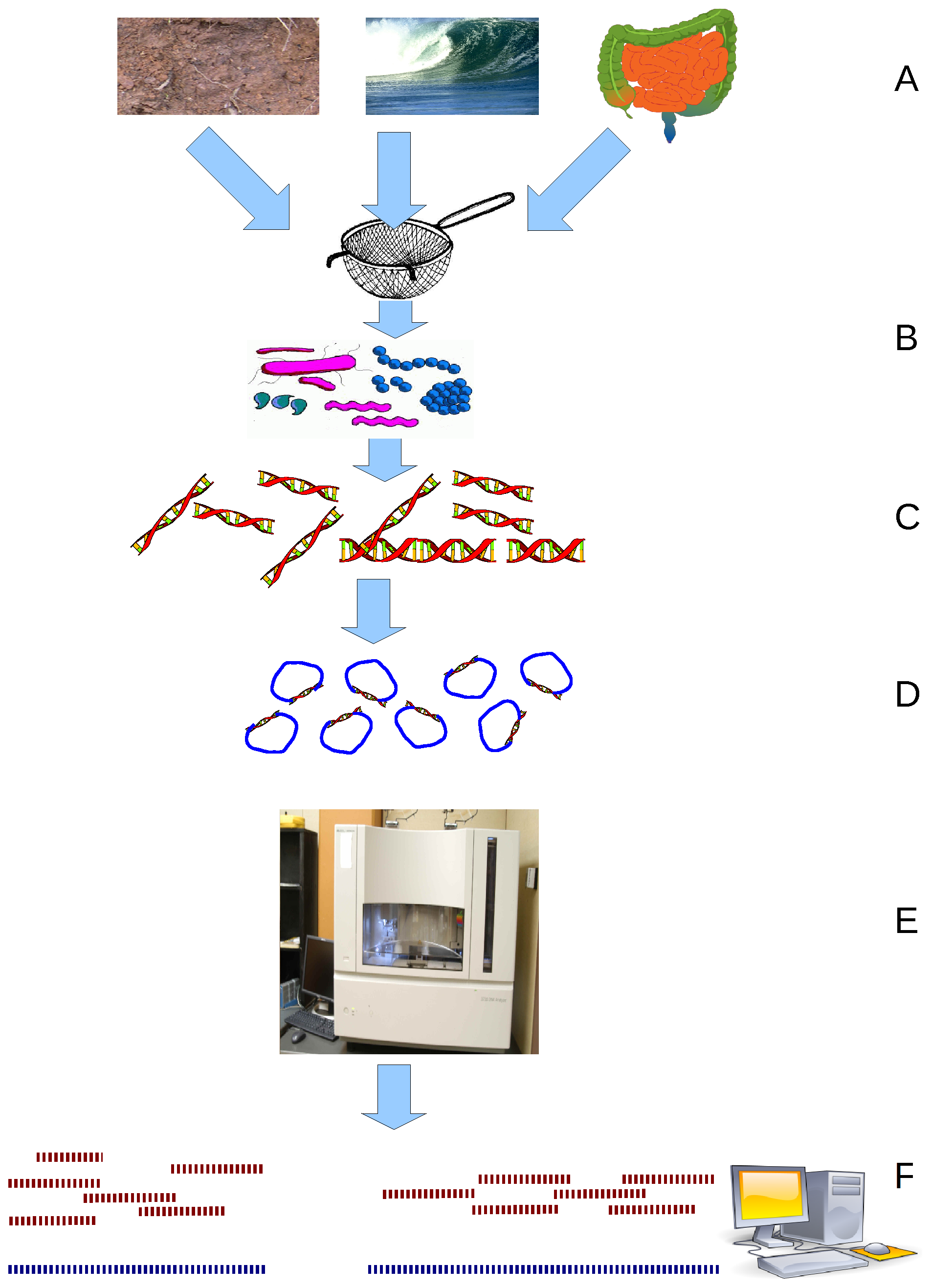 |
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of all genetics, genetic material from all organisms in a particular environment, providing insights into their composition, diversity, and functional potential. Metagenomics has allowed researchers to profile the microbial composition of Natural environment, environmental and clinical samples without the need for time-consuming Microbiological culture, culture of individual species. Metagenomics has transformed microbial ecology and evolutionary biology by uncovering previously hidden biodiversity and metabolic capabilities. As the cost of DNA sequencing continues to decline, metagenomic studies now routinely profile hundreds to thousands of samples, enabling large-scale exploration of microbial communities and their roles in health and global ecosystems. Metagenomic studies most commonly employ shotgun sequencing though Third-generation sequencing, long-read sequencing is being increasingly utilised as technologies advance. The field is also referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Celera
Celera Corporation is a subsidiary of Quest Diagnostics which focuses on genetic sequencing and related technologies. It was founded in 1998 as a business unit of Applera, spun off into an independent company in 2008, and finally acquired by Quest Diagnostics in 2011. History Originally headquartered in Rockville, Maryland (relocated to Alameda, California), it was established in May 1998 by PE Corporation (later renamed to Applera), with Dr. J. Craig Venter from The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) as its first president. While at TIGR, Venter and Hamilton Smith led the first successful effort to sequence an entire organism's genome, that of the ''Haemophilus influenzae'' bacterium. Celera was formed for the purpose of generating and commercializing genomic information. Its stock is a tracking stock of Applera, along with the tracking stock of Applera's larger Applied Biosystems Group business unit. Celera sequenced the human genome at a fraction of the cost of the pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Shotgun Sequencing
In genetics, shotgun sequencing is a method used for sequencing random DNA strands. It is named by analogy with the rapidly expanding, quasi-random shot grouping of a shotgun. The Sanger sequencing#Method, chain-termination method of DNA sequencing ("Sanger sequencing") can only be used for short DNA strands of 100 to 1000 base pairs. Due to this size limit, longer sequences are subdivided into smaller fragments that can be sequenced separately, and these sequences are sequence assembly, assembled to give the overall sequence. In shotgun sequencing, DNA is broken up randomly into numerous small segments, which are sequenced using the chain termination method to obtain ''reads''. Multiple overlapping reads for the target DNA are obtained by performing several rounds of this fragmentation and sequencing. Computer programs then use the overlapping ends of different reads to assemble them into a continuous sequence. Shotgun sequencing was one of the precursor technologies that was resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Leroy Hood
Leroy "Lee" Edward Hood (born October 10, 1938) is an American biologist who has served on the faculties at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) and the University of Washington. Hood has developed ground-breaking scientific instruments which made possible major advances in the biological sciences and the medical sciences. These include the first gas phase protein sequencer (1982), for determining the sequence of amino acids in a given protein; a DNA synthesis, DNA synthesizer (1983), to synthesize short sections of DNA; a peptide synthesizer (1984), to combine amino acids into longer peptides and short proteins; the first automated DNA sequencer (1986), to identify the order of nucleotides in DNA; ink-jet oligonucleotide technology for synthesizing DNA and nanostring technology for analyzing single molecules of DNA and RNA. The protein sequencer, DNA synthesizer, peptide synthesizer, and DNA sequencer were commercialized through Applied Biosystems, Applied Biosystem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor of 9.4. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the past, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open-access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues are available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Richard Arratia
Richard Alejandro Arratia is a mathematician noted for his work in combinatorics and probability theory. Contributions Arratia developed the ideas of interlace polynomials with Béla Bollobás and Gregory Sorkin,. found an equivalent formulation of the Stanley–Wilf conjecture as the convergence of a limit, and was the first to investigate the lengths of superpatterns of permutations. He has also written highly cited papers on the Chen–Stein method on distances between probability distributions,.. on random walks with exclusion,. and on sequence alignment... He is a coauthor of the book ''Logarithmic Combinatorial Structures: A Probabilistic Approach''.. Education and employment Arratia earned his Ph.D. in 1979 from the University of Wisconsin–Madison under the supervision of David Griffeath. He is currently a professor of mathematics at the University of Southern California The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Bob Waterston
Robert Hugh "Bob" Waterston, (born September 17, 1943) is an American biologist. He is best known for his work on the Human Genome Project, for which he was a pioneer along with John Sulston. Education Waterston attended Princeton as an undergraduate where he majored in engineering; he wrote his senior dissertation on the plays of Eugene O'Neill. While on a visit to Germany he took courses in biology – in German – and returned to take up a place at the school of medicine of the University of Chicago. In 1972, he acquired both MD and PhD degrees, with his thesis focusing on immunology. Career Following a postdoctoral position in the laboratory of Sydney Brenner at the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB) in Cambridge, he joined the Washington University School of Medicine as assistant professor of anatomy and neurobiology in 1976. A few years later, he switched to the Department of Genetics, where by 1991 he became chair. In the mid-1980s he made a sabbatical visit to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Michael Christopher Wendl
Michael Christopher Wendl is a mathematician and biomedical engineer who has worked on DNA sequencing theory, covering and matching problems in probability, theoretical fluid mechanics, and co-wrote Phred. He was a scientist on the Human Genome Project and has done bioinformatics and biostatistics work in cancer. Wendl is of ethnic German heritage and is the son of the aerospace engineer Michael J. Wendl.P Hummel and N Fuhry: "Sackelhausen im Banat" Volume 3, published by Heimatsortsgemeinschaft Sackelhausen, Reutlingen FRG, 2007, pages 2236-2237. Research Work Theoretical Fluid Mechanics The problem of low Reynolds number flow in the gap between 2 infinite cylinders, so-called Couette flow, was solved in 1845 by Stokes. Wendl reported the generalization of this solution for finite-length cylinders, which can actually be built for experimental work, in 1999, as a series of modified Bessel functions I_1 and K_1. He also examined a variety of other low Reynolds number rotational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Jared Roach
Jared C. Roach is an American biologist who invented the pairwise end sequencing strategy while a graduate student at the University of Washington. Education and early career Roach attended Cornell University, where he received his Bachelor of Science in biology in 1990. He then attended the University of Washington, where he received his PhD in immunology in 1998, and his MD in 1999. He trained in internal medicine at the University of Utah through 2001. Career Starting as a graduate student in the 1990s, Roach worked on the Human Genome Project from its early days through its conclusion in 2003. He invented pairwise end-sequencing while a graduate student in Leroy Hood's laboratory. Roach was a senior fellow at the department of molecular biotechnology at the University of Washington from 1999 to 2000. In 2001, he became a research scientist at the Institute for Systems Biology. In 2009, Roach was first author on a project which sequenced the whole genomes of a family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
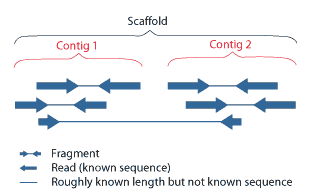 |
Contig
A contig (from ''contiguous'') is a set of overlapping DNA segments that together represent a consensus region of DNA.Gregory, S. ''Contig Assembly''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. In bottom-up sequencing projects, a contig refers to overlapping sequence data ( reads); in top-down sequencing projects, contig refers to the overlapping clones that form a physical map of the genome that is used to guide sequencing and assembly.Dear, P. H. ''Genome Mapping''. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, 2005. . Contigs can thus refer both to overlapping DNA sequences and to overlapping physical segments (fragments) contained in clones depending on the context. Original definition of contig In 1980, Staden wrote: ''In order to make it easier to talk about our data gained by the shotgun method of sequencing we have invented the word "contig". A contig is a set of gel readings that are related to one another by overlap of their sequences. All gel readings belong to one and only one cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |