|
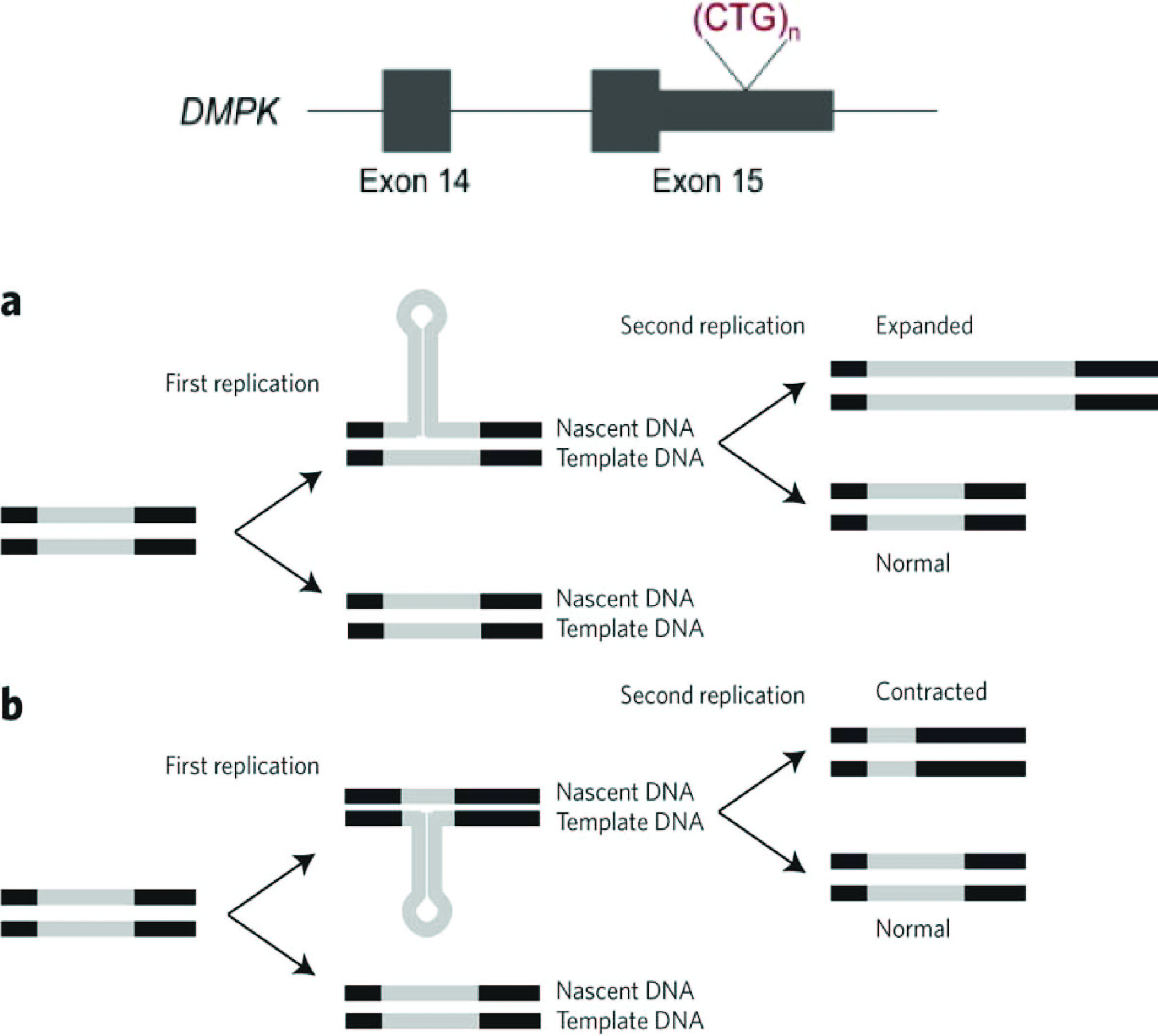
DMPK CTG Repeat
{{disambiguation ...
DMPK may refer to: * Dystrophia myotonica protein kinase or myotonic dystrophy protein kinase * Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotonic Dystrophy Protein Kinase
Myotonin-protein kinase (MT-PK) also known as myotonic dystrophy protein kinase (MDPK) or dystrophia myotonica protein kinase (DMPK) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the '' DMPK'' gene. The dmpk gene product is a Ser/Thr protein kinase homologous to the MRCK p21-activated kinases and Rho kinase family. Data obtained by using antibodies that detect specific isoforms of DMPK indicate that the most abundant isoform of DMPK is an 80-kDa protein expressed almost exclusively in smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscles. This kinase exists both as a membrane-associated and as a soluble form in human left ventricular samples. The different C termini of DMPK that arise from alternative splicing determine its localization to the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, or cytosol in transfected COS-1 cells. Among the substrates for DMPK proposed by in vitro studies are phospholemman, the dihydropyridine receptor, and the myosin phosphatase targeting subunit. However, an in vivo demonstratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
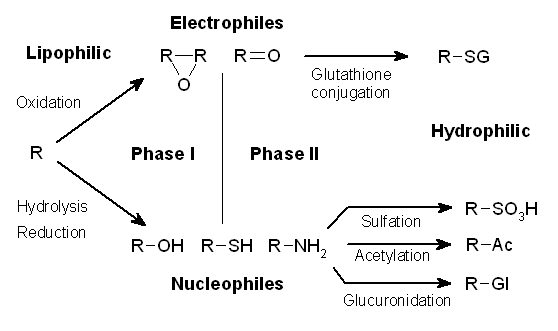
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is called pharmacokinetics. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important aspect of pharmacology and medicine. For example, the rate of metabolism determines the duration and intensity of a drug's pharmacologic action. Drug metabolism also affects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |