|
Damu
Damu ( sux, 𒀭𒁕𒈬) was a Mesopotamian god. While originally regarded as a dying god connected to vegetation, similar to Dumuzi or Ningishzida, with time he acquired the traits of a god of healing. He was regarded as the son of the medicine goddess Ninisina, or of her equivalents such as Gula or Ninkarrak. It is unclear which city was originally associated with him, but he is best attested in association with the cult center of his mother, Isin. Damu is also a theophoric element in many personal names from Ebla. It has been proposed that in this context the term should be understood as a deified kinship group rather than a deity, and it is assumed it is not connected to the Mesopotamian god. Character Damu was originally a dying god. In contrast with Dumuzi, who was described as a shepherd and was associated with herding animals, Damu was most likely connected with trees. From the Old Babylonian period onward he was known chiefly as a healing deity instead. This asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isar-Damu
Isar-Damu (reigned c. 2320 BC), was the king ( Malikum) of the first Eblaite kingdom. Isar-Damu fought a long war with Mari which ended in Eblaite victory; he was probably the last king of the first kingdom. Reign Isar-Damu succeeded his father Irkab-Damu as a young child; his mother, Dusigu, seems to have taken advantage of her position as her husband favorite consort and her probable familial relation to the powerful vizier Ibrium in order to elevate her son to the throne, despite him being one of Irkab-Damu youngest sons. The first years of Isar-Damus's reign were dominated by his mother and the vizier; texts from Ebla show that Isar-Damu's name appeared on official documents after that of his mother. Ibrium was the commander of the army and he conducted multiple campaigns against rebellious vassal-rulers or neighboring kingdoms. Isar-Damu concluded an alliance with Nagar and the relations progressed toward a dynastic marriage between princess Tagrish-Damu, Isar-Damu's da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irkab-Damu
Irkab-Damu (reigned c. 2340 BC), was the king ( Malikum) of the first Eblaite kingdom, whose era saw Ebla's turning into the dominant power in the Levant. During his reign, the vizier started to acquire an important role in running the affair of the state and the military. Irkab-Damu's reign is also noted for the wide diplomatic relations between Ebla and the surrounding kingdoms. Reign Irkab-Damu succeeded king Igrish-Halam, whose reign was characterized by an Eblaite weakness, and tribute paying to the kingdom of Mari with whom Ebla fought a long war. Irkab-Damu started his reign by concluding a peace and trading treaty with Abarsal (probably located along the Euphrates river east of Ebla), one of the first recorded treaties in history. Ebla paid tribute to Mari during Irkab-Damu's first years on the throne. A letter from king Enna-Dagan of Mari was discovered at Ebla, and was used by the Mariote monarch as a tool to assert Mari's authority, as it contained a historic telli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninisina
Ninisina (Sumerian: "Mistress of Isin") was a Mesopotamian goddess who served as the tutelary deity of the city of Isin. She was considered a healing deity. She was believed to be skilled in the medical arts, and could be described as a divine physician or midwife. As an extension of her medical role, she was also believed to be capable of expelling various demons. Her symbols included dogs, commonly associated with healing goddesses in Mesopotamia, as well as tools and garments associated with practitioners of medicine. While Ninisina was initially considered to be an unmarried and childless goddess, the god Pabilsag eventually came to be viewed as her husband. Her children were Damu and Gunura, like her considered to be healing deities, as well as Šumaḫ, who also served as her sukkal, a type of divine attendant. Further members of her court included Ninarali, a goddess associated with the underworld, harpist goddesses Ninigizibara and Ninḫinuna, and sometimes Ninshu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumuzid
Dumuzid or Tammuz ( sux, , ''Dumuzid''; akk, Duʾūzu, Dûzu; he, תַּמּוּז, Tammûz),; ar, تمّوز ' known to the Sumerians as Dumuzid the Shepherd ( sux, , ''Dumuzid sipad''), is an ancient Mesopotamian god associated with shepherds, who was also the first and primary consort of the goddess Inanna (later known as Ishtar). In Sumerian mythology, Dumuzid's sister was Geshtinanna, the goddess of agriculture, fertility, and dream interpretation. In the ''Sumerian King List'', Dumuzid is listed as an antediluvian king of the city of Bad-tibira and also an early king of the city of Uruk. In '' Inanna's Descent into the Underworld'', Inanna perceives that Dumuzid has failed to properly mourn her death and, when she returns from the Underworld, allows the '' galla'' demons to drag him down to the Underworld as her replacement. Inanna later regrets this decision and decrees that Dumuzid will spend half the year in the Underworld, but the other half of the year with her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
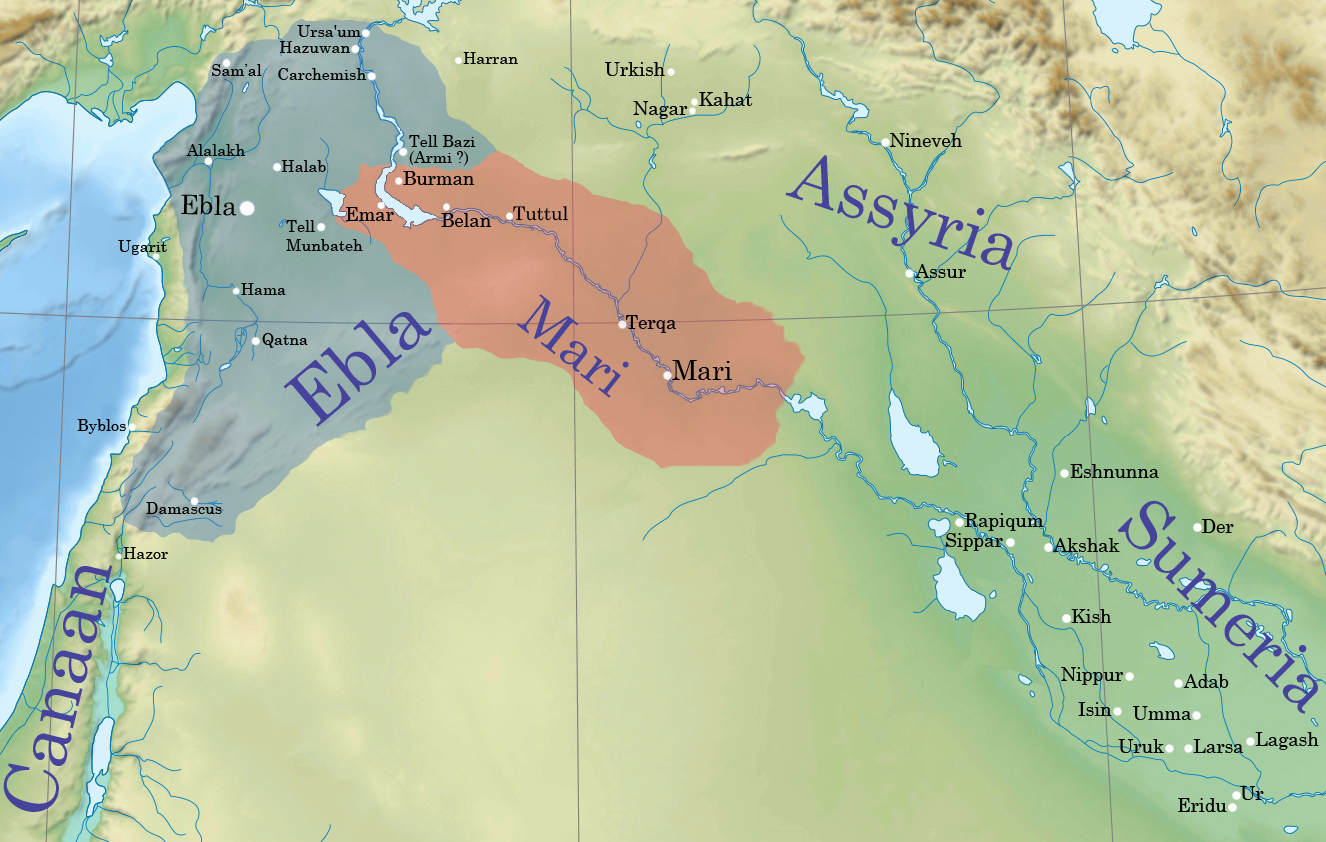
Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kings Of Ebla ...
The list of kings of Ebla includes the known monarchs of Ebla who ruled three consecutive kingdoms. For the first kingdom's monarchs, tablets listing offerings to kings mention ten names, and another list mentions 33 kings. No kings are known from the second kingdom and all dates are estimates according to the Middle chronology. The list Notes References Citations Sources * *Alfonso Archi and Maria Giovanna Biga, "A Victory over Mari and the Fall of Ebla", Journal of Cuneiform Studies, vol. 55, pp. 1–44, 2003 * * * * * * * * * * * * {{refend Ebla Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunura
Gunura was a Mesopotamian goddess, best known as a daughter and member of the entourage of the medicine goddess Ninisina. She was also associated with other similar goddesses, Gula and Nintinugga. Her original cult center is unknown, though she was worshiped in Isin, Nippur, Ur, Babylon and Assur. She is attested in a number of laments, in which she mourns the death of her brother Damu, and in a narrative about a journey of her mother Ninisina to Nippur. Character The etymology of Gunura's name is unknown, and early attempts at explaining it relied on the incorrect reading '' dGu-šir5-ra'' rather than ''dGu-nu-ra''. She was considered to be a daughter of the medicine goddess Ninisina and her husband Pabilsag, and sister of Damu and Šumaḫ. Alternatively, she could be associated with other similar goddesses, such as Gula or Nintinugga. Three texts from Nippur from the Ur III period attest an association between her and latter deity. She also appears alongside her in an Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vizier (Ebla)
Vizier ( or ), is the title used by modern scholars to indicate the head of the administration in the first Eblaite kingdom. The title holder held the highest position after the king and controlled the army. During the reign of king Isar-Damu, the office of vizier became hereditary. Title and responsibilities Vizier is a rendering presented by Alfonso Archi to indicate the second in command official of Ebla, whose native title was probably "head of the administration" (lugal sa-za). Eblaite viziers' authority was of great importance, that they were thought of as kings during the earliest stages of deciphering the tablets of Ebla, as the names of actual monarchs rarely appeared in administrative tablets. Aside from heading the administration, the vizier was in command of the kingdom's trade, army and acted as the head of provincial governors. History The title was not created until after the period of king Igrish-Halam (fl c. 2360 BC), but high officials were already prominent duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamian God
Deities in ancient Mesopotamia were almost exclusively anthropomorphic. They were thought to possess extraordinary powers and were often envisioned as being of tremendous physical size. The deities typically wore ''melam'', an ambiguous substance which "covered them in terrifying splendor" and which could also be worn by heroes, kings, giants, and even demons. The effect that seeing a deity's ''melam'' has on a human is described as ''ni'', a word for the " physical creeping of the flesh". Both the Sumerian and Akkadian languages contain many words to express the sensation of ''ni'', including the word ''puluhtu'', meaning "fear". Deities were almost always depicted wearing horned caps, consisting of up to seven superimposed pairs of ox-horns. They were also sometimes depicted wearing clothes with elaborate decorative gold and silver ornaments sewn into them. The ancient Mesopotamians believed that their deities lived in Heaven, but that a god's statue was a physical embodiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gula (goddess)
Gula (Sumerian: "the great") was a Mesopotamian goddess of medicine, portrayed as a divine physician and midwife. Over the course of the second and first millennia BCE, she became one of the main deities of the Mesopotamian pantheon, and eventually started to be viewed as the second highest ranked goddess after Ishtar. She was associated with dogs, and could be depicted alongside these animals, for example on '' kudurru'' (inscribed boundary stones), and receive figurines representing them as votive offerings. While Gula was initially regarded as unmarried, in the Kassite period she came to be associated with Ninurta. In Babylon his role could also be fulfilled by Mandanu, while the god list '' An = Anum'' links Gula with Pabilsag and Abu. The circle of deities closely associated with her also included Damu and Gunura, who eventually started to be regarded as her children, as well as her sukkal (divine vizier) Urmašum, who might have been imagined as a dog-like being. Thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibbi-Zikir
Ibbi-Sipish or Ibbi-Zikir (ca. 23rd century BC) was the vizier of Ebla for king Ishar-Damu for 17 years. He was the son of his predecessor, Ibrium, who had been Ishar-Damu's vizier for 15 years. Ibbi-Sipish visited cities abroad, such as Kish. He also concluded a treaty with Armi It is further known from one tablet that Ibbi-Sipish vanquished king Hida'ar of Mari, Ebla's main rival in the region, in the 32nd year of Ishar-Damu's reign. However, Ebla's destruction was to come only three years later, presumably at the hands of the Akkadian ruler Sargon the Great Sargon of Akkad (; akk, ''Šarrugi''), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is high .... Until 1985, the consensus of scholars had been that Ibbi-Sipish, Ibrium, and Ibrium's predecessor Ar-ennum, had all been reigning monarchs in Ebla; consequently, it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kura (deity)
Kura was a god worshiped in Ebla (modern Tell Mardikh in Syria) in the third millennium BCE. He was the tutelary god of the city, as well as the head of the local pantheon. While his functions are difficult to ascertain, it is well attested that he was connected to the institution of kingship. The etymology of his name is presently unknown, and it is commonly assumed that it belongs to an unknown linguistic substrate, similar to the names of some of the other Eblaite deities, such as Aštabi, Hadabal or Ishara. Kura's spouse was the goddess Barama, who like him was only worshiped in Ebla. After the destruction of the city both of them disappear from records. A number of proposals have been made regarding identification of deities attested from later periods with Kura, but most of them are not widely accepted. Name and origin The oldest attestations of Kura come from administrative texts predating the destruction of Ebla by thirty five to forty years. The name of the god is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_EnKi_(Sumerian).jpg)
