|
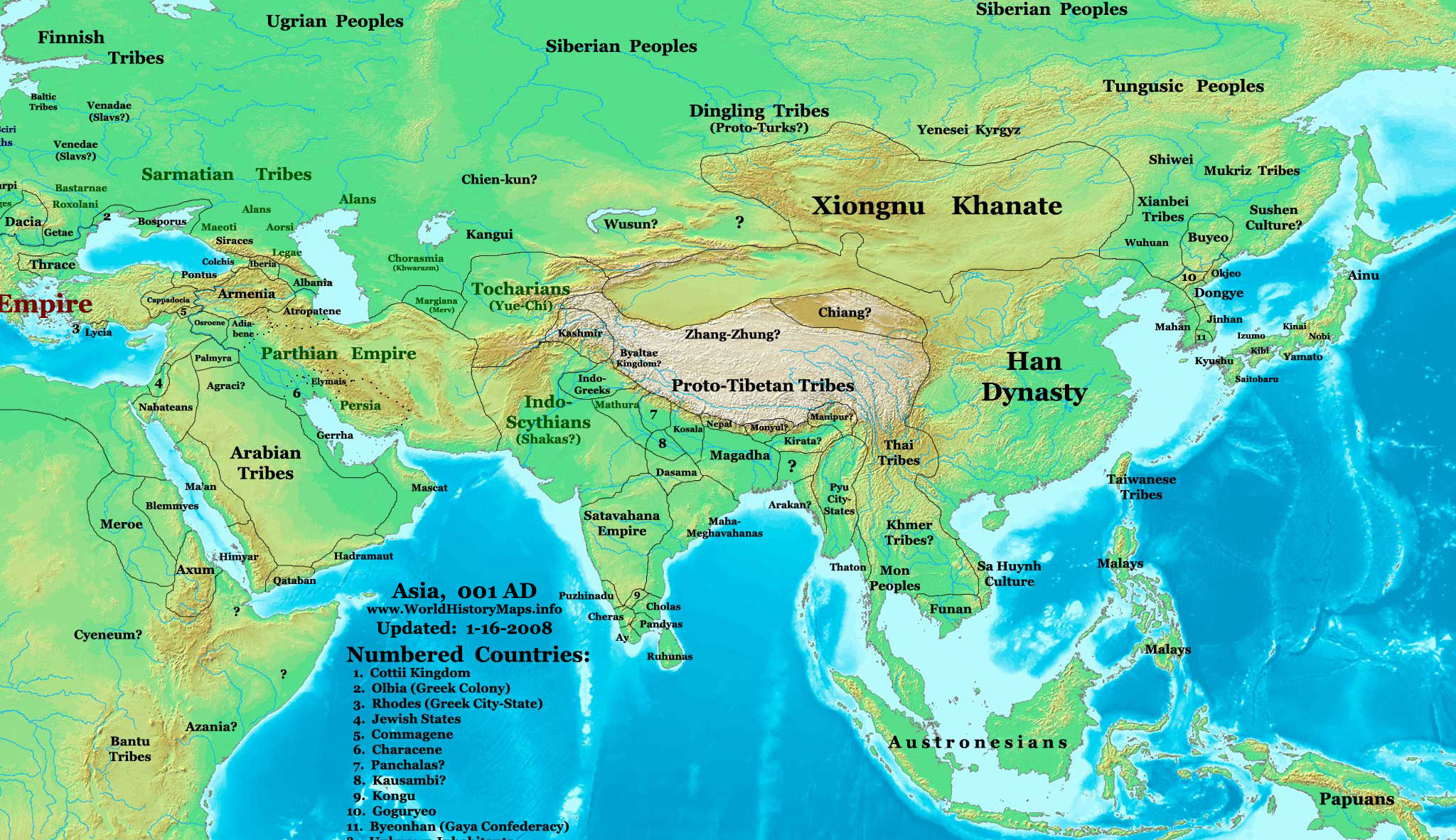
Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *'' î…ë-…£u…ën'', < (c. 78 BCE): *'' î√¢-w√¢n'' < *''Awar'') were a Proto-MongolicPulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Press p. 452 of pp. 411‚Äì466. or |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols (who spoke either pre-Proto-Mongolic,, quote: "The Xianbei confederation appears to have contained speakers of Pre-Proto-Mongolic, perhaps the largest constituent linguistic group, as well as former Xiongnu subjects, who spoke other languages, Turkic almost certainly being one of them."Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Pressp. 452of pp. 411–466. or Para-Mongolic languages), and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donghu People
The Donghu (; ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic Hu (people), Hu people that were first recorded from the 7th century BCE and was taken over by the Xiongnu in 150 BCE. They lived in northern Hebei, southeastern Inner Mongolia and the western part of Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang along the Yan Mountains and Greater Khingan Range. Name Nomenclature The Classical Chinese name literally means "Eastern Barbarians". The term ''D≈çngh√∫'' contrasts with the term ''Xƒ´h√∫'' meaning "Western barbarians" (, meaning "non-Chinese peoples in the west" and Five Barbarians ‰∫îËÉ° (''W«î H√∫'') "five northern nomadic tribes involved in the Uprising of the Five Barbarians (304–316 CE)". Hill (2009:59) translates ''Xƒ´h√∫'' as "Western Hu" and notes: In 307 BCE, the ËÉ° ''Hu (people), H√∫'' proper, encompassing both the eastern ''D≈çngh√∫'' (Êù±ËÉ°, "Eastern Hu") and the western ''Linhu'' (ÊûóËÉ°, "Forest Hu"), were mentioned as a non-Chinese people who were neighbors of Zhao (sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiuliju
Qiuliju ( 180s–190s) was a leader of the Wuhuan tribes in Liaoxi Commandery (遼西郡; commandery capital in present-day Yi County, Liaodong) during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He had about 5,000 tribal clans under his rule. Life Around 187, the Han minister Zhang Wen recruited 3,000 Wuhuan elite cavalry from You Province to assist Han government forces in suppressing the Liang Province Rebellion. Zhang Chun (張純), a former official serving in Zhongshan Princedom (中山國), requested to be appointed as the commander of the Wuhuan cavalry. Zhang Wen denied his request and put Gongsun Zan in charge of the cavalry instead. However, when the Wuhuan cavalry reached Ji (薊; around present-day Beijing), many of them deserted and went home because of lack of supplies. Zhang Chun felt disgruntled when his request was denied, so he secretly formed an alliance with Zhang Ju (張舉), a former Administrator of Taishan Commandery (泰山郡), and the Wuhuan leader Qiulij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Para-Mongolic Languages
Para-Mongolic is a proposed group of languages that is considered to be an extinct sister branch of the Mongolic languages. Para-Mongolic contains certain historically attested extinct languages, among them Khitan and Tuyuhun. Languages The languages of the Xiongnu, Donghu and Wuhuan might be Para-Mongolic, as might those of the Xianbei and the Tuoba (the founders of the Northern Wei) and Khitan. Because the surviving evidence for Xianbei and Tuoba is very sparse, one can only hypothesize that a genetic relationship ''could'' be possible. In the case of Khitan, there is rich evidence, but most of it is written in the two Khitan scripts (large and small) that have yet to be fully deciphered. However, from the available evidence it has been concluded that a genetic relationship to Mongolic is likely. Tuoba Alexander Vovin (2007) identifies the extinct Tuoba language (Tabɣač) as a Mongolic language. However, Chen (2005) argues that Tuoba was a Turkic language. Shimunek c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Mongols
The proto-Mongols emerged from an area that had been inhabited by humans as far back as 45,000 years ago during the Upper Paleolithic. The people there went through the Bronze Age, Bronze and Iron Ages, forming tribal alliances, peopling, and coming into conflict with early polities in the Zhongyuan, Central Plain. The proto-Mongols formed various tribal kingdoms who fought against one other for supremacy, such as the Rouran Khaganate (330–555) until it was defeated by the Göktürks, who founded the First Turkic Khaganate (552–744), which in turn was subdued by the growing strength of the Tang dynasty. The destruction of the Uyghur Khaganate (744–848) by the Yenisei Kyrgyz resulted in the end of Turkic dominance on the Mongolian Plateau. The para-Mongol Khitan people founded also referred to by Chineses sources as Liao dynasty (916–1125) and ruled Mongolia and portions of the eastern coast of Siberia now known as the Russian Far East, northern Korea, and North China. Ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanggu Commandery
Shanggu Commandery ( zh, 上谷郡) was a commandery in imperial China from the Warring States period to Tang dynasty. It was located in present-day Hebei and Beijing. The commandery was established by the state of Yan for the defense against the Xiongnu. In Western Han dynasty, it administered 15 counties, including Juyang (沮陽), Quanshang (泉上), Pan (潘), Jundu (軍都), Juyong (居庸), Goumao (雊瞀), Yiyu (夷輿), Ning (寧), Changping (昌平), Guangning (廣寧), Zhuolu (涿鹿), Qieju (且居), Ru (茹), Nüqi (女祈) and Xialuo (下落). Guangyang Commandery was merged into Shanggu in Emperor Guangwu of Han's reign, but was restored in 96 AD, and two former Shanggu counties – Jundu and Changping – was transferred there. Later during Eastern Han, only 8 counties remained, namely Juyang, Pan, Ning, Guangning, Juyong, Goumao, Zhuolu and Xialuo. The total number of households was 36,008 in 2 AD, while the population was 117,762. In 140 AD, the population was 51 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later or Eastern Han. The book was compiled by Fan Ye and others in the 5th century during the Liu Song dynasty, using a number of earlier histories and documents as sources. Background In 23 CE, Han dynasty official Wang Mang was overthrown by a peasants' revolt known as the Red Eyebrows. His fall separates the Early (or Western) Han dynasty from the Later (or Eastern) Han dynasty. As an orthodox history, the book is unusual in being completed over two hundred years after the fall of the dynasty. Fan Ye's primary source was the '' Dongguan Hanji'' (東觀漢記; "Han Records of the Eastern Lodge"), which was written during the Han dynasty itself. Contents References Citations Sources ; General * Chavannes, Édouard (1906) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Guangwu Of Han
Emperor Guangwu of Han (; 15 January 5 BC29 March AD 57), born Liu Xiu (), courtesy name Wenshu (), was a Chinese monarch. He served as an emperor of the Han dynasty by restoring the dynasty in AD 25, thus founding the Eastern Han dynasty. He ruled over parts of China at first since his dynasty was formed through rebellion against the short-lived Xin dynasty, and through suppression and conquest of regional warlords, the whole of China proper was consolidated by the time of his death in AD 57. During his reign, Taoism was made the official religion of China, and the Chinese folk religion began to decline. Liu Xiu was one of the many descendants of the Han imperial family. Following the usurpation of the Han throne by Wang Mang and the ensuing civil war during the disintegration of Wang's Xin dynasty, he emerged as one of several descendants of the fallen dynasty claiming the imperial throne. After assembling forces and proclaiming himself emperor in the face of competitors, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
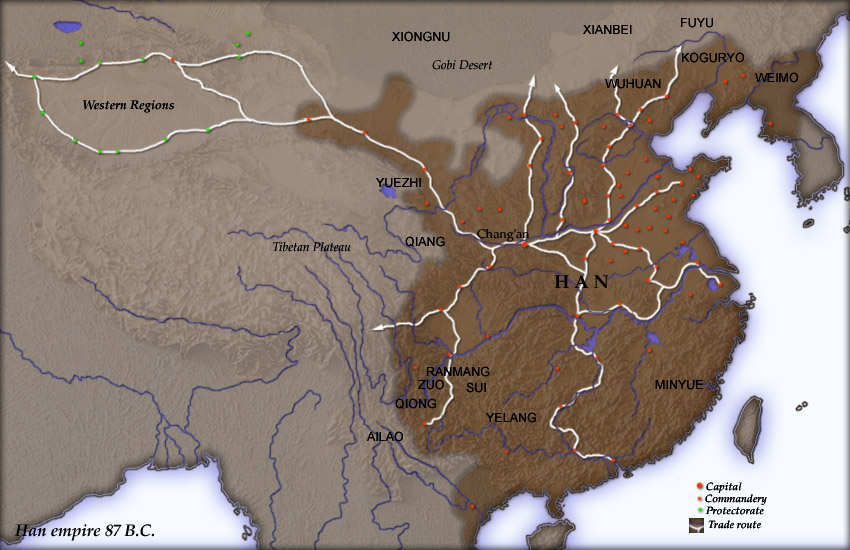
Chang'an
Chang'an (; zh, t=長安, s=长安, p=Cháng'ān, first=t) is the traditional name of the city now named Xi'an and was the capital of several Chinese dynasties, ranging from 202 BCE to 907 CE. The site has been inhabited since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in what is now the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin Shi Huang of the Qin dynasty, China's first emperor, held his imperial court and constructed his massive mausoleum guarded by the Terracotta Army. From its capital at Xianyang, the Qin dynasty ruled a larger area than either of the preceding dynasties. The imperial city of Chang'an during the Han dynasty was located northwest of today's Xi'an. During the Tang dynasty, the area that came to be known as Chang'an included the area inside the Ming Xi'an fortification, plus some small areas to its east and west, and a substantial part of its southern suburbs. Thus, Tang Chang'an was eight t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huo Qubing
Huo Qubing (140 BC – October 117 BC, formerly ''Ho Ch'ii-ping'') was a Chinese military general and politician of the Western Han dynasty during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han. He was a nephew of the general Wei Qing and Empress Wei Zifu (Emperor Wu's wife), and a half-brother of the statesman Huo Guang. Along with Wei Qing, he led a campaign into the Gobi Desert of what is now Mongolia to defeat the Xiongnu nomadic confederation, winning decisive victories such as the Battle of Mobei in 119 BC. Huo Qubing was one of the most legendary commanders in Chinese history, and still lives on in Chinese culture today. Early life Huo Qubing was an illegitimate son from the love affair between Wei Shaoer (), the daughter of a lowly maid from the household of Princess Pingyang (Emperor Wu's older sister), and Huo Zhongru (), a low-ranking civil servant employed there at the time. However, Huo Zhongru did not want to marry a lower class serf girl like Wei Shaoer, so he abandoned her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaoxi Commandery
Liaoxi Commandery ( zh, 遼西郡) was a commandery in imperial China from the Warring States period to Tang dynasty. It was located in modern eastern Hebei and western Liaoning, to the west of the Liao River. The commandery was created by the state of Yan on its northern border during the Warring States period. In Western Han dynasty, It administered 14 counties, including Qielü (且慮), Haiyang (海陽), Xin'anping (新安平), Liucheng (柳城), Lingzhi (令支), Feiru (肥如), Bincong (賓從), Jiaoli (交黎), Yangle (陽樂), Husu (狐蘇), Tuhe (徒河), Wencheng (文成), Linyu (臨渝) and Lei (絫). In 2 AD, the population was 352,325, in 72,654 households. In Eastern Han, its territory and population were both much reduced. Five counties remained, including Yangle, Haiyang, Lingzhi, Feiru and Linyu. In 140 AD, the population was 81,714, in 14,150 households. In 280 AD, the commandery had 3 counties, namely Yangle, Feiru and Haiyang, and a population of 2,800 househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |