|
Wimborne Town F.C. Managers
Wimborne Minster (often referred to as Wimborne, ) is a market town in Dorset in South West England, and the name of the Church of England church in that town. It lies at the confluence of the River Stour and the River Allen, north of Poole, on the Dorset Heaths, and is part of the South East Dorset conurbation. According to Office for National Statistics data the population of the Wimborne Minster built-up area was 15,552. Governance The town and its administrative area are served by eleven councillors plus one from the nearby ward of Cranfield. The electoral ward of Wimborne Minster is slightly bigger than the parish, with a 2011 population of 7,014. Wimborne Minster is part of the Mid Dorset and North Poole parliamentary constituency. After 2019 structural changes to local government in England, Wimborne Minster is covered by Wimborne Minster and Colehill and Wimborne Minster East for elections to the Dorset Council unitary authority. Buildings and architecture Wim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wimborne Minster (church)
Wimborne Minster is the parish church of Wimborne Minster, Wimborne, Dorset, England. The minster has existed for over 1300 years and is recognised for its unusual chained library (one of only a few surviving chained libraries in the world). The minster is a former monastery and Benedictine nunnery, and Æthelred of Wessex, King Æthelred of Wessex is buried there. History Wimborne Abbey The minster is dedicated to Cuthburh, Saint Cuthburga (sister to Ine of Wessex, Ine, King of Wessex and wife of Aldfrith of Northumbria, Aldfrith, King of Northumbria) who founded a Benedictine abbey of nuns at the present day minster 705. Saint Walpurga was educated in the monastery, where she spent 26 years before travelling to Germany, following the missionary call of her mother's brother Saint Boniface. Leoba was also educated in this place. A monastery for men was also built around this time, adjacent to the abbey. Over the next hundred years the abbey and monastery grew in size and importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colehill And Wimborne Minster East (ward)
Colehill and Wimborne Minster East is an electoral ward in Dorset. Since 2019, the ward has elected 2 councillors to Dorset Council. Geography The Colehill and Wimborne Minster East ward covers the Colehill area as well as eastern parts of Wimborne Minster. The southern areas of Furzehill are also in the ward. Councillors Election 2019 Dorset Council election 2024 Dorset Council election References See also * List of electoral wards in Dorset This is a list of Wards and electoral divisions of the United Kingdom, electoral divisions and wards in the ceremonial county of Dorset in South West England. All changes since the re-organisation of local government following the passing of the ... {{Dorset (Unitary Authority) Wards Wards of Dorset Wimborne Minster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
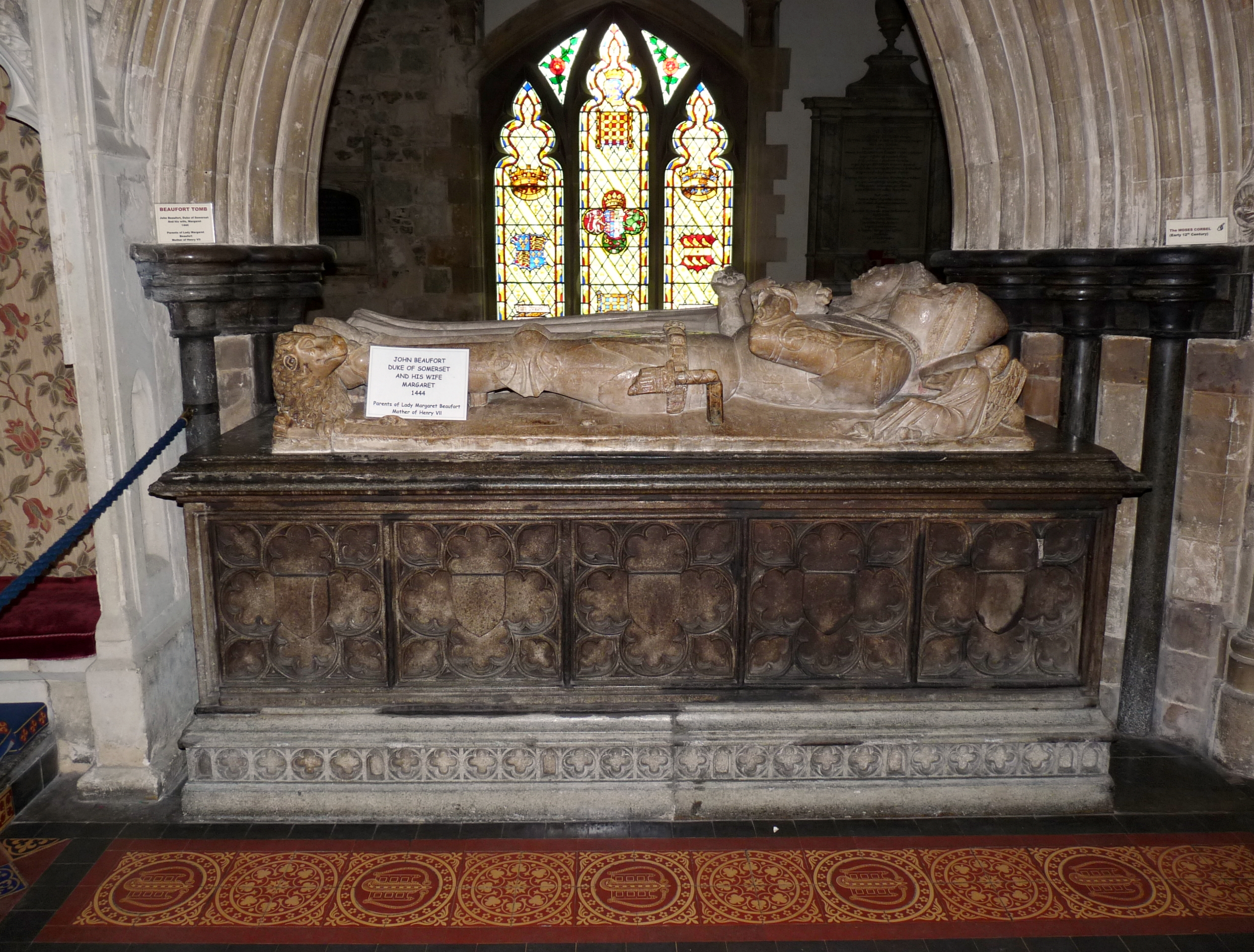
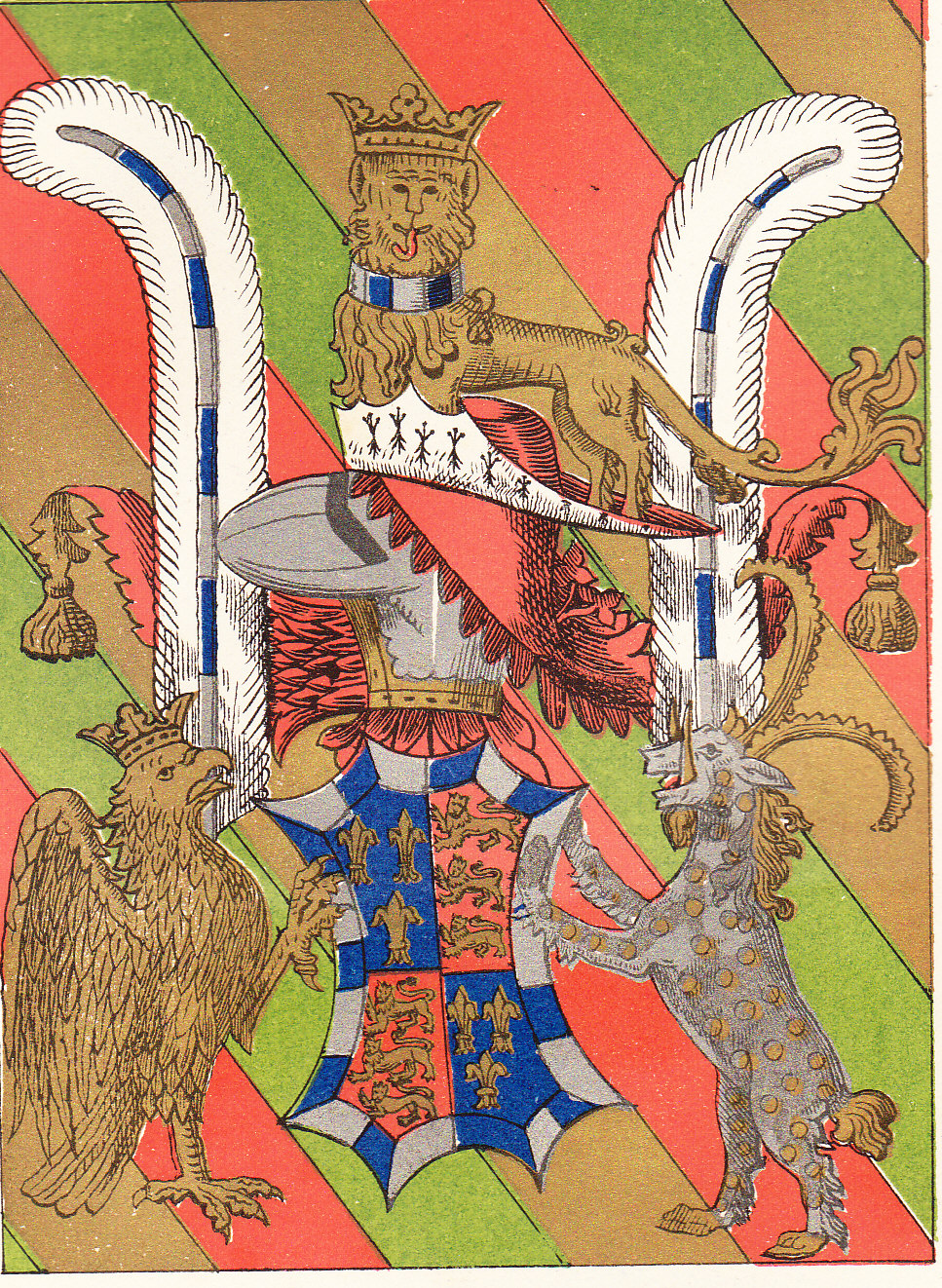
John Beaufort, 1st Duke Of Somerset
John Beaufort, 1st Duke of Somerset, 3rd Earl of Somerset (25 March 1404 – 27 May 1444) was an English nobleman and military commander during the Hundred Years' War. He was a paternal first cousin of King Henry V and the maternal grandfather of Henry VII. Origins Born on 25 March 1404, he was the second son of John Beaufort, 1st Earl of Somerset, the eldest of the four legitimised children of John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, by his mistress Katherine Swynford. John of Gaunt was the third surviving son of King Edward III. His mother was Margaret Holland, a daughter of Thomas Holland, 2nd Earl of Kent, the son of Joan "the Fair Maid of Kent", a granddaughter of King Edward I and wife of Edward the Black Prince (eldest brother of John of Gaunt) and mother of King Richard II. Career In 1418 he became 3rd Earl of Somerset, having succeeded his elder brother Henry Beaufort, 2nd Earl of Somerset (1401–1418), who died unmarried, aged 17, whilst fighting for the Lancast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred The Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfred was young. Three of Alfred's brothers, Æthelbald, King of Wessex, Æthelbald, Æthelberht, King of Wessex, Æthelberht and Æthelred I of Wessex, Æthelred, reigned in turn before him. Under Alfred's rule, considerable administrative and military reforms were introduced, prompting lasting change in England. After ascending the throne, Alfred spent several years fighting Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, dividing England between Anglo-Saxon territory and the Viking-ruled Danelaw, composed of Scandinavian York, the north-east Midlands and East Anglia. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum to Christianity. He defended his kingdom again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æthelred I Of Wessex
Æthelred I (alt. Aethelred, Ethelred; ; 845/848 to 871) was King of Wessex from 865 until his death in 871. He was the fourth of five sons of King Æthelwulf of Wessex, four of whom in turn became king. Æthelred succeeded his elder brother Æthelberht, King of Wessex, Æthelberht and was followed by his youngest brother, Alfred the Great. Æthelred had two sons, Æthelhelm and Æthelwold ætheling, Æthelwold, who were passed over for the kingship on their father's death because they were still infants. Alfred was succeeded by his son, Edward the Elder, and Æthelwold unsuccessfully disputed the throne with him. Æthelred's accession coincided with the arrival of the Viking Great Heathen Army in England. Over the next five years the Vikings conquered Northumbria and Kingdom of East Anglia, East Anglia, and at the end of 870 they launched a full-scale attack on Wessex. In early January 871, Æthelred was defeated at the Battle of Reading (871), Battle of Reading. Four days la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chained Library
A chained library is a library where the books are attached to their bookcase by a chain, which is sufficiently long enough to allow the books to be taken from their shelves and read, but not removed from the library itself. The practice was usual for reference library, reference libraries (that is, the vast majority of libraries) from the Middle Ages to around the 18th century. This would prevent theft of the library's materials.Weston, J. (10 May 2013).The Last of the Great Chained Libraries. Since the chaining process was also expensive, it was not used on all books, only the more valuable books such as reference works or large books in a collection were chained.Byrne, D. "Chained libraries". History Today, May 1987, 37, pp. 5–6. Librarians in the Middle Ages often invoked curses as well to keep books from being stolen. Once such curse written into the books was, It is standard for chained libraries to have the chain fitted to the corner or cover of a book. This is becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the Classical architecture, architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the Pointed arch (architecture), pointed arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Basilica of Saint-Denis, Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Architecture
The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monastery, monasteries, abbeys, churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches (particularly over windows and doorways) and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style. Origins These Romanesque architecture, Romanesque styles originated in Normandy and became widespread in northwestern Europe, particularly in England, which contributed considerable development and where the largest number of examples survived. At about the same time, Hauteville family, a Norman dynasty that ruled in Sicily produced a distinctive va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon Architecture
Anglo-Saxon architecture was a period in the history of architecture in England from the mid-5th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. Anglo-Saxon secular buildings in Britain were generally simple, constructed mainly using timber with thatch for roofing. No universally accepted example survives above ground. Generally preferring not to settle within the old Roman cities, the Anglo-Saxons built small towns near their centres of agriculture, at fords in rivers or sited to serve as ports. In each town, a main hall was in the centre, provided with a central hearth. There are many remains of Anglo-Saxon church architecture. At least fifty churches are of Anglo-Saxon origin with major Anglo-Saxon architectural features, with many more claiming to be, although in some cases the Anglo-Saxon part is small and much-altered. It is often impossible to reliably distinguish between pre- and post-Conquest 11th century work in buildings where most parts are later additions or alterations. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Beaufort Grave
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died ), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (died ), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus Christ * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope John (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920s to early 1930s, through styling and design of the exterior and interior of anything from large structures to small objects, including clothing, fashion, and jewelry. Art Deco has influenced buildings from skyscrapers to cinemas, bridges, ocean liners, trains, cars, trucks, buses, furniture, and everyday objects, including radios and vacuum cleaners. The name Art Deco came into use after the 1925 (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris. It has its origin in the bold geometric forms of the Vienna Secession and Cubism. From the outset, Art Deco was influenced by the bright colors of Fauvism and the Ballets Russes, and the exoticized styles of art from Chinese art, China, Japanese art, Japan, Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tivoli Theatre (Wimborne Minster)
The Tivoli Theatre in Wimborne Minster, Dorset, England, was built in 1936 as a theatre and cinema.Tivoli Theatre ''Cinema Treasures''. Retrieved 9 September 2009. It has a variety of features, including original chrome and door handles. Threatened with demolition in 1979 for a road-building scheme that was later abandoned,About Us ". ''The Tivoli Theatre''. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |