|
Wilderness Medicine
Wilderness medicine is a medical specialty concerned with medical care in remote, wilderness and expedition environments. The specialty includes prior planning, public health issues, a number of sub-specialties as well as responding to emergencies. One modern definition of wilderness medicine is "medical care delivered in those areas where fixed or transient geographic challenges reduce the availability of, or alter requirements for, medical or patient movement resources". This rapidly evolving field is of increasing importance as more people engage in outdoor activities, with more participants coming from the extremes of age, and with more people engaging in high risk activities. The exact aegis of wilderness medicine as a specialty is in constant flux to match the requirements of patients underlying wilderness or remote activities. While wilderness medicine is the preferred terminology for this medical speciality in the United States, terminology such as extreme medicine, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition Medicine
Expedition Medicine (sometimes known as expeditionary medicine) is the field of medicine focusing on providing embedded medical support to an expedition, usually in medically austere or isolated areas. Expedition medicine provides the physical and psychological wellbeing of expedition members before, during, and after an expedition. Expedition medicine may be practiced in support of commercial, non-governmental organizations, and government expeditions. Some medical governing bodies consider expedition medicine as a field within wilderness medicine, whilst others considered it be a separate discipline. History Ancient Era This field of expedition medicine has ancient origins and has been practised almost since the advent of medicine and Exploration, expeditions. Many ancient civilizations embedded medical staff with military units. Medieval Era As expedition and merchant crews grew during the later medieval era, Barber surgeon, barber surgeons and other medical staff were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveler's Diarrhea
Travelers' diarrhea (TD) is a stomach and intestinal infection. TD is defined as the passage of unformed stool (one or more by some definitions, three or more by others) while traveling. It may be accompanied by abdominal cramps, nausea, fever, headache and bloating. Occasionally dysentery may occur. Most travelers recover within three to four days with little or no treatment. About 12% of people may have symptoms for a week. Bacteria are responsible for more than half of cases, typically via foodborne illness and waterborne diseases. The bacteria enterotoxigenic ''Escherichia coli'' (ETEC) are typically the most common except in Southeast Asia, where '' Campylobacter'' is more prominent. About 10 to 20 percent of cases are due to norovirus. Protozoa such as ''Giardia'' may cause longer term disease. The risk is greatest in the first two weeks of travel and among young adults. People affected are more often from the developed world. Recommendations for prevention include eat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envenomation
Envenomation is the process by which venom is injected by the bite or sting of a venomous animal. Many kinds of animals, including mammals (e.g., the northern short-tailed shrew, ''Blarina brevicauda''), reptiles (e.g., many snakes), spiders, insects (e.g., wasps) and other arthropods, and fish (e.g., stone fish) employ venom for hunting and for self-defense. In particular, snakebite is considered to be a neglected tropical disease causing over 100,000 deaths and maiming over 400,000 people per year. Mechanisms Some venoms are applied externally, especially to sensitive tissues such as the eyes, but most venoms are administered by piercing the skin of the victim. Venom in the saliva of the Gila monster and some other reptiles enters prey through bites of grooved teeth. More commonly animals have specialized organs such as hollow teeth (fangs) and tubular stingers that penetrate the prey's skin, whereupon muscles attached to the attacker's venom reservoir squirt venom deep wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drowning
Drowning is a type of Asphyxia, suffocation induced by the submersion of the mouth and nose in a liquid. Submersion injury refers to both drowning and near-miss incidents. Most instances of fatal drowning occur alone or in situations where others present are either unaware of the victim's situation or unable to offer assistance. After successful resuscitation, drowning victims may experience breathing problems, confusion, or unconsciousness. Occasionally, victims may not begin experiencing these symptoms until several hours after they are rescued. An incident of drowning can also cause further complications for victims due to Hypothermia, low body temperature, Pulmonary aspiration, aspiration, or acute respiratory distress syndrome (respiratory failure from lung inflammation). Drowning is more likely to happen when spending extended periods of time near large bodies of water. Risk factors for drowning include alcohol use, drug use, epilepsy, minimal swim training or a complete l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightning
Lightning is a natural phenomenon consisting of electrostatic discharges occurring through the atmosphere between two electrically charged regions. One or both regions are within the atmosphere, with the second region sometimes occurring on the land, ground. Following the lightning, the regions become partially or wholly electrically neutralized. Lightning involves a near-instantaneous release of energy on a scale averaging between 200 megajoules and 7 gigajoules. The air around the lightning flash rapidly heats to temperatures of about . There is an emission of electromagnetic radiation across a wide range of wavelengths, some visible as a bright flash. Lightning also causes thunder, a sound from the shock wave which develops as heated gases in the vicinity of the discharge experience a sudden increase in pressure. The most common occurrence of a lightning event is known as a thunderstorm, though they can also commonly occur in other types of energetic weather systems, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search And Rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search is conducted over. These include mountain rescue; ground search and rescue, including the use of search and rescue dogs (such as K9 units); urban search and rescue in cities; combat search and rescue on the battlefield and air-sea rescue over water. International Search and Rescue Advisory Group (INSARAG) is a UN organisation that promotes the exchange of information between national urban search and rescue organisations. The duty to render assistance is covered by Article 98 of the UNCLOS. Definitions There are many different definitions of search and rescue, depending on the agency involved and country in question. *Canadian Armed Forces and Canadian Coast Guard: "Search and Rescue comprises the search for, and provision of ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the Human tooth, teeth, gums, and Human mouth, mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition (the development and arrangement of teeth) as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist. The history of dentistry is almost as ancient as the history of humanity and civilization, with the earliest evidence dating from 7000 BC to 5500 BC. Dentistry is thought to have been the first specialization in medicine which has gone on to develop its own accredited degree with its own specializations. Dentistry is often also understood to subsume the now largely defunct medical specialty of stomatology (the study of the mouth and its disorders and dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. In aviation, altitude is typically measured relative to mean sea level or above ground level to ensure safe navigation and flight operations. In geometry and geographical surveys, altitude helps create accurate topographic maps and understand the terrain's elevation. For high-altitude trekking and sports, knowing and adapting to altitude is vital for performance and safety. Higher altitudes mean reduced oxygen levels, which can lead to altitude sickness if proper acclimatization measures are not taken. Vertical distance measurements in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HACE
High-altitude cerebral edema (H.A.C.E) is a medical condition in which the brain swells with fluid because of the physiological effects of traveling to a high altitude. It generally appears in patients who have acute mountain sickness and involves disorientation, lethargy, and nausea among other symptoms. It occurs when the body fails to acclimatize while ascending to a high altitude. It appears to be a vasogenic edema (fluid penetration of the blood–brain barrier), although cytotoxic edema (cellular retention of fluids) may play a role as well. Individuals with the condition must immediately descend to a lower altitude or coma and death can occur. Patients are usually given supplemental oxygen and dexamethasone as well. HACE can be prevented by ascending to heights slowly to allow the body more time to acclimatize. Acetazolamide also helps prevent the condition. Untreated patients usually die within 48 hours. Those who receive treatment may take weeks to fully recover. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
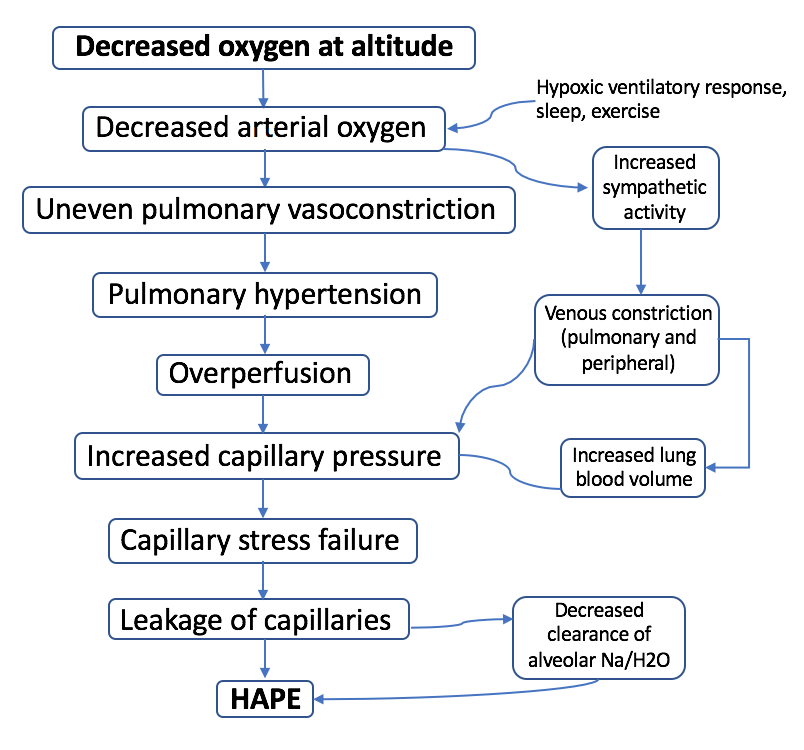
HAPE
High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) is a life-threatening form of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema that occurs in otherwise healthy people at altitudes typically above . HAPE is a severe presentation of altitude sickness. Cases have also been reported between in people who are at a higher risk or are more vulnerable to the effects of high altitude. Classically, HAPE occurs in persons normally living at low altitude who travel to an altitude above . Re-entry HAPE is also an entity that has been described in persons who normally live at high altitude but who develop pulmonary edema after returning from a stay at low altitude. If HAPE is not treated, there is a 50% risk of mortality. Symptoms include crackling sounds when breathing, dyspnea (at rest), and cyanosis. There are many factors that can make a person more susceptible to developing HAPE, including genetic factors. The understanding of the risk factors and how to prevent HAPE is not clear. HAPE remains the major cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude Sickness
Altitude sickness, the mildest form being acute mountain sickness (AMS), is a harmful effect of high altitude, caused by rapid exposure to low amounts of oxygen at high elevation. People's bodies can respond to high altitude in different ways. Symptoms of altitude sickness may include headaches, vomiting, tiredness, confusion, trouble sleeping, and dizziness. Acute mountain sickness can progress to high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) with associated shortness of breath or high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) with associated confusion. Chronic mountain sickness may occur after long-term exposure to high altitude. Altitude sickness typically occurs only above , though some people are affected at lower altitudes. Risk factors include a prior episode of altitude sickness, a high degree of activity, and a rapid increase in elevation. Being physically fit does not decrease the risk. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and is supported for those who have more than a minor reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especially Sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or sometimes Non-penetrative sex#Manual sex, manual sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of transmitting them to others. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes cases with no Signs and symptoms#Symptomatic, symptomatic disease. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, genital ulcers, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include Chlamydia infection, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital warts, genital herpes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |