|
Wikipedia Bots
Wikipedia bots are Internet bots (computer programs) that perform simple, repetitive tasks on Wikipedia. One prominent example of an internet bot used in Wikipedia is Lsjbot, which has generated millions of short articles across various language editions of Wikipedia. Activities Computer programs, called bots, have often been used to automate simple and repetitive tasks, such as correcting common misspellings and stylistic issues, or to start articles, such as geography entries, in a standard format from statistical data. Additionally, there are bots designed to automatically notify editors when they make common editing errors (such as unmatched quotes or unmatched parentheses). Anti-vandalism bots like ClueBot NG, created in 2010 are programmed to detect and revert vandalism quickly. Bots are able to indicate edits from particular accounts or IP address ranges, as occurred at the time of the shooting down of the MH17 jet incident in July 2014 when it was reported edits wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screenshot Of AWB Script Code 2022
A screenshot (also known as screen capture or screen grab) is an analog or digital image that shows the contents of a computer display. A screenshot is created by a (film) camera shooting the screen or the operating system or software running on the device powering the display. Screenshot techniques Digital techniques The first screenshots were created with the first interactive computers around 1960. Through the 1980s, computer operating systems did not universally have built-in functionality for capturing screenshots. Sometimes text-only screens could be dumped to a text file, but the result would only capture the content of the screen, not the appearance, nor were graphics screens preservable this way. Some systems had a BSAVE command that could be used to capture the area of memory where screen data was stored, but this required access to a BASIC prompt. Systems with composite video output could be connected to a VCR, and entire screencasts preserved this way. Most sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bot Policy
Bot or BOT may refer to: Sciences Computing and technology * Chatbot, a computer program that converses in natural language * Internet bot, a software application that runs automated tasks (scripts) over the Internet **Spambot, an internet bot designed to assist in the sending of spam * Internet Relay Chat bot, a set of scripts or an independent program that connects to IRC as a client * Robot, or "bot", a mechanical device that can perform physical tasks * Social bot, a type of chatbot that is employed in social media networks to automatically generate messages **Twitter bot, a program used to produce automated posts on the Twitter microblogging service * Video game bot, a computer-controlled player or opponent * Wikipedia bot, an internet bot which performs tasks in Wikipedia * Zombie computer, part of a botnet Biology and medicine * BOT, base of tongue, in medicine * Bot, the lesion caused by a botfly larva * Borderline ovarian tumor, a tumor of the ovaries Places * Bni O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pull Technology
Pull coding or client pull is a style of network communication, where the initial request for data originates from the client, and then is responded to by the server. The reverse is known as push technology, where the server ''pushes'' data to clients. Pull requests form the foundation of network computing, where many clients request data from centralized servers. Pull is used extensively on the Internet for HTTP page requests from websites. A ''push'' can also be simulated using multiple ''pulls'' within a short amount of time. For example, when pulling POP3 email messages from a server, a client can make regular pull requests, every few minutes. To the user, the email then appears to be pushed, as emails appear to arrive close to real-time. A trade-off of this system is that it places a heavier load on both the server and network to function correctly. Many web feeds, such as RSS are technically pulled by the client. With RSS, the user's RSS reader polls the server period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push Technology
Push technology, also known as server Push, refers to a communication method, where the communication is initiated by a server rather than a client. This approach is different from the " pull" method where the communication is initiated by a client. In push technology, clients can express their preferences for certain types of information or data, typically through a process known as the publish–subscribe model. In this model, a client "subscribes" to specific information channels hosted by a server. When new content becomes available on these channels, the server automatically sends, or "pushes," this information to the subscribed client. Under certain conditions, such as restrictive security policies that block incoming HTTP requests, push technology is sometimes simulated using a technique called polling. In these cases, the client periodically checks with the server to see if new information is available, rather than receiving automatic updates. General use Synchronous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recommender System
A recommender system (RecSys), or a recommendation system (sometimes replacing ''system'' with terms such as ''platform'', ''engine'', or ''algorithm'') and sometimes only called "the algorithm" or "algorithm", is a subclass of information filtering system that provides suggestions for items that are most pertinent to a particular user. Recommender systems are particularly useful when an individual needs to choose an item from a potentially overwhelming number of items that a service may offer. Modern recommendation systems such as those used on large social media sites make extensive use of AI, machine learning and related techniques to learn the behavior and preferences of each user and categorize content to tailor their feed individually. Typically, the suggestions refer to various decision-making processes, such as what product to purchase, what music to listen to, or what online news to read. Recommender systems are used in a variety of areas, with commonly recognised ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
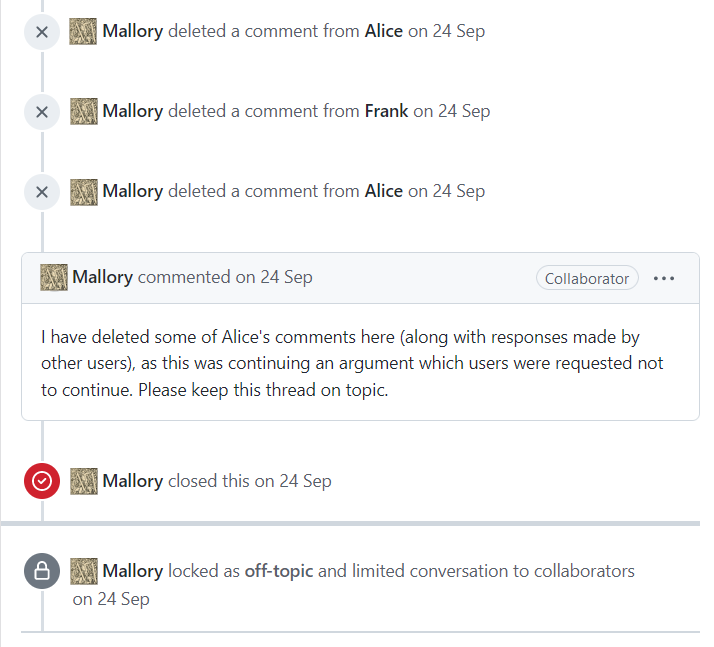
Moderation System
On websites that allow users to create content, content moderation is the process of detecting contributions that are irrelevant, obscene, illegal, harmful, or insulting. The purpose of content moderation is to remove or apply a warning label to problematic content or allow users to block and filter content themselves. It is part of the wider discipline of trust and safety. Various types of Internet sites permit user-generated content such as posts, comments, videos including Internet forums, blogs, and news sites powered by scripts such as phpBB, a wiki, PHP-Nuke, etc. Depending on the site's content and intended audience, the site's administrators will decide what kinds of user comments are appropriate, then delegate the responsibility of sifting through comments to lesser moderators. Most often, they will attempt to eliminate trolling, spamming, or flaming, although this varies widely from site to site. Major platforms use a combination of algorithmic tools, user rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archive
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials, in any medium, or the physical facility in which they are located. Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organization's lifetime, and are kept to show the history and function of that person or organization. Professional archivists and historians generally understand archives to be records that have been naturally and necessarily generated as a product of regular legal, commercial, administrative, or social activities. They have been metaphorically defined as "the secretions of an organism", and are distinguished from documents that have been consciously written or created to communicate a particular message to posterity. In general, archives consist of records that have been selected for permanent or long-term preservation on the grounds of their enduring cultural, historical, or evidentiary value. Archival records are normally unpublished and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerk
A clerk is a white-collar worker who conducts record keeping as well as general office tasks, or a worker who performs similar sales-related tasks in a retail environment. The responsibilities of clerical workers commonly include Records management, record keeping, filing, staffing service counters, screening callers, and other administrative tasks. In City of London Livery company, livery companies, the clerk is the chief executive officer. History and etymology The word ''clerk'' is derived from the Latin ''clericus'' meaning "cleric" or "clergyman", which is the Latinisation of names, latinisation of the Greek language, Greek ''κληρικός'' (''klērikos'') from a word meaning a "lot" (in the sense of drawing lots) and hence an "apportionment" or "area of land". Henry George Liddell, Robert S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labels
A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product. Labels are most often affixed to packaging and containers using an adhesive, or sewing when affixed to clothing. Labels contain printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed directly on a container or article can also be considered labelling. Labels have many uses, including promotion and providing information on a product's origin, the manufacturer (e.g., brand name), use, safety, shelf-life and disposal, some or all of which may be governed by legislation such as that for food in the UK or United States. Methods of production and attachment to packaging are many and various and may also be subject to internationally recognised standards. In many countries, hazardous products such as poisons or flammable liquids must have a warning label. Uses Labels may be used for any combination of identification, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperlinks
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference providing direct access to data by a user's clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text with hyperlinks. The text that is linked from is known as anchor text. A software system that is used for viewing and creating hypertext is a ''hypertext system'', and to create a hyperlink is ''to hyperlink'' (or simply ''to link''). A user following hyperlinks is said to ''navigate'' or ''browse'' the hypertext. The document containing a hyperlink is known as its source document. For example, in content from Wikipedia or Google Search, many words and terms in the text are hyperlinked to definitions of those terms. Hyperlinks are often used to implement reference mechanisms such as tables of contents, footnotes, bibliographies, indexes, and glossaries. In some hypertext, hyperlinks can be bidirectional: they can be followed in two direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link Rot
Link rot (also called link death, link breaking, or reference rot) is the phenomenon of hyperlinks tending over time to cease to point to their originally targeted file, web page, or server due to that resource being relocated to a new address or becoming permanently unavailable. A link that no longer points to its target may be called ''broken'', ''dead'', or ''orphaned''. The rate of link rot is a subject of study and research due to its significance to the internet's ability to preserve information. Estimates of that rate vary dramatically between studies. Information professionals have warned that link rot could make important archival data disappear, potentially impacting the legal system and scholarship. Prevalence A number of studies have examined the prevalence of link rot within the World Wide Web, in academic literature that uses URLs to cite web content, and within digital libraries. In a 2023 study of the Million Dollar Homepage external links, it was found t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copy Editing
Copy editing (also known as copyediting and manuscript editing) is the process of revising written material (" copy") to improve quality and readability, as well as ensuring that a text is free of errors in grammar, style, and accuracy. '' The Chicago Manual of Style'' states that manuscript editing encompasses "simple mechanical corrections (mechanical editing) through sentence-level interventions (linear editing) to substantial remedial work on literary style and clarity, disorganized passages, baggy prose, muddled tables and figures, and the like (substantive editing)". In the context of print publication, copy editing is done before typesetting and again before proofreading. Outside traditional book and journal publishing, the term "copy editing" is used more broadly, and is sometimes referred to as proofreading; the term sometimes encompasses additional tasks. Although copy editors are generally expected to make simple revisions to smooth awkward passages, they do not hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |