|
White Hat (computer Security)
A white hat (or a white-hat hacker, a whitehat) is an ethical security hacker. Ethical hacking is a term meant to imply a broader category than just penetration testing. Under the owner's consent, white-hat hackers aim to identify any vulnerabilities or security issues the current system has. The white hat is contrasted with the black hat, a malicious hacker; this definitional dichotomy comes from Western films, where heroic and antagonistic cowboys might traditionally wear a white and a black hat, respectively. There is a third kind of hacker known as a grey hat who hacks with good intentions but at times without permission. White-hat hackers may also work in teams called " sneakers and/or hacker clubs", red teams, or tiger teams. History One of the first instances of an ethical hack being used was a "security evaluation" conducted by the United States Air Force, in which the Multics operating systems were tested for "potential use as a two-level (secret/top secret) system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Security Hacker
A security hacker or security researcher is someone who explores methods for breaching or bypassing defenses and exploiting weaknesses in a computer system or network. Hackers may be motivated by a multitude of reasons, such as profit, protest, sabotage, information gathering, challenge, recreation, or evaluation of a system weaknesses to assist in formulating defenses against potential hackers. Longstanding controversy surrounds the meaning of the term "hacker". In this controversy, computer programmers reclaim the term ''hacker'', arguing that it refers simply to someone with an advanced understanding of computers and computer networks, and that ''cracker'' is the more appropriate term for those who break into computers, whether computer criminals ( black hats) or computer security experts ( white hats). A 2014 article noted that "the black-hat meaning still prevails among the general public". The subculture that has evolved around hackers is often referred to as the "co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Hack The Pentagon
Hack may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Games * ''Hack'' (Unix video game), a 1984 roguelike video game * ''.hack'' (video game series), a series of video games by the multimedia franchise ''.hack'' Music * ''Hack'' (album), a 1990 album by Information Society Film * '' Hack!'', a 2007 film starring Danica McKellar * ''Hacked'' (film), a 2011 Bollywood thriller film * ''The Den'' (2013 film), a 2013 American film also known as ''Hacked'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Hack (comedy), a joke that is considered obvious, frequently used, or stolen * Hack (comics), a Marvel Comics Universe mutant character * ''Hack'' (radio program), an Australian current affairs program * ''Hack'' (TV series), an American television series * .hack, a Japanese multimedia franchise * Lifehacker, a weblog about life hacks and software Computing * Hack (computer science), an inelegant but effective solution to a computing problem * Hack (computer security), to gain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Nessus (software)
Nessus is a proprietary software, proprietary vulnerability scanner developed by Tenable, Inc. History In 1998 Renaud Deraison created ''The Nessus Project'' as a free remote security scanner. On October 5 2005, with the release of Nessus 3, the project changed from the GNU General Public License to a Closed source, proprietary license. The Nessus 2 engine and some of the plugins are still using the GNU General Public License, leading to Fork (software development), forks based on Nessus like OpenVAS and Greenbone Sustainable Resilience. See also *Metasploit Project *OpenVAS *Security Administrator Tool for Analyzing Networks (SATAN) *SAINT (software) *Snort (software) *Wireshark References External links * Nessus 2.2.11 files and source codeNessus source code up to 2.2.9 Pentesting software toolkits Network analyzers Linux security software Formerly open-source or free software Software using the GNU General Public License {{Security-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Burp Suite
Burp Suite is a proprietary software tool for Information technology security assessment, security assessment and penetration testing of web applications. It was initially developed in 2003-2006 by Dafydd Stuttard to automate his own security testing needs, after realizing the capabilities of automatable web tools like Selenium (software), Selenium. Stuttard created the company PortSwigger to flagship Burp Suite's development. A community, professional, and enterprise version of this product are available. Notable capabilities in this suite include features to proxy web-crawls (Burp Proxy), log HTTP requests/responses (Burp Logger and HTTP History), capture/intercept in-motion HTTP requests (Burp Intercept), and aggregate reports which indicate weaknesses (Burp Scanner). This software uses a built-in database containing known-unsafe syntax patterns and keywords to search within captured HTTP requests/responses. Burp Suite possesses several penetration-type functionalities. A few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accomplishes a task with very little (if any) insight into exactly how it does so. Depending on the system under consideration and the technologies employed, the knowledge gained during reverse engineering can help with repurposing obsolete objects, doing security analysis, or learning how something works. Although the process is specific to the object on which it is being performed, all reverse engineering processes consist of three basic steps: information extraction, modeling, and review. Information extraction is the practice of gathering all relevant information for performing the operation. Modeling is the practice of combining the gathered information into an abstract model, which can be used as a guide for designing the new object or syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Metasploit
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company, Rapid7. Its best-known sub-project is the open-source Metasploit Framework, a tool for developing and executing exploit code against a remote target machine. Other important sub-projects include the Opcode Database, shellcode archive and related research. The Metasploit Project includes anti-forensic and evasion tools, some of which are built into the Metasploit Framework. In various operating systems it comes pre installed. History Metasploit was created by H. D. Moore in 2003 as a portable network tool using Perl. By 2007, the Metasploit Framework had been completely rewritten in Ruby. On October 21, 2009, the Metasploit Project announced that it had been acquired by Rapid7, a security company that provides unified vulnerability management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Denial-of-service Attack
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. The range of attacks varies widely, spanning from inundating a server with millions of requests to slow its performance, overwhelming a server with a substantial amount of invalid data, to submitting requests with an illegitimate IP address. In a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), the incoming traffic flooding the victim originates from many different sources. More sophisticated strategies are required to mitigate this type of attack; simply attempting to block a single source is insuffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Memory Forensics
Memory forensics is forensic analysis of a computer's memory dump. Its primary application is investigation of advanced cyberattacks which are stealthy enough to avoid leaving data on the computer's hard drive. Consequently, the memory (e.g. RAM) must be analyzed for forensic information. History Zeroth generation tools Until the early 2000s, memory forensics was done on an ad hoc basis (termed ''unstructured analysis''), often using generic data analysis tools like strings and grep. These tools are not specifically created for memory forensics, and therefore are difficult to use.They also provide limited information. In general, their primary usage is to extract text from the memory dump. Many operating systems provide features to kernel developers and end-users to actually create a snapshot of the physical memory for either debugging (e.g. core dump or Blue Screen of Death) purposes or experience enhancement (e.g. hibernation). In the case of Microsoft Windows, crash dump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Penetration Testing
A penetration test, colloquially known as a pentest, is an authorized simulated cyberattack on a computer system, performed to evaluate the security of the system; this is not to be confused with a vulnerability assessment. The test is performed to identify weaknesses (or vulnerabilities), including the potential for unauthorized parties to gain access to the system's features and data, as well as strengths, enabling a full risk assessment to be completed. The process typically identifies the target systems and a particular goal, then reviews available information and undertakes various means to attain that goal. A penetration test target may be a white box (about which background and system information are provided in advance to the tester) or a black box (about which only basic information other than the company name is provided). A gray box penetration test is a combination of the two (where limited knowledge of the target is shared with the auditor). A penetration test can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Security Administrator Tool For Analyzing Networks
Security Administrator Tool for Analyzing Networks (SATAN) was a free software vulnerability scanner for analyzing networked computers. SATAN captured the attention of a broad technical audience, appearing in ''PC Magazine'' and drawing threats from the United States Department of Justice. It featured a web interface, complete with forms to enter targets, tables to display results, and context-sensitive tutorials that appeared when a vulnerability had been found. Naming For those offended by the name SATAN, the software contained a special command called ''repent'', which rearranged the letters in the program's acronym from "SATAN" to "SANTA". Description The tool was developed by Dan Farmer and Wietse Venema. Neil Gaiman drew thartworkfor the SATAN documentation. SATAN was designed to help systems administrators automate the process of testing their systems for known vulnerabilities that can be exploited via the network. This was particularly useful for networked systems wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
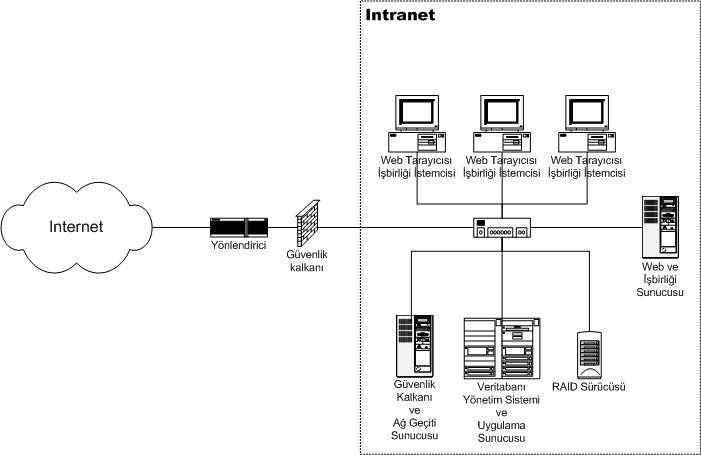 |
Intranets
An intranet is a computer network for sharing information, easier communication, collaboration tools, operational systems, and other computing services within an organization, usually to the exclusion of access by outsiders. The term is used in contrast to public networks, such as the Internet, but uses the same technology based on the Internet protocol suite. An organization-wide intranet can constitute an important focal point of internal communication and collaboration, and provide a single starting point to access internal and external resources. In its simplest form, an intranet is established with the technologies for local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs). Many modern intranets have search engines, user profiles, blogs, mobile apps with notifications, and events planning within their infrastructure. An intranet is sometimes contrasted to an extranet. While an intranet is generally restricted to employees of the organization, extranets may also be accesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |