|
Westmoreland Parish
Westmoreland () is the westernmost parish in Jamaica, on the south side of the island. It lies south of Hanover, southwest of Saint James, and northwest of Saint Elizabeth, in the county of Cornwall. The chief town and capital is Savanna-la-Mar. Negril, a famous tourist destination, is also situated in the parish. History The earliest inhabitants of Westmoreland were the Arawak and Ciboney Indians. The Ciboney were first to arrive, from the coast of South America, around 500 BC. Known as "cave dwellers", they lived along the cliffs of Negril. The labyrinth of caves and passageways beneath what is now the Xtabi Hotel in Negril are one of the first known settlements of Ciboney Indians in Jamaica. Christopher Columbus stopped at what became Westmoreland on his second voyage when he landed in Jamaica. One of the first Spanish settlements was also built at present-day Bluefields in this parish. The English took over the island from Spanish rule in 1655. Colonists named the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negril
Negril is a small, widely dispersed beach resort and town located in Westmoreland and Hanover parishes at the far western part of Jamaica, southwest from Sangster International Airport in Montego Bay. Westmoreland is the westernmost parish in Jamaica, located on the south side of the island. Downtown Negril, the West End cliff resorts to the south of downtown, and the southern portion of the so-called beach are in Westmoreland Parish. The northernmost resorts are along the Negril Beach and are nearer if not across the border where Westmoreland Parish meets the Hanover Parish. The nearest large town is Savanna-la-Mar, the capital of Westmoreland Parish if traveling South West. Whereas going in the opposite direction along the A1 highway is Lucea, the Capital Town of Hanover. History Spanish colonialism The name ''Negril'' is a shortened version of ''Negrillo'' ( Spanish: ''Little black one''), as it was originally named by the Spaniards in 1494. A theory holds that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
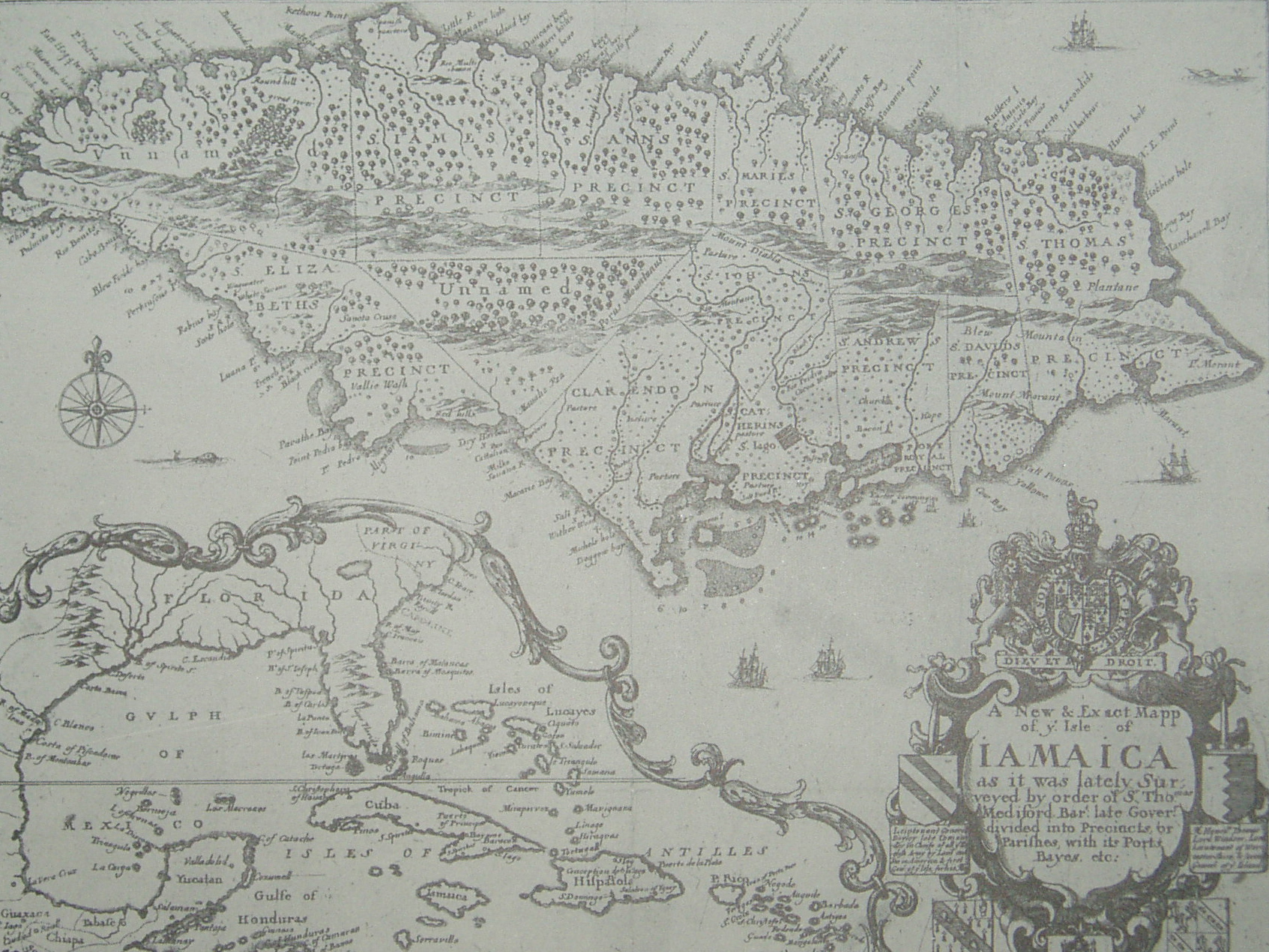
Parishes Of Jamaica
The parishes of Jamaica are the main units of local government in Jamaica. They were created following the English Invasion of Jamaica, settlement of Jamaica in 1655. This administrative structure for the Colony of Jamaica developed slowly. However, since 1 May 1867, Jamaica has been divided into the current fourteen Parish (administrative division), parishes. These were retained after Independence of Jamaica, independence in 1962. They are grouped into three historic County, counties, which no longer have any administrative relevance. Every parish has a coast; none are landlocked. List History Early history Following the English conquest of Jamaica the first phase of colonisation was carried out by the Army, with a system of Regimental plantations. These were drawn up on the southern flat lands, with the Regimental commanders charged with ordering their men to plant provisions. Certain key figures such as Luke Stokes (1656) and Thomas Modyford (1664) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern and Western European populations, exhibiting a high degree of continuity with other Indo-European-derived ethnic groups in the region. Spain is also home to a diverse array of national and regional identities, shaped by its complex history. These include various languages and dialects, many of which are direct descendants of Latin, the language imposed during Roman rule. Among them, Spanish (also known as Castilian) is the most widely spoken and the only official language across the entire country. Commonly spoken regional languages include, most notably, the sole surviving indigenous language of Iberia, Basque, as well as other Latin-descended Romance languages like Spanish itself, Catalan and Galician. Many populations outside Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a dependent territory or colony. The commemoration of the independence day of a country or nation celebrates when a country is free from all forms of colonialism; free to build a country or nation without any interference from other nations. Definition Whether the attainment of independence is different from revolution has long been contested, and has often been debated over the question of violence as legitimate means to achieving sovereignty. In general, revolutions aim only to redistribute power with or without an element of emancipation, such as in democratization ''within'' a state, which as such may remain unaltered. For example, the Mexican Revolution (1910) chiefly refers to a multi-factional conflict that eventually led to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-government
Self-governance, self-government, self-sovereignty or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any form of institution, such as family units, social groups, affinity groups, legal bodies, industry bodies, religions, and political entities of various degrees. Self-governance is closely related to various philosophical and socio-political concepts such as autonomy, independence, self-control, self-discipline, and sovereignty. In the context of nation states, self-governance is called national sovereignty which is an important concept in international law. In the context of administrative division, a self-governing territory is called an autonomous region. Self-governance is also associated with political contexts in which a population or demographic becomes independent from colonial rule, absolute government, absolute monarchy, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed. When these principles are written down into a single document or set of legal documents, those documents may be said to embody a ''written constitution''; if they are encompassed in a single comprehensive document, it is said to embody a ''codified constitution''. The Constitution of the United Kingdom is a notable example of an ''uncodified constitution''; it is instead written in numerous fundamental acts of a legislature, court cases, and treaties. Constitutions concern different levels of organizations, from sovereign countries to companies and unincorporated associations. A treaty that establishes an international organization is also its constitution, in that it would define how that organization is constituted. Within states, a constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffrage
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to vote is called active suffrage, as distinct from passive suffrage, which is the right to stand for election. The combination of active and passive suffrage is sometimes called ''full suffrage''. In most democracies, eligible voters can vote in elections for representatives. Voting on issues by referendum ( direct democracy) may also be available. For example, in Switzerland, this is permitted at all levels of government. In the United States, some states allow citizens the opportunity to write, propose, and vote on referendums ( popular initiatives); other states and the federal government do not. Referendums in the United Kingdom are rare. Suffrage continues to be especially restricted on the basis of age, residency and citizenship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estate (house)
An estate is a large parcel of land under single ownership, which generates income for its owner. British context In the United Kingdom, historically an estate comprises the houses, outbuildings, supporting farmland, tenanted buildings, and natural resources (such as woodland) that surround the gardens and grounds of a very large property, such as a country house, mansion, palace or castle. It is the modern term for a manor, but lacks a manor's now-abolished jurisdiction. Country house estate The "estate" formed an economic system where the profits from its produce and rents (of housing or agricultural land) sustained the main household, formerly known as the manor house. Thus, "the estate" may refer to all other cottages and villages in the same ownership as the mansion itself, covering more than one former manor. Examples of such great estates are Woburn Abbey in Bedfordshire, England, and Blenheim Palace, in Oxfordshire, England, built to replace the former manor hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ..., fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double sugars, are molecules made of two bonded monosaccharides; common examples are sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (two molecules of glucose). White sugar is almost pure sucrose. In the body, compound sugars are hydrolysed into simple sugars. Longer chains of monosaccharides (>2) are not regarded as sugars and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. Starch is a glucose polymer found in plants, the most abundant source of energy in human foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riot
A riot or mob violence is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people. Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted varies depending on the riot and the inclinations of those involved. Targets can include Shopping mall, shops, cars, restaurants, state-owned institutions, and religious buildings. Riots often occur in reaction to a grievance or out of dissent. Historically, riots have occurred due to poverty, unemployment, poor quality of life, living conditions, governmental oppression, taxation or conscription, conflicts between ethnic groups (race riot) or religions (e.g., sectarian violence, pogrom), the outcome of a sporting event (e.g., sports riot, football hooliganism) or frustration with legal channels through which to air grievances. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots typically consist of disorganize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westmoreland Regiment Of Foot
The 55th Regiment of Foot was a British Army infantry regiment, raised in 1755. After 1782 it had a county designation added, becoming known as the 55th (Westmorland) Regiment of Foot. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 34th (Cumberland) Regiment of Foot to form the Border Regiment in 1881. History Formation The regiment was raised in Stirling by Colonel George Perry as the 57th Regiment of Foot in 1755 for service in the Seven Years' War. It was re-ranked as the 55th Regiment of Foot, following the disbandment of the existing 50th and 51st regiments, in 1756. French and Indian War service The regiment embarked for North America for service in the French and Indian War and arrived in Nova Scotia on 8 July 1757 with the objective of taking part in the abandoned attack on the Fortress of Louisbourg. Following the death of Colonel Perry, Lord George Augustus Viscount Howe was appointed Colonel of the regiment in September 1757. After the regiment arrived in Alb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |