|
Western Oceanic Languages
The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by . They make up a majority of the Austronesian languages spoken in New Guinea New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is .... Classification The West Oceanic linkage is made up of three sub-linkages:. * North New Guinea linkage * Meso-Melanesian linkage * Papuan Tip linkage The center of dispersal was evidently near the Willaumez Peninsula on the north coast of New Britain. Notes References * * {{Austronesian languages Oceanic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesia and the Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken on the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family in insular Southeast Asia show the strong influence of Sanskrit, Tamil and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they retain a rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North New Guinea Languages
The North New Guinea languages of Papua New Guinea and Indonesia form a possible linkage of Western Oceanic languages. They have been in heavy contact with Papuan languages. Classification According to Lynch, Ross, & Crowley (2002), the structure of the family is as follows: *? Sarmi–Jayapura family * Schouten linkage * Huon Gulf family * Ngero–Vitiaz linkage The center of dispersal was evidently near the Vitiaz Strait between New Britain New Britain () is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi Island, Umboi the Dampie ... and the New Guinea mainland. The inclusion of Sarmi and Jayapura Bay is uncertain, and it may constitute a separate branch of Western Oceanic. References * Ross, Malcolm (1988). ''Proto Oceanic and the Austronesian languages of western Melanesia.'' Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. {{Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meso-Melanesian Languages
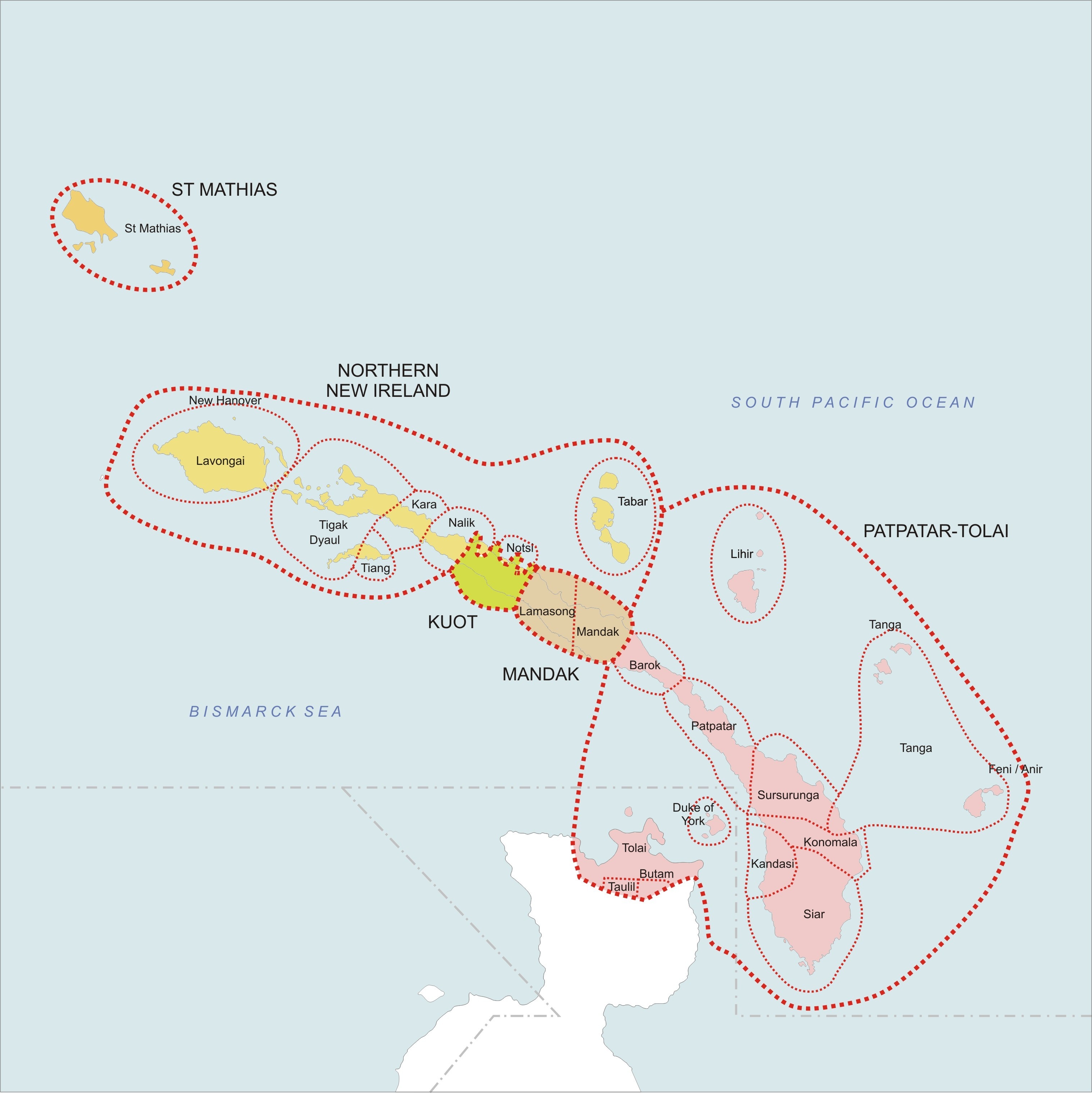
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: * Willaumez linkage: Bola, Bulu, Meramera, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Bali (Uneapa), Vitu (Muduapa) ay be a single language*New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak, Tungag, Nalik, Laxudumau, Kara, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Madara (Tabar), Lihir, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak ** Tomoip ** St George linkage *** Niwer Mil *** Warwar Feni *** Fanamaket *** Sursurunga *** Konomala ***Patpatar–Tolai: Patpatar, Lungalunga (Minigir), Tolai (Kuanua) ***Label–Bilur: Label, Bilur ***Kandas–Ramoaaina: Kandas, Ramoaaina *** Siar *** Northwest Solomonic linkage ''Ethnologue'' adds Guramalum to the St George linkage. The Willaumez Peninsula on the nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Tip Languages
The Papuan Tip languages are a branch of the Western Oceanic languages consisting of 60 languages. Contact All Papuan Tip languages, except Nimoa, Sudest, and the Kilivila languages (all spoken on islands off the coast of mainland Papua New Guinea), have subject–object–verb (SOV) word order due to influences from nearby Papuan languages (Lynch, Ross, & Crowley 2002:104). Universally, this is considered to be a typologically unusual change. Since these non- Austronesian influences can be reconstructed for Proto-Papuan Tip, they did not simply result from recent contact among individual daughter languages. Languages According to Lynch, Ross, & Crowley (2002), the structure of the family is as follows: *Nuclear Papuan Tip linkage **Suauic linkage: Buhutu, 'Auhelawa, Oya'oya, Unubahe, Saliba, Suau, Bwanabwana, Wagawaga **North Mainland – D'Entrecasteaux linkage *** Anuki *** Gumawana ***Bwaidoga: Bwaidoka, Diodio (West Goodenough), Iamalele, Iduna, Koluwawa, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage (linguistics)
In historical linguistics, a linkage is a network of related dialects or languages that formed from a gradual diffusion and differentiation of a proto-language. The term was introduced by Malcolm Ross in his study of Western Oceanic languages . It is contrasted with a family, which arises when the proto-language speech community separates into groups that remain isolated from each other and do not form a network. Principle Linkages are formed when languages emerged historically from the diversification of an earlier dialect continuum. Its members may have diverged despite sharing subsequent innovations, or such dialects may have come into contact and so converged. In any dialect continuum, innovations are shared between neighbouring dialects in intersecting patterns. The patterns of intersecting innovations continue to be evident as the dialect continuum turns into a linkage. According to the comparative method, a group of languages that exclusively shares a set of innovat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willaumez Peninsula
The Willaumez Peninsula is located on the north coast of New Britain in the West New Britain Province of Papua New Guinea. It was named after Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez by Antoine Bruni d'Entrecasteaux. The peninsula extends into the Bismarck Sea as an elongated headland and is of volcanic origin. The Dakataua Caldera is located at the northern tip of the Willaumez Peninsula. Kimbe Bay Kimbe Bay is a large bay in West New Britain Province, off the northern coast of New Britain, Papua New Guinea, at . Kimbe Bay is an important biodiversity hotspot. 60 percent of the coral species of the entire Indo-Pacific region live here. Kimbe ... is to the east of the peninsula. On the western side is Riebeck Bay. West New Britain Province Peninsulas of Papua New Guinea {{WestNewBritainProvince-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Britain
New Britain () is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi Island, Umboi the Dampier Strait (Papua New Guinea), Dampier and Vitiaz Straits) and from New Ireland (island), New Ireland by St. George's Channel (Papua New Guinea), St. George's Channel. The main towns of New Britain are Rabaul/Kokopo and Kimbe. The island is roughly the size of Taiwan. When the island was part of German New Guinea, its name was Neupommern ("New Pomerania"). In common with most of the Bismarcks it was largely formed by volcanic processes, and has active volcanoes including Ulawun (highest volcano nationally), Langila, the Garbuna Group, the Sulu Range, and the volcanoes Tavurvur and Vulcan (volcano), Vulcan of the Rabaul caldera. A major eruption of Tavurvur in 1994 destroyed the East New Britain provincial capital of Rabaul. Most of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Oceanic Languages
''The Oceanic Languages'' is a 2002 reference work by John Lynch, Malcolm Ross, and Terry Crowley, about the Oceanic family of languages – a large subgroup within the Austronesian phylum. It is the only formal survey of the field and a standard reference work for scholars of the Oceanic languages. The book's ubiquity among Oceanic linguists has led to its being referred to simply as "the blue book". The book contains five introductory chapters which describe the history of the languages, their structure, the sociolinguistic considerations, and the relationship the languages have with each other, as well as a look at their last common ancestor, Proto-Oceanic. These five chapters are then followed by a sample of sketches for forty-three languages. The book was written in part to expand on the previous works of Robert Henry Codrington and Sidney Herbert Ray whose work was then outdated and constrained mostly to Melanesian languages. Although it contains a substantial n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Oceanic Language
Proto-Oceanic (abbreviated as POc) is a proto-language that historical linguists since Otto Dempwolff have reconstructed as the hypothetical common ancestor of the Oceanic subgroup of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Oceanic is a descendant of the Proto-Austronesian language (PAN), the common ancestor of the Austronesian languages. Proto-Oceanic was probably spoken around the late 2nd millennium BCE in the Bismarck Archipelago, east of Papua New Guinea. Archaeologists and linguists currently agree that its community more or less coincides with the Lapita culture. Linguistic characteristics The methodology of comparative linguistics, together with the relative homogeneity of Oceanic languages, make it possible to reconstruct with reasonable certainty the principal linguistic properties of their common ancestor, Proto-Oceanic. Like all scientific hypotheses, these reconstructions must be understood as obviously reflecting the state of science at a particular moment in ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |