|
West Fijian Languages
The Central Pacific languages, also known as Fijian–Polynesian languages, are a branch of the Oceanic languages spoken in Fiji and Polynesia. Classification Ross et al. (2002) classify the languages as a linkage. Lynch, John, Malcolm Ross & Terry Crowley. 2002. ''The Oceanic languages.'' Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press. *Central Pacific **Western *** Rotuman ***Western Fijian linkage **** Namosi-Naitasiri-Serua **** Western Fijian (Nadroga, Waya) **East Central Pacific linkage ***Eastern Fijian linkage ****Bauan Bauan, officially the Municipality of Bauan (), is a municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 90,819 people. Etymology Bauan derived its name from the following Tagalog wor ... (standard Fijian) **** Gone Dau **** Lauan **** Lomaiviti *** Polynesian family The West Fijian languages are more closely related to Rotuman, and East Fijian to Polynesian, than they are to each other, but subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about . The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts, either in the capital city of Suva, or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi (where tourism is the major local industry) or Lautoka (where the Sugarcane, sugar-cane industry is dominant). The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain. The majority of Fiji's islands were formed by Volcano, volcanic activity starting around 150 million years ago. Some geothermal activity still occurs today on the islands of Vanua Levu and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namosi-Naitasiri-Serua Language
Namosi-Naitasiri-Serua is an Oceanic language spoken in Fiji Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ... by about 1,600 people. References Further reading * * * West Fijian languages Languages of Fiji {{CPacific-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
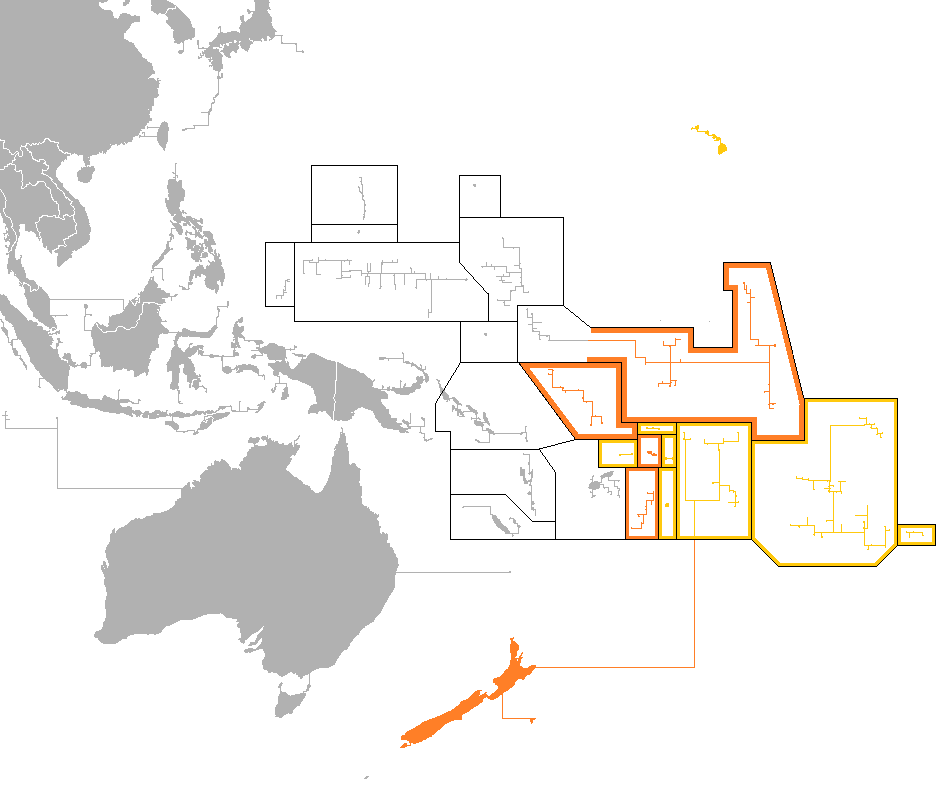
Central Pacific Languages
The Central Pacific languages, also known as Fijian–Polynesian languages, are a branch of the Oceanic languages spoken in Fiji and Polynesia Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in .... Classification Ross et al. (2002) classify the languages as a linkage. Lynch, John, Malcolm Ross & Terry Crowley. 2002. ''The Oceanic languages.'' Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press. *Central Pacific **Western *** Rotuman ***Western Fijian linkage **** Namosi-Naitasiri-Serua **** Western Fijian (Nadroga, Waya) **East Central Pacific linkage ***Eastern Fijian linkage **** Bauan (standard Fijian) **** Gone Dau **** Lauan **** Lomaiviti *** Polynesian family The West Fijian languages are more closely related to Rotuman, and East Fijian to Polynesian, than they are to each other, but subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflex Set
In biology, a reflex, or reflex action, is an involuntary, unplanned sequence or action and nearly instantaneous response to a stimulus. Reflexes are found with varying levels of complexity in organisms with a nervous system. A reflex occurs via neural pathways in the nervous system called reflex arcs. A stimulus initiates a neural signal, which is carried to a synapse. The signal is then transferred across the synapse to a motor neuron, which evokes a target response. These neural signals do not always travel to the brain, so many reflexes are an automatic response to a stimulus that does not receive or need conscious thought. Many reflexes are fine-tuned to increase organism survival and self-defense. This is observed in reflexes such as the startle reflex, which provides an automatic response to an unexpected stimulus, and the feline righting reflex, which reorients a cat's body when falling to ensure safe landing. The simplest type of reflex, a short-latency reflex, has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Languages
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family. There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austronesian family. While half of them are spoken in geographical Polynesia (the Polynesian triangle), the other half – known as Polynesian outliers – are spoken in other parts of the Pacific: from Micronesia to atolls scattered in Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands or Vanuatu. The most prominent Polynesian languages, by number of speakers, are Samoan, Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Hawaiian. The ancestors of modern Polynesians were Lapita navigators, who settled in the Tonga and Samoa areas about 3,000 years ago. Linguists and archaeologists estimate that this first population went through common development over approximately 1,000 years, giving rise to Proto-Polynesian, the linguistic ancestor of all modern Polynesian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomaiviti Language
Lomaiviti may refer to: * Lomaiviti Islands * Lomaiviti District * Lomaiviti Province Lomaiviti Province () is one of the 14 provinces of Fiji. Administratively, it forms part of Fiji's Eastern Division and of the Kubuna Confederacy, one of three traditional chiefly hierarchies in Fiji. Geographically it consists of the Lomaiv ... * Lomaiviti language * Lomaiviti (Fijian Communal Constituency, Fiji) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauan Language
Lauan is an East Fijian language spoken by about 16,000 people on a number of islands of eastern Fiji. Lauan is spoken in the Lau Province. However, the number of Lauan speakers has been declining due to the presence of other languages, which have become more dominant. References External links * Kaipuleohone Kaipuleohone is a digital ethnographic archive that houses audio and visual files, photographs, as well as hundreds of textual material such as notes, dictionaries, and transcriptions relating to small and endangered languages. The archive is stored ... has an archive of Lauan written materials East Fijian languages Languages of Fiji {{CPacific-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gone Dau Language
Gone Dau () is an East Fijian language spoken by about 500 people on the islands of Gone and Dau, Fiji Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about .... References East Fijian languages Languages of Fiji {{CPacific-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fijian Language
Fijian (') or iTaukei is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, Malayo-Polynesian family spoken by some 350,000–450,000 ethnic Fijians as a native language. The 1997 Constitution of Fiji#New Constitution for 2013, 2013 Constitution established Fijian as an official languages of Fiji, language of Fiji, along with English and Fiji Hindi and there is discussion about establishing it as the "national language". Fijian is a verb–object–subject, VOS language. Standard Fijian is based on the Bau (island)#Language, Bau dialect, which is an East Fijian language. Pidgin Fijian, A pidginized form is used by many Indo-Fijians and Chinese in Fiji, Chinese on the islands, while Pidgin Hindustani is used by many rural ethnic Fijians and Chinese in areas dominated by Indo-Fijians. History History of the language The Fijian language was introduced to Fiji 3500 years ago by the islands' first settlers. For millennia, it was the only spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Fijian Language
Western Fijian, also known as Wayan is an Oceanic language spoken in Fiji by about 57,000 people. It is distinct from Eastern Fijian (also known as Bauan or Standard Fijian). Phonology is heard in the Wayan dialect. Most Fijian languages have a unique prenasalized alveolar trill, transcribed here as . Western Fijian in particular, is unique among Fijian languages for having labialized velar consonants. All vowels come in long and short forms, and so does the bilabial nasal The voiced bilabial nasal is a type of consonantal sound which has been observed to occur in about 96% of spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is m. ... (/m/). References West Fijian languages Languages of Fiji {{austronesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotuman Language
Rotuman, also referred to as ''Rotunan'', ''Rutuman'' or ''Fäeag Rotuạm'' (citation form: ''Faega Rotuma''), is an Austronesian language spoken by the Indigenous Rotuma people in the South Pacific. Linguistically, as well as culturally, Rotuma has had a Polynesian influence in its culture and was incorporated as a dependency into the Colony of Fiji in 1881. Contemporary Rotuman is a result of significant Polynesian borrowing, following Samoan and Tongan migrations into Rotuma. The Rotuman language has sparked much interest with linguists because the language uses metathesis to invert the ultimate vowel in a word with the immediately preceding consonant, resulting in a vowel system characterized by umlaut, vowel shortening or extending and diphthongization. Unlike its Pacific neighbors, Rotuman is typically considered an AVO (agent–verb–object) language. Phonology Rotuman has no phonemic vowel length and is underlyingly a language of open syllables. Thus, only c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including Polynesian languages, linguistic relations, Polynesian culture, cultural practices, and Tradition, traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and Polynesian navigation, using stars to navigate at night. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Société de Géographie of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the South Seas, southern Pacific have also often been called the South Sea Islands, and their inhabitants have been called South Sea Islanders. The Hawai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |