|
Wartburg Theological Seminary Alumni
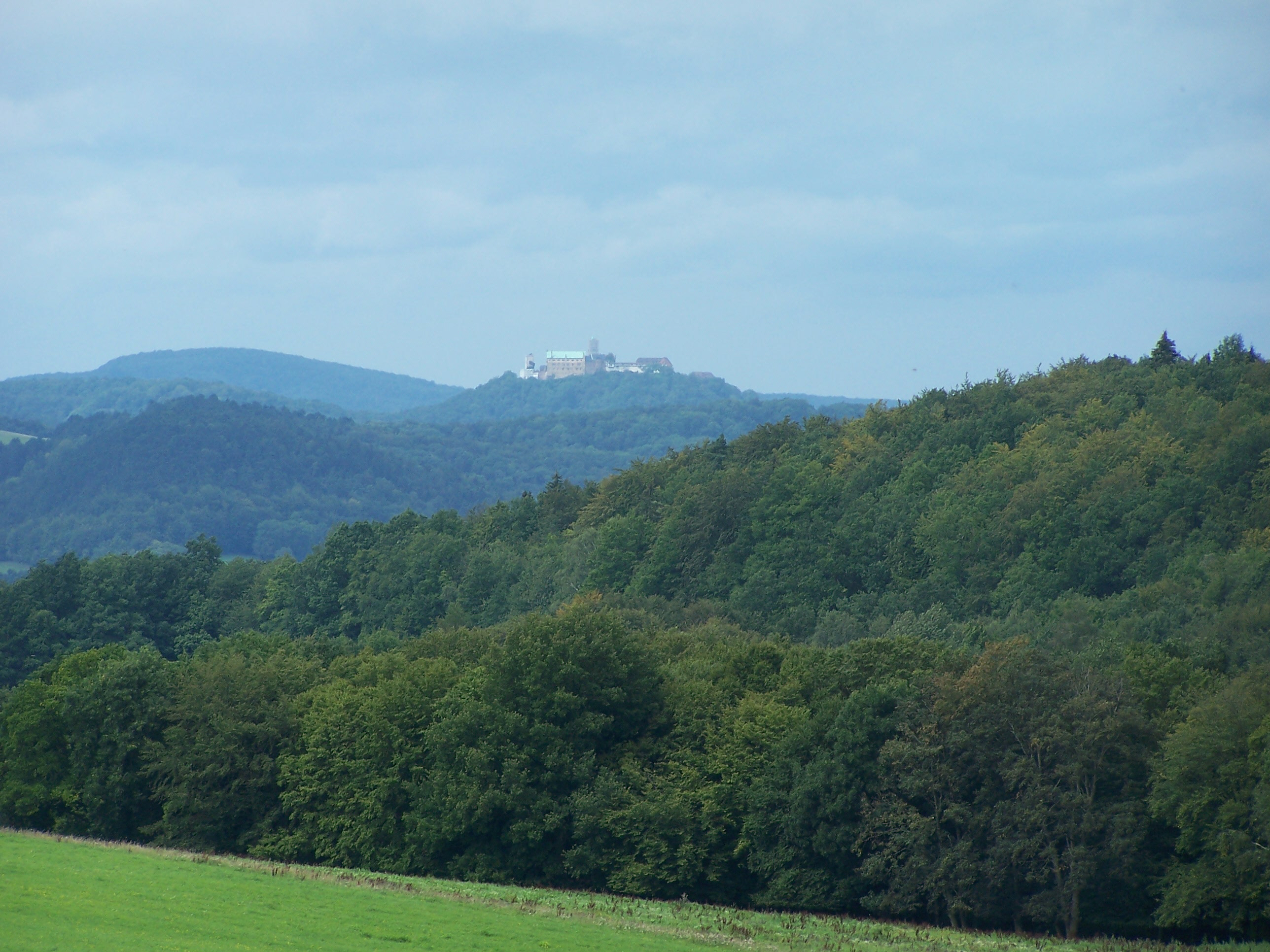
The Wartburg () is a castle originally built in the Middle Ages. It is situated on a precipice of to the southwest of and overlooking the town of Eisenach, in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It was the home of St. Elisabeth of Hungary, the place where Martin Luther translated the New Testament of the Bible into German, the site of the Wartburg festival of 1817 and the supposed setting for the possibly legendary ''Sängerkrieg''. It was an important inspiration for Ludwig II when he decided to build Neuschwanstein Castle. Wartburg is the most visited tourist attraction in Thuringia after Weimar. Although the castle today still contains substantial original structures from the 12th through 15th centuries, much of the interior dates back only to the 19th century. In 1999, Wartburg Castle was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List because of its quintessential medieval architecture and its historical and religious significance. Etymology The name of the castle is probabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisenach
Eisenach () is a Town#Germany, town in Thuringia, Germany with 42,000 inhabitants, west of Erfurt, southeast of Kassel and northeast of Frankfurt. It is the main urban centre of western Thuringia, and bordering northeastern Hesse, Hessian regions, is near the former Inner German border. A major attraction is Wartburg castle, which has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1999. Eisenach was an early capital of Thuringia in the 12th and 13th centuries. St.Elizabeth of Hungary, Elizabeth lived at the court of the Ludowingians here between 1211 and 1228. Later Martin Luther came to Eisenach and translated the Luther Bible, Bible into German. In 1685 Johann Sebastian Bach was born here. During the early modern period Eisenach was a residence of the Ernestine House of Wettin, Wettins and was visited by numerous representatives of Weimar classicism like Johann Wolfgang Goethe. In 1869 the Social Democratic Workers' Party of Germany, SDAP, one of the two precursors of the Social D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
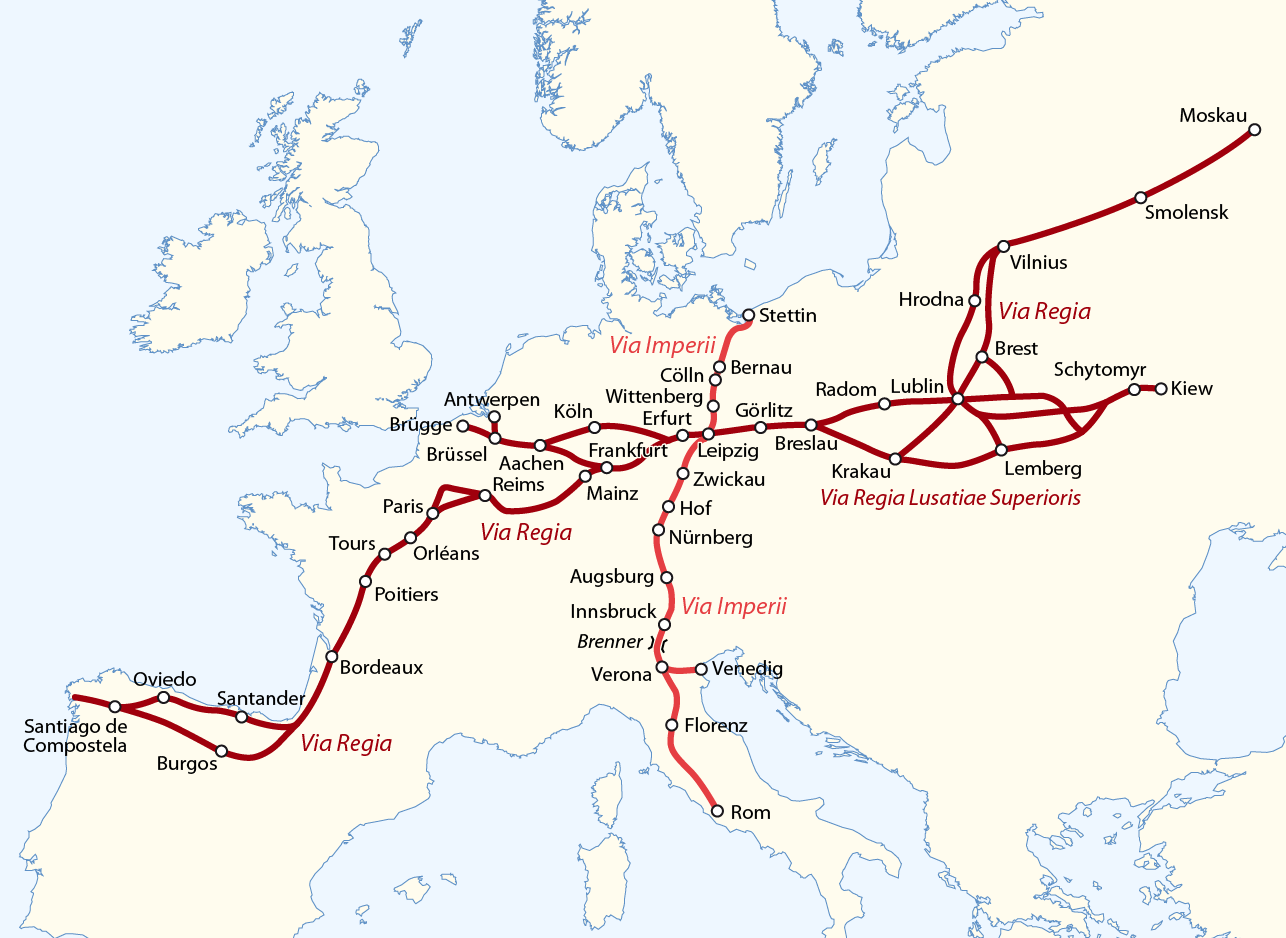
Via Regia
The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a European Cultural Route following the route of the Historic roads, historic road of the Middle Ages. There were many such ''viae regiae'' associated with the king in the medieval Holy Roman Empire. History Origins The Via Regia ran west–east through the centre of the Holy Roman Empire, from the Rhine at Mainz-Kastel (''Elisabethenstraße'') to Frankfurt am Main, trade city and site of the Imperial election, election of the King of the Romans, continuing along Hanau, the ''Kaiserpfalz'' at Gelnhausen, the towns of Steinau an der Straße, Neuhof, Hesse, Neuhof, Fulda and Eisenach to Erfurt, a centre of Isatis tinctoria, woad production. It ran further eastwards to Eckartsberga, crossing the Saale river between Bad Kösen and Naumburg and reached Leipzig, another trade city. The eastern part continued through Upper Lusatia (''Via Regia Lusatiae Superioris'') along Großenhain, Königsbrück, Kamenz, Bautzen and Görlitz to Wrocław in Silesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landgrave
Landgrave (, , , ; , ', ', ', ', ') was a rank of nobility used in the Holy Roman Empire, and its former territories. The German titles of ', ' ("margrave"), and ' ("count palatine") are of roughly equal rank, subordinate to ' ("duke"), and superior to the rank of a ' ("count"). Etymology The English word landgrave is the equivalent of the German ''Landgraf'', a compound of the words ''Land'' and ''Graf'' (English: Count). Description The title referred originally to a count who possessed imperial immediacy, or a feudal duty owed directly to the Holy Roman Emperor. His jurisdiction stretched over a sometimes quite considerable territory, which was not subservient to an intermediate power, such as a duke, a bishop or count palatine. The title originated within the Holy Roman Empire (first recorded in Lower Lotharingia from 1086: Henry III, Count of Louvain, as landgrave of Brabant). By definition, a landgrave exercised sovereign rights. His decision-making power was compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis I, Landgrave Of Thuringia
Louis I (died January 12, 1140) was ruler of Thuringia from 1123 to 1140. Biography The son of Count Louis the Springer ("the jumper") and his wife Adelheid, he was appointed Landgrave of Thuringia by the Emperor Lothair III in 1131. According to the succession in his line he should have been called Louis III, but he won Thuringia for his family and, in case of territorial expansion, it was customary to start counting from one. Thanks to his marriage with Hedwig of Gudensberg he obtained the rule over an extensive heritage, after the death of his father-in-law, Count Giso IV, which led to the union of Thuringia and Hesse. In 1137 Louis became Landgrave of Hesse-Gudensberg as well. His close relationship to the King Lothair III favoured his rise into the rank of a prince. After the death of Lothair, in 1137, Louis decided to support the Hohenstaufen in their struggle for power in the Reich against the Welf party. The Landgrave died on January 12, 1140, and was buried insi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salian Dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty () was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125). After the death of the last Ottonian emperor in 1024, the Kingdom of Germany and later the entire Holy Roman Empire passed to Conrad II, a Salian. He was followed by three more Salian rulers: Henry III, Henry IV, and Henry V. They established their monarchy as a major European power. The Salian dynasty developed a permanent administrative system based on a class of public officials answerable to the crown. Origins and name Modern historians suppose that the Salians descended from the Widonids, a prominent noble kindred emerging in the 7th century. Their estates were located at the confluence of rivers Moselle and Saar and they supported the Carolingians. The Widonids' eastward expansion towards the river Rhine started after they founded Hornbach Abbey in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV (; 11 November 1050 – 7 August 1106) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and List of kings of Burgundy, Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the son of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor—the second monarch of the Salian dynasty—and Agnes of Poitou. After his father's death on 5 October 1056, Henry was placed under his mother's guardianship. She made grants to German aristocrats to secure their support. Unlike her late husband, she could not control the election of the popes, thus the idea of the Libertas ecclesiae, "liberty of the Church" strengthened during her rule. Taking advantage of her weakness, Archbishop Anno II of Cologne kidnapped Henry in April 1062. He administered Germany until Henry came of age in 1065. Henry endeavoured to recover the royal estates that had been lost during his minority. He employed low-ranking officials to carry out his new policies, causing disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest (, , ) was a conflict between church and state in medieval Europe, the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture), abbots of monasteries, and the Pope himself. A series of popes in the Christianity in the 11th century, 11th and Christianity in the 12th century, 12th centuries undercut the power of the Holy Roman Emperor and other European monarchies, and the controversy led to nearly 50 years of conflict. It began as a power struggle between Pope Gregory VII and Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry IV (then King, later Holy Roman Emperor) in 1076. The conflict ended in 1122, when Pope Callixtus II and Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Henry V agreed on the Concordat of Worms. The agreement required bishops to swear an oath of fealty to the secular monarch, who held authority "by the lance" but left selection to the church. It affirmed the right of the church to invest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno The Saxon
Bruno the Saxon (Latin: ''Bruno Saxonicus''), also known as Bruno of Merseburg (German: ''Brun von Merseburg'') or Bruno of Magdeburg, was a German chronicler of the eleventh century and author of the ''Historia de Bello Saxonico'' ('History of the Saxon War'). Life Little is known of his life. Bruno was probably from an aristocratic background. He was a Saxon monk belonging to the household of Archbishop Werner of Magdeburg, who was a vigorous opponent of Henry IV and one of the leaders of the Saxon uprising against the emperor. After the death of the archbishop in 1078 at the hands of peasants, Bruno attached himself to Werner of Wolkenburg, Prince-Bishop of Merseburg, to whom, in 1082, he dedicated the work, "De Bello Saxonico" by which he is chiefly known. As its name indicates, it is a record of the struggles of the Saxons with the Emperor Henry IV. The author begins with an account of the youth of Henry and the evil influence exerted over him by Archbishop Adalbert of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuenburg Castle (Freyburg)
Neuenburg Castle (German language, German: ''Schloss Neuenburg'') is a hilltop castle in the south of the Germany, German state of Saxony-Anhalt, on the spur-like foothills of a plateau above the eastern bank of the river Unstrut. Below the castle to the north lies the wine-growing town of Freyburg, Germany, Freyburg, which in turn is about seven kilometers north of Naumburg (Saale). The castle is a stop on the Romanesque Road, a route through the state of significant cultural and historic sites.The castle is owned and managed by the Saxony-Anhalt Cultural Foundation. The castle was built around 1090 by the Thuringian count Louis the Springer, Ludwig der Springer, securing his territory in the east, as did its sister castle Wartburg in the west. The name Neuenburg derives from German for "new castle". From 1656 until 1746 it was a secondary residence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
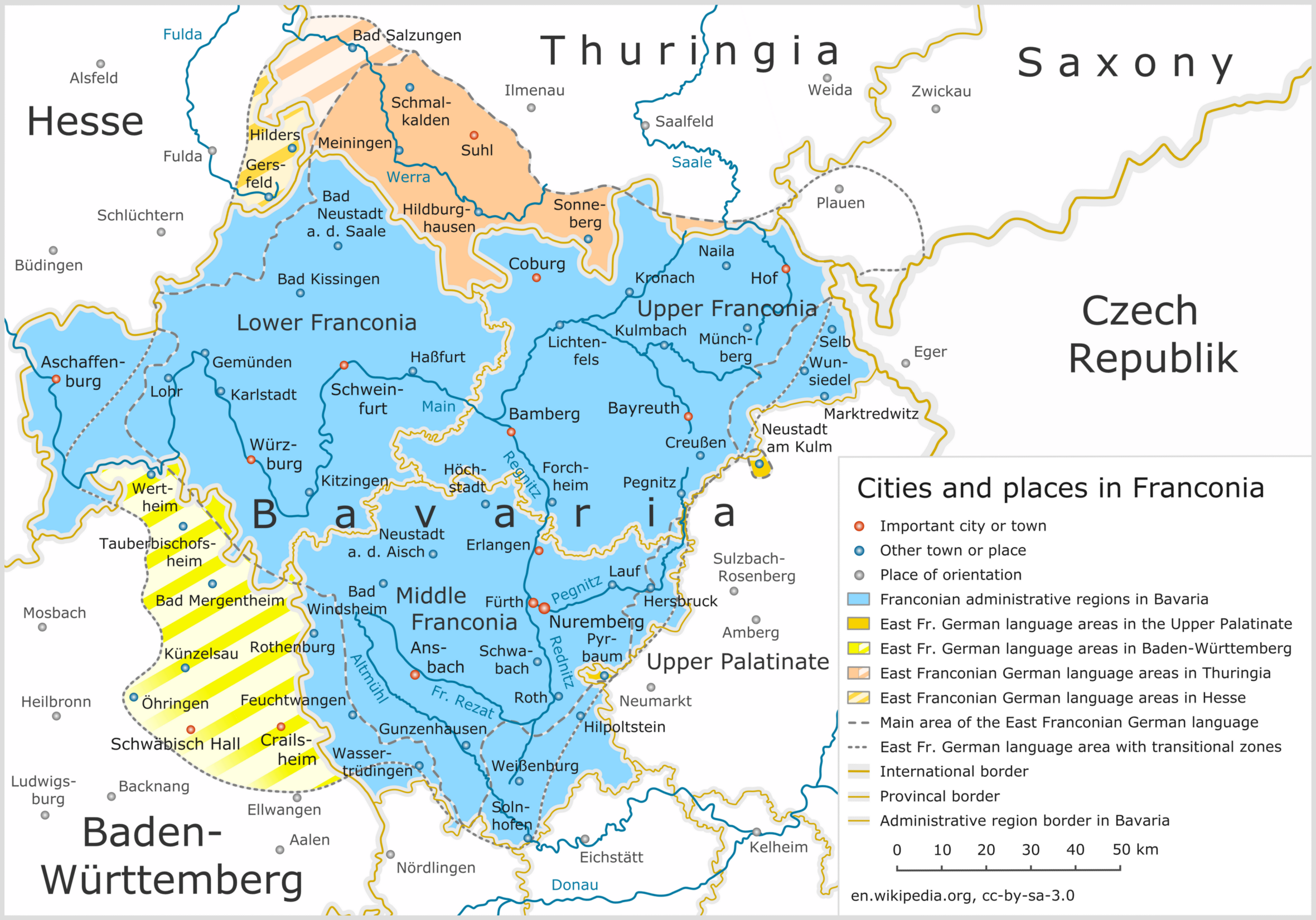
Franconia
Franconia ( ; ; ) is a geographical region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect (). Franconia is made up of the three (governmental districts) of Lower Franconia, Lower, Middle Franconia, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, East Franconian, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian dialect, Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia west of the Spessart (largest city: Aschaffenburg) do consider themselves Franconian, although not speaking the dialect. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Rieneck
The County of Rieneck was a comital domain within the Holy Roman Empire that lay in what is now northwestern Bavaria (in the west of Lower Franconia). It bore the same name as its original ruling family, the Counts of Rieneck, from whom the county and its main seat, the town of Rieneck, got their names. History The first documentary evidence of what is now the town of Rieneck surfaces in AD 790. Rieneck gained its name from the , who founded the line of Burgraves of Gerhart at the end of the 11th century from the over the Archbishopric of Mainz between Neustadt am Main, Lohr am Main and Karlstadt am Main. The family line died out with Gerhard I, Count of Rieneck in 1108. His only daughter married Arnold, Count of Loon (1101–39), inheriting Rienecker territory and, around 1156/7 by Louis I, Count of Loon, the family name,Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The Springer
Louis the Springer (), sometimes called Louis the Jumper or Louis the Leaper, was a German nobleman and count in Thuringia from the death of his father until his own death on 8 May 1123. Little is known about him, although he is mentioned in many legends. He was a prominent opponent of the Salian emperors Henry IV and Henry V during the Investiture Controversy. Life Louis was a son of Louis the Bearded and a member of the Franconian noble Ludowingians dynasty. He was baptized in the parish church in Altenbergen (today part of Leinatal). Around 1080, Louis and his brother Beringe founded the Schönrain Priory. In a document dated 1100, the two brothers are called "of Schauenburg", after a castle which their father had built near Friedrichroda. Louis continued the policy of his father of expanding his influence into the Thuringian Basin by founding castles and monasteries. His marriage to Adelheid of Stade, widow of the Saxon count palatine Frederick III, brought him into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |