|
Vortices
In fluid dynamics, a vortex (: vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rankine Vortex
The Rankine vortex is a simple mathematical model of a vortex in a viscous fluid. It is named after its discoverer, William John Macquorn Rankine. The vortices observed in nature are usually modelled with an irrotational (potential or free) vortex. However, in a potential vortex, the velocity becomes infinite at the vortex center. In reality, very close to the origin, the motion resembles a solid body rotation. The Rankine vortex model assumes a solid-body rotation inside a cylinder of radius a and a potential vortex outside the cylinder. The radius a is referred to as the vortex-core radius. The velocity components (v_r,v_\theta,v_z) of the Rankine vortex, expressed in terms of the cylindrical-coordinate system (r,\theta,z) are given by :v_r=0,\quad v_\theta(r) = \frac\begin r/a^2 & r \le a, \\ 1/ r & r > a \end, \quad v_z = 0 where \Gamma is the circulation strength of the Rankine vortex. Since solid-body rotation is characterized by an azimuthal velocity \Omega r, where \O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
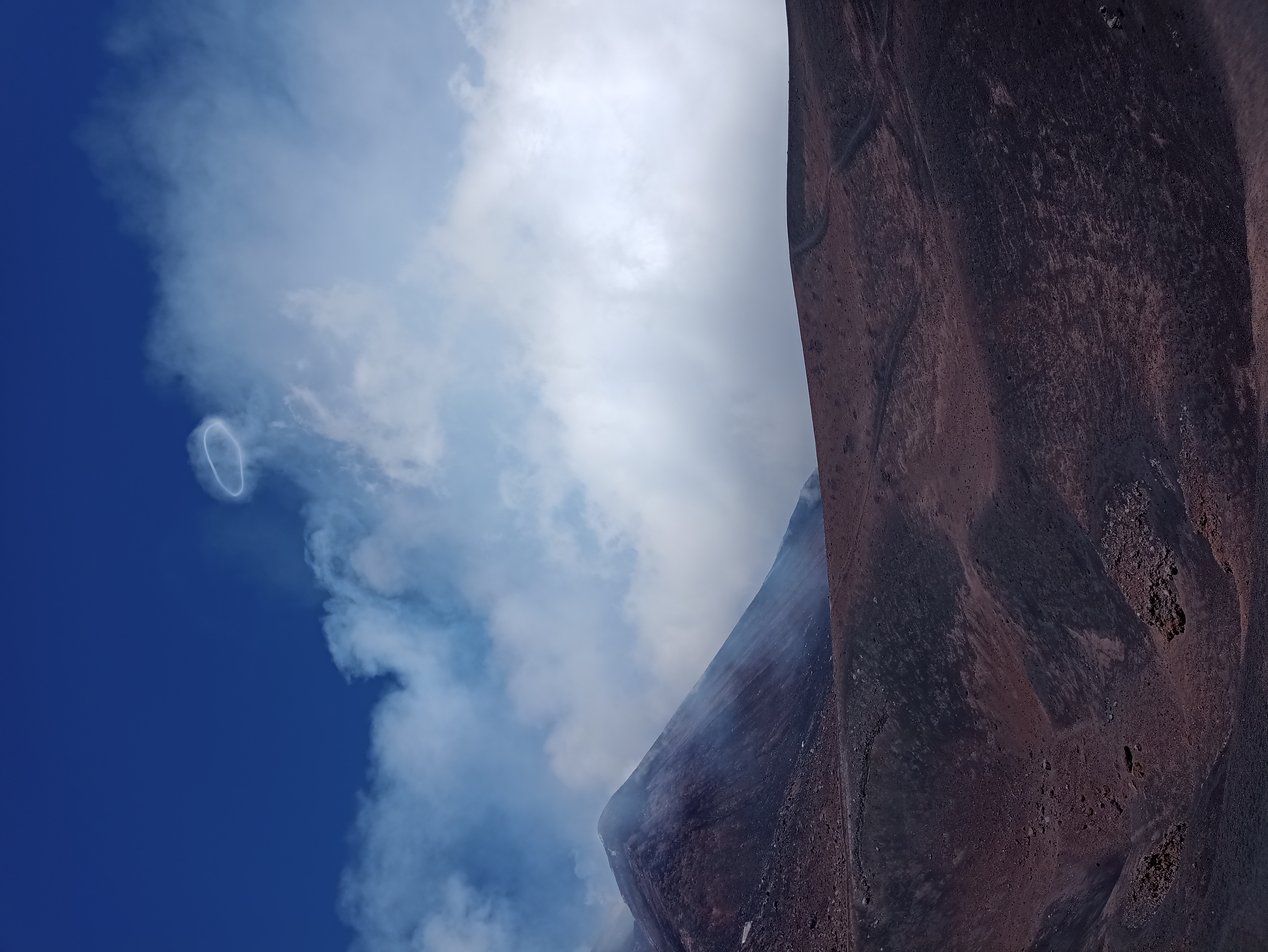
Smoke Rings
A smoke ring is a visible vortex ring formed by smoke in a clear atmosphere. Smokers may blow smoke rings from the mouth, intentionally or accidentally. Smoke rings may also be formed by sudden bursts of fire (such as lighting and immediately putting out a cigarette lighter), by shaking a smoke source (such as an incense stick) up and down, by firing certain types of artillery, or by the use of special devices, such as vortex ring guns and vortex ring toys. The head of a mushroom cloud is a large smoke ring. A smoke ring is commonly formed when a puff of smoke is suddenly injected into clear air, especially through a narrow opening. The outer parts of the puff are slowed by the still air (or by edges of the opening) relative to the central part, imparting it the characteristic poloidal flow pattern. The smoke makes the ring visible, but does not significantly affect the flow. The same phenomenon occurs with any fluid, producing vortex rings which are invisible but o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust Devil
A dust devil (also known regionally as a dirt devil) is a strong, well-formed, and relatively short-lived whirlwind. Its size ranges from small (18 in/half a metre wide and a few yards/metres tall) to large (more than 30 ft/10 m wide and more than half a mile/1 km tall). The primary vertical motion is upward. Dust devils are usually harmless, but can on rare occasions grow large enough to pose a threat to both people and property. They are comparable to tornadoes in that both are a weather phenomenon involving a vertically oriented rotating column of wind. Most tornadoes are associated with a larger parent circulation, the mesocyclone on the back of a supercell thunderstorm. Dust devils form as a swirling updraft under sunny conditions during fair weather, rarely coming close to the intensity of a tornado. Formation Dust devils form when a pocket of hot air near the surface rises quickly through cooler air above it, forming an updraft. If conditions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often (but not always) visible in the form of a funnel cloud, condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than , are about across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The Tornado records#Highest winds observed in a tornado, most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whirlpools
A whirlpool is a body of rotating water produced by opposing currents or a current running into an obstacle. Small whirlpools form when a bath or a sink is draining. More powerful ones formed in seas or oceans may be called maelstroms ( ). ''Vortex'' is the proper term for a whirlpool that has a downdraft. In narrow ocean straits with fast flowing water, whirlpools are often caused by tides. Many stories tell of ships being sucked into a maelstrom, although only smaller craft are actually in danger. Smaller whirlpools appear at Rapids, river rapids and can be observed downstream of artificial structures such as weirs and dams. Large waterfall, cataracts, such as Niagara Falls, produce strong whirlpools. Notable whirlpools Saltstraumen Saltstraumen is a narrow strait located close to the Arctic Circle, south-east of the city of Bodø (town), Bodø, Norway. It has one of the strongest tidal currents in the world. Whirlpools up to in diameter and in depth are formed when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoke Ring
A smoke ring is a visible vortex ring formed by smoke in a clear atmosphere. Smoking, Smokers may blow smoke rings from the mouth, intentionally or accidentally. Smoke rings may also be formed by sudden bursts of fire (such as lighting and immediately putting out a lighter, cigarette lighter), by shaking a smoke source (such as an incense stick) up and down, by firing certain types of artillery, or by the use of special devices, such as vortex ring guns and vortex ring toys. The head of a mushroom cloud is a large smoke ring. A smoke ring is commonly formed when a puff of smoke is suddenly injected into clear air, especially through a narrow opening. The outer parts of the puff are slowed by the still air (or by edges of the opening) relative to the central part, imparting it the characteristic poloidal flow pattern. The smoke makes the ring visible, but does not significantly affect the flow. The same phenomenon occurs with any fluid, producing vortex rings which are inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wake (physics)
In fluid dynamics, a wake may either be: * the region of recirculating flow immediately behind a moving or stationary blunt body, caused by viscosity, which may be accompanied by flow separation and turbulence, or * the wave pattern on the water surface downstream of an object in a flow, or produced by a moving object (e.g. a ship), caused by density differences of the fluids above and below the free surface and gravity (or surface tension). Viscosity The wake is the region of disturbed flow (often turbulent) downstream of a solid body moving through a fluid, caused by the flow of the fluid around the body. For a blunt body in subsonic external flow, for example the Apollo or Orion capsules during descent and landing, the wake is massively separated and behind the body is a reverse flow region where the flow is moving toward the body. This phenomenon is often observed in wind tunnel testing of aircraft, and is especially important when parachute systems are involved, becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-hand Rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a Convention (norm), convention and a mnemonic, utilized to define the orientation (vector space), orientation of Cartesian coordinate system, axes in three-dimensional space and to determine the direction of the cross product of two Euclidean vector, vectors, as well as to establish the direction of the force on a Electric current, current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. The various right- and left-hand rules arise from the fact that the three axes of three-dimensional space have two possible orientations. This can be seen by holding your hands together with palms up and fingers curled. If the curl of the fingers represents a movement from the first or x-axis to the second or y-axis, then the third or z-axis can point along either right thumb or left thumb. History The right-hand rule dates back to the 19th century when it was implemented as a way for identifying the positive direction of coordinate axes in three dime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulation (fluid Dynamics)
In physics, circulation is the line integral of a vector field around a closed curve embedded in the field. In fluid dynamics, the field is the fluid velocity field. In electrodynamics, it can be the electric or the magnetic field. In aerodynamics, it finds applications in the calculation of lift, for which circulation was first used independently by Frederick Lanchester, Ludwig Prandtl, Martin Kutta and Nikolay Zhukovsky. It is usually denoted (uppercase gamma). Definition and properties If is a vector field and is a vector representing the differential length of a small element of a defined curve, the contribution of that differential length to circulation is : \mathrm\Gamma = \mathbf \cdot \mathrm\mathbf = \left, \mathbf\ \left, \mathrm\mathbf\ \cos \theta. Here, is the angle between the vectors and . The circulation of a vector field around a closed curve is the line integral: \Gamma = \oint_\mathbf \cdot \mathrm d \mathbf. In a conservative vector field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |