|
Viverrids
Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized feliform mammals, comprising 14 genera with 33 species. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, in southern Europe, South and Southeast Asia on both sides of the Wallace Line. The word viverridae comes from the Latin word . The species of the subfamily Genettinae are known as genets and oyans. The viverrids of the subfamily Viverrinae are commonly called civets; the Paradoxurinae and most Hemigalinae species are called palm civets. Characteristics Viverrids have four or five toes on each foot and half-retractile claws. They have six incisors in each jaw and molars with two tubercular grinders behind in the upper jaw, and one in the lower jaw. The tongue is rough with sharp prickles. A pouch or gland occurs beneath the anus, but there is no cecum. The male's urethral opening is directed backward. Viverrids are the most primitive of all the families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetta
A genet (pronounced or ) is a member of the genus ''Genetta'', which consists of 17 species of small African carnivorans. The common genet is the only genet present in Europe and occurs in the Iberian Peninsula, Italy and France. Genet fossils from the Late Miocene and later have been found at sites in Ethiopia, Kenya and Morocco. Classification ''Genetta'' was scientific name, named and described by Frédéric Cuvier in 1816. The number of species in the genus is controversial. The following were proposed as valid in 2005: Extinct species * ''Genetta nyakitongwer'' – Early Pleistocene of Kenya * ''Genetta plesictoides'' – Late Pleistocene of Cyprus ''Genetta'' and ''Poiana (genus), Poiana'' are estimated to have diverged about . ''Genetta'' species are estimated to have diverged at least starting with the Hausa genet, followed by the giant genet . Characteristics Genets are slender cat-like animals with a long body, a long ringed tail, large ears, a pointed muzzle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viverrinae
The Viverrinae represent the largest subfamily of the Viverridae comprising three genera, which are subdivided into six species native to Africa and Southeast Asia. This subfamily was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Classification Gray defined the Viverrinae as comprising the genera '' Proteles'', '' Viverra'', ''Bassaris'' and '' Viverricula''. He subordinated the genera '' Genetta'' and ''Fossa'' to the Genettina, the genera '' Prionodon'' and ''Poiana'' to the Prionodontinae. Reginald Innes Pocock suggested that the African genets (''Genetta'') are also most nearly related to the Viverrinae, but should perhaps form a separate subfamily. William King Gregory and Milo Hellman placed the ''Viverra'', ''Viverricula'', ''Civettictis'', ''Genetta'', '' Osbornictis'', ''Poiana'' and the North-American eu creodine genera '' Didymictis'' and ''Viverravus'' of the Eocene into this viverrid subfamily. Ellerman and Morrison-Scott also included the genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplogale
Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei''), also known as Hose's civet, is a viverrid species endemic to the island of Borneo. It is listed on the IUCN Red List as Vulnerable species, Vulnerable because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 30% over the last three generations (inferred to be 15 years) and suspected to be more than 30% in the next three generations due to declines in population inferred from habitat destruction and environmental degradation, degradation. ''Diplogale'' is a Monotypic taxon, monospecific genus (biology), genus. Hose's palm civet was named after the zoologist Charles Hose by Oldfield Thomas in 1892. Hose collected the first specimen in Sarawak in 1891. What little is known of the species comes primarily from 17 museum specimens worldwide. Only in 1997, the first living specimen was obtained and released after two months. Hose's civet is not kept in captivity anywhere in the world. Characteristics The upperparts (from nose to tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemigalus
The banded palm civet (''Hemigalus derbyanus''), also called the banded civet, is a viverrid native to Indomalaya. They primarily inhabit lowland conifer habitat, which is under threat from encroaching human activity. It is estimated the population of the banded palm civet has decreased by around 30% in just three generations. Banded palm civets are usually approximately the size of a domestic cat; their fur is pale but with dark bands on the back. They are believed to be closely related to Hose's palm civets, which are similar in appearance and distribution. The banded palm civet is the only species in its genus, first scientifically described in 1837. The species comprises four subspecies, distributed across Indonesia and Southeast Asia. Two of the subspecies diverged from each other as long ago as 2.7 million years. Banded palm civets are affected by a variety of parasites, such as nematodes, and are primarily carnivorous, eating small animals such as rodents and bugs. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanuites
''Kanuites'' is an extinct genus of paradoxurine viverrid carnivore. It lived in Africa, during the Miocene epoch. Description ''Kanuites'' was about long, and looked remarkably similar to modern genets. ''Kanuites'' was probably an omnivore An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize t ... and may have had retractable claws, like a feline. It may have lived at least part of its life in trees. References Viverrids Miocene carnivorans Miocene mammals of Africa Monotypic prehistoric carnivoran genera {{paleo-carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
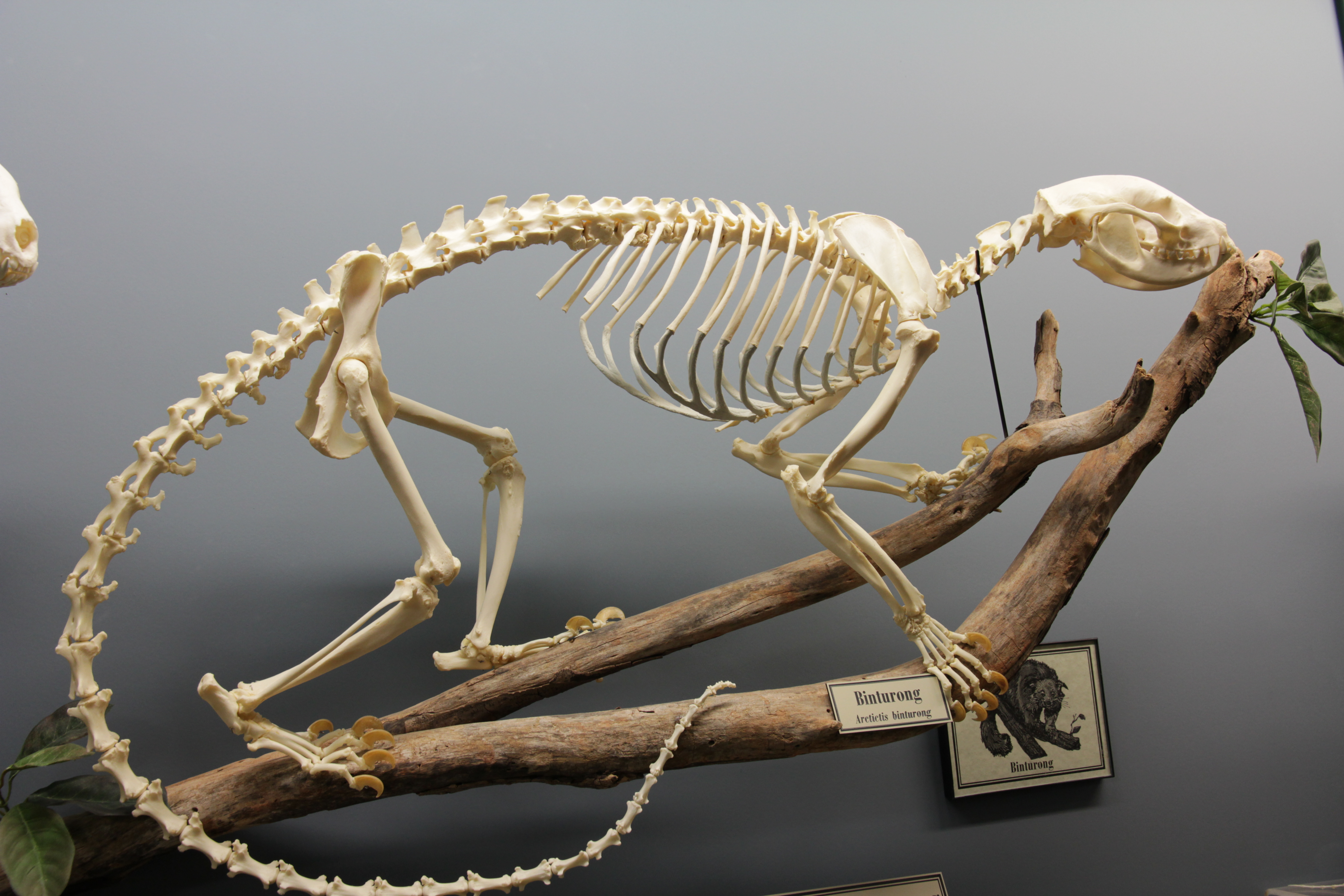
Arctictis
The binturong (''Arctictis binturong'') (, ), also known as the bearcat, is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia. It is uncommon in much of its range, and has been assessed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because of a declining population. It is estimated to have declined at least 30% since the mid-1980s. The binturong is the only species in the genus ''Arctictis''. Etymology "Binturong" is its common name in Borneo, and is related to the Western Malayo-Polynesian root "ma-tuRun". In Riau, it is called "benturong" and "tenturun". The scientific name ''Arctictis'' means 'bear-weasel', from the Greek '' arkt-'' "bear" + '' iktis'' "weasel". Taxonomy ''Viverra binturong'' was the scientific name proposed by Thomas Stamford Raffles in 1822 for a specimen from Malacca. The generic name ''Arctictis'' was proposed by Coenraad Jacob Temminck in 1824. ''Arctictis'' is a monotypic taxon; its morphology is similar to that of members of the genera ''Paradoxurus'' and ''Paguma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradoxurinae
Paradoxurinae is a subfamily of the feliform Viverridae, viverrids that was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Reginald Innes Pocock, Pocock subordinated the Genus (biology), genera ''Paradoxurus'', ''Paguma'' and ''Arctictis'' to this subfamily. Classification Living species Phylogenetic tree The phylogenetic relationships of Paradoxurinae are shown in the following cladogram: Extinct genera *''Kichechia'' *''Tugenictis'' *''Kanuites'' *''Siamictis'' References Viverrids Taxa named by John Edward Gray Long stubs with short prose {{carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrogalidia
The Sulawesi palm civet (''Macrogalidia musschenbroekii''), also known as Sulawesi civet, musang and brown palm civet is a little-known viverrid endemic to Sulawesi. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List due to population decline estimated to have been more than 30% over the last three generations (suspected to be 15 years) inferred from habitat destruction and degradation. ''Macrogalidia'' is a monospecific genus. It is the only carnivoran native to Sulawesi. Characteristics The Sulawesi civet has a light brownish-chestnut coloured soft and short coat with numerous light hairs intermixed. The underparts vary from fulvous to white; the breast is rufescent. There is a pair of indistinct longitudinal stripes and some faint spots on the hinder part of the back. The whiskers are mixed brown and white. The tail is marked with alternating rings of dark and pale brown, which are indistinct on the under surface, and disappear towards the dark tip. The length of head and bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradoxurus
''Paradoxurus'' is a genus of three palm civets within the viverrid family that was denominated and first described by Frédéric Cuvier in 1822. The ''Paradoxurus'' species have a broad head, a narrow muzzle with a large rhinarium that is deeply sulcate in the middle. Their large ears are rounded at the tip. The tail is nearly as long as the head and body. The three species are the Asian palm civet, the Golden palm civet, and the Brown palm civet. Characteristics ''Paradoxurus'' species have a broad head, a narrow muzzle with a large rhinarium that is deeply sulcate in the middle. Their large ears are rounded at the tip, the interior ridges and bursae are well developed. The skull exhibits marked muscular moulding, and the postorbital area is deeply constricted shortly behind the well-developed postorbital processes. It is considerably narrower than the interorbital area and than the muzzle above the canines. The dental formula is . The palate is not produced behind to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynogale
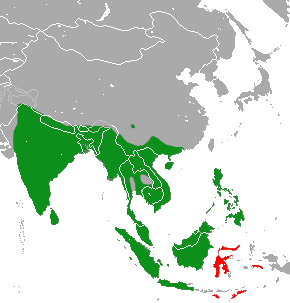
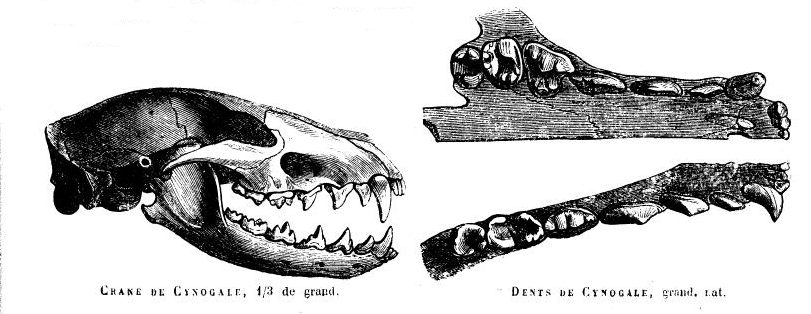
The otter civet (''Cynogale bennettii'') is a semiaquatic viverrid native to Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Brunei. It is believed to be undergoing severe population decline due to habitat destruction and is classified as an endangered species by the IUCN Red List. ''Cynogale'' is a monospecific genus. Characteristics The otter civet possesses webbed feet, which is an adaptation to its aquatic habitat. Its long, stiff whiskers may be used for foraging. Distribution and habitat Otter civets are distributed in Sumatra, Borneo and peninsular Thailand. Lowland primary forest is apparently the ideal habitat for the species, although it is also known to occur in secondary forest. Their presence in northern Vietnam is uncertain. They are believed to prefer peat swamp forests, but been sighted at low elevations in tropical dry forests. In March 2005, an otter civet was photographed by a camera trap within an acacia plantation in central Sarawak during 1,632 trap-nights. Betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrotogale
Owston's palm civet (''Chrotogale owstoni'') is a viverrid native to Vietnam, Laos and a very small portion of southern China, in three counties located in the Yunnan province: Hekou, Luchun, and Jinping, and has never been found west of the Mekong River. It is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 50% over the last three generations, inferred from over-exploitation, habitat destruction and degradation. Taxonomy The Owston's palm civet was described by Oldfield Thomas in 1912 on the basis of a skull and skin of zoological specimen collected by Alan Owston by a river in Tonkin. ''Chrotogale'' is a monospecific genus. Characteristics The Owston's palm civet has a tawny buff-grey body with highly contrasted black markings on its back and tail, and four bands on its back. These bands run from around the eyes to the first third of the tail. It has large rounded ears and black eyes. is a mid-sized palm civet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemigalinae
The Hemigalinae are a subfamily of the viverrids denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Hemigalinae species are native to Southeast Asia from southern China through Indochina, Malay Peninsula to Sumatra, Borneo and Sulawesi. Characteristics The tails of Hemigalinae species are ringed. The toes and the middle of the lower part of the tarsus are bald. The frenum, upper part, and sides of the lower part are hairy. The orbit is imperfect. Classification The Hemigalinae subfamily comprises the following five monospecific genera Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...: References External links Viverrids Mammals of Asia Taxa named by John Edward Gray Mammal subfamilies {{carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |