|
Vendiamorpha
Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata. The typical vendiamorph had an oval-shaped or round-shaped body divided completely into segmented isomers, that were arranged alternately in two rows with reference to the longitudinal axis of the body. Description The phenomenon of left-right alternating segments is called ''glide reflection symmetry'', and is a diagnostic feature of proarticulates. Transverse elements decrease in size from one end to the other and are inclined in the same direction. Typically, the first few, or largest initial isomers are fused together to form a headshield-like structure, leading some researchers to have originally considered them to be ancestral or related to arthropods, though, overwhelming evidence of them being proarticulates have since led researchers to discard this hypothetical relationship. Some vendiamorphs (e.g., ''Vendia'' and ''Paravendia'') supposedly demonstrate a digestive-distributive sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, near-bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as ''Dickinsonia'', '' Vendia'', '' Cephalonega'', '' Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
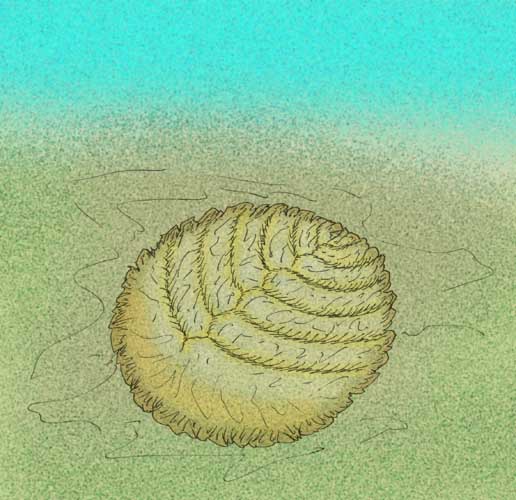
Karakhtia
''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a species of Proarticulate from the Ediacaran period, around 555 Million Years Ago. K. nessovi is the only species in the genus ''Karakhtia''. The genus '' Haootia'' has been compared minorly to ''Karakhtia'' in the way that the fossils of ''Haootia'' superficially resemble the crumpled margins of ''Karakhtia''. Discovery and name The holotype fossil of ''Karakhtia'' was found from the Ustʹ Pinega Formation, in the White Sea of Russia, and described in 2004. The generic name ''Karakhtia'' is derived from the place name ''Karakhta River'', near to where the fossil material was found. The specific name ''nessovi'' is derived from the surname of ''L.A. Nessov'', a Leningrad paleontologist. Description ''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a Proarticulate from the Vendiidae family, growing up to in length, and like other members of its family, it has a headshield-like structure. Unlike anything seen in other Proarticulates, it features a margin with radial fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, near-bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as ''Dickinsonia'', '' Vendia'', '' Cephalonega'', '' Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakhtia Nessovi
''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a species of Proarticulate from the Ediacaran period, around 555 Million Years Ago. K. nessovi is the only species in the genus ''Karakhtia''. The genus ''Haootia'' has been compared minorly to ''Karakhtia'' in the way that the fossils of ''Haootia'' superficially resemble the crumpled margins of ''Karakhtia''. Discovery and name The holotype fossil of ''Karakhtia'' was found from the Ustʹ Pinega Formation, in the White Sea of Russia, and described in 2004. The generic name ''Karakhtia'' is derived from the place name ''Karakhta River'', near to where the fossil material was found. The specific name ''nessovi'' is derived from the surname of ''L.A. Nessov'', a Leningrad paleontologist. Description ''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a Proarticulate from the Vendiidae family, growing up to in length, and like other members of its family, it has a headshield-like structure. Unlike anything seen in other Proarticulates, it features a margin with radial folds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paravendia
''Paravendia'' is an extinct genus of proarticulate vendiamorph that lived in the Ediacaran period, about 553 million years ago. It shares the Vendiidae family with ''Vendia'' and ''Karakhtia''. It is a monotypic genus, with the species ''Paravendia janae''. Description It is an animal that presents 'bilateral' symmetry, similar in appearance to the previously mentioned genus '' Vendia '', with new isomers replacing the older ones. Distribution Ediacaran of the Russian Federation (Arkhangelsk). See also *List of ediacaran genera The existence of life, especially that of animals, before the Cambrian had long been the subject of debate in paleontology. The apparent suddenness of the Cambrian explosion had no firm explanation, and Charles Darwin himself recognized the chal ... References Notes Zakrevskaya, Maria. Paleoecological reconstruction of the Ediacaran benthic macroscopic communities of the White Sea (Russia). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendia
''Vendia'' is an extinct vendiamorph from the late Ediacaran, estimated to be around 567 - 550 Ma years old, it contains two species, ''V. sokolovi'' and ''V. rachiata'', both of which are restricted to the Ust' Pinega Formation in Northwestern Russia. Discovery and naming The first fossil materials of ''Vendia'' were found in a core from a Yarensk borehole that was collected from the Ust' Pinega Formation of the Arkhangelsk Oblast, northwestern Russia in 1963,V. V. Menner. (1963). "The Other Problematical Organic Remains". In: "Stratigraphy of the USSR: Upper Precambrian" Gos. Nauchno-Tekh. Izd., Moscow. pp. 504-507. (In Russian) and was formally described and named in 1969 as ''Vendia sokolovi''.B. M. Keller. (1969). "Imprint of unknown animal from Valdai Series of Russian Platform". In: A. Y. Rozanov and et al. (Eds.), "Tommotian Stage and the Cambrian lower boundary problem". ''Geol. Inst. Trans''. Vol. 206, p. 175. (In Russian) A Further two species were found and named i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer (Proarticulata)
Isomer (Greek ''isos'' = "equal", ''méros'' = "part") is an element of transverse body articulation of the bilateral fossil animals of the Phylum Proarticulata from the Ediacaran (Vendian) period. This term has been proposed by Andrey Yu. Ivantsov, a Russian paleontologist from the Laboratory of the Precambrian organisms, Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences. Morphology Proarticulatan isomers are distinct from the segments of the Annelida and Panarthropoda, as each of these elements occupies only half of width of a body and are organized in an alternating pattern relatively to the axis of the body. In other words, although proarticulatans are bilaterally symmetrical, one side is not the direct mirror image of its opposite. Opposite isomers of left and right side are located with displacement of half of its width. This phenomenon is described as the symmetry of gliding reflection.M. A. Fedonkin (1985). "Systematic Description of Vendian Metazoa". In Sokolov, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudofossil
Pseudofossils are inorganic objects, markings, or impressions that might be mistaken for fossils. Pseudofossils may be misleading, as some types of mineral deposits can mimic lifeforms by forming what appear to be highly detailed or organized structures. One common example is when manganese oxides crystallize with a characteristic tree-like or dendritic pattern along a rock fracture. The formation of frost dendrites on a window is another common example of this crystal growth. Concretions are sometimes thought to be fossils, and occasionally one contains a fossil, but are generally not fossils themselves. Chert or flint nodules in limestone can often take forms that resemble fossils. Background Pyrite disks or spindles are sometimes mistaken for fossils of sand dollars or other forms (see marcasite). Cracks, bumps, gas bubbles, and such can be difficult to distinguish from true fossils. Specimens that cannot be attributed with certainty to either fossils or pseudofossils are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |