|
Vandal Kingdom
The Vandal Kingdom () or Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans () was a confederation of Vandals and Alans, which was a barbarian kingdoms, barbarian kingdom established under Gaiseric, a Vandals, Vandalic warlord. It ruled parts of North Africa and the Mediterranean for 99 years from 435 to 534 AD. In 429 AD, the Vandals, estimated to number 80,000 people, had crossed by boat from Hispania to North Africa. They advanced eastward, conquering the coastal regions of what is now Tunisia, and Algeria. In 435, the Western Roman Empire, then ruling North Africa, allowed the Vandals to settle in the provinces of Numidia (Roman province), Numidia and Mauretania Caesariensis, Mauretania when it became clear that the Vandal army could not be defeated by Roman military forces. In 439, the Vandals renewed their advance eastward and captured Carthage, the most important city of North Africa. The fledgling kingdom then conquered the Roman-ruled islands of Mallorca, Sicily, Sardinia, and Corsica in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandalic Conquest Of Roman Africa
The Vandal conquest of Roman Africa, also known as the Vandal conquest of North Africa, was the conquest of Mauretania Tingitana, Mauretania Caesariensis, and Africa Proconsolaris by the migrating Vandals and Alans. The conflict lasted 13 years with a period of four years of peace, and led to the establishment of the Vandal Kingdom in 435. Primary sources Saint Augustine of Hippo, Bishop Capreolus, Honoratus Antoninus, Prosper of Aquitaine, Theodoret, and Possidius wrote contemporary accounts of the Vandal invasion. Hydatius documented the Vandals' activities in the Iberian peninsula before crossing into Africa. ''Life of Augustine'' by Possidius was written before the Vandalic seizure of Carthage in 439. Victor Vitensis's ''A History of the African Province Persecution, in the Times of Genseric and Huneric, the Kings of the Vandals'' covered the Vandalic conquest and Roman counterattacks. Background The Roman Empire had been in a state of decline by the beginning of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaiseric
Gaiseric ( – 25 January 477), also known as Geiseric or Genseric (; reconstructed Vandalic: ) was king of the Vandals and Alans from 428 to 477. He ruled over a kingdom and played a key role in the decline of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century. The murder of Roman Emperor Valentinian III, who had betrothed his daughter to Gaiseric's son Huneric, led the Vandal king to invade Italy. The invasion culminated in his most famous exploit, the capture and plundering of Rome in June 455. Gaiseric repulsed two major attempts by both halves of the Roman Empire to reclaim North Africa, inflicting devastating defeats on the forces of Majorian in 460 and Basiliscus in 468. As a result, the Romans abandoned their campaign against the Vandals and concluded peace with Gaiseric. Gaiseric died in Carthage in 477 and was succeeded by his son, Huneric. Through his nearly fifty years of rule, Gaiseric raised a relatively inconsequential Germanic tribe to the status of a major Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares maritime borders with Italy through the islands of Sicily and Sardinia to the north and Malta to the east. It features the archaeological sites of Carthage dating back to the 9th century BC, as well as the Great Mosque of Kairouan. Known for its ancient architecture, Souks of Tunis, souks, and blue coasts, it covers , and has a population of 12.1 million. It contains the eastern end of the Atlas Mountains and the northern reaches of the Sahara desert; much of its remaining territory is arable land. Its of coastline includes the African conjunction of the western and eastern parts of the Mediterranean Basin. Tunisia is home to Africa's northernmost point, Cape Angela. Located on the northeastern coast, Tunis is the capital and List of cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western part of Tarraconensis was split off, initially as Hispania Nova, which was later renamed "Callaecia" (or Gallaecia, whence modern Galicia (Spain), Galicia). From Diocletian's Tetrarchy (AD 293) onwards, the south of the remainder of Tarraconensis was again split off as Hispania Carthaginensis, Carthaginensis, and all of the mainland Hispanic provinces, along with the Hispania Balearica, Balearic Islands and the North African province of Mauretania Tingitana, were later grouped into a Roman diocese, civil diocese headed by a ''vicarius''. The name Hispania was also used in the period of Visigothic Kingdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of the Western Sahara in the west, to Egypt and Sudan's Red Sea coast in the east. The most common definition for the region's boundaries includes Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Tunisia, and Western Sahara, the territory territorial dispute, disputed between Morocco and the list of states with limited recognition, partially recognized Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. The United Nations’ definition includes all these countries as well as Sudan. The African Union defines the region similarly, only differing from the UN in excluding the Sudan and including Mauritania. The Sahel, south of the Sahara, Sahara Desert, can be considered as the southern boundary of North Africa. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarian Kingdoms
The barbarian kingdoms were states founded by various non-Roman, primarily Germanic, peoples in Western Europe and North Africa following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century CE. The barbarian kingdoms were the principal governments in Western Europe in the Early Middle Ages. The time of the barbarian kingdoms is considered to have come to an end with Charlemagne's coronation as emperor in 800, though a handful of small Anglo-Saxon kingdoms persisted until being unified by Alfred the Great in 886. The formation of the barbarian kingdoms was a complicated, gradual, and largely unintentional process. Their origin can be traced to the Roman state failing to handle barbarian migrants on the imperial borders, which led to both invasions and invitations into imperial territory from the 3rd century onwards. Despite an increasing influx of barbarians, the Romans simultaneously denied them the ability to properly integrate into the imperial framework. Barbaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
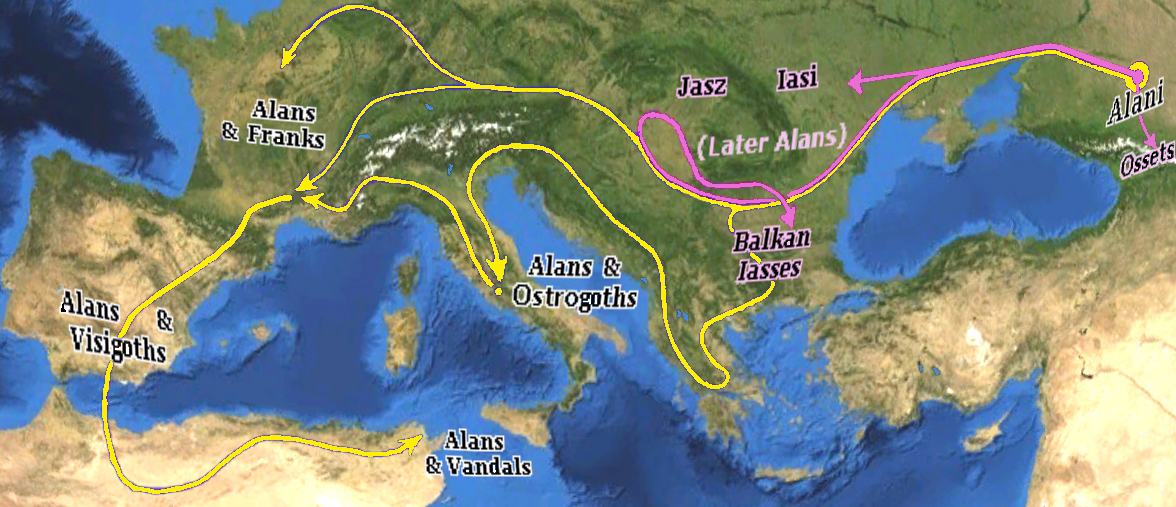
Alans
The Alans () were an ancient and medieval Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, nomadic pastoral people who migrated to what is today North Caucasus – while some continued on to Europe and later North Africa. They are generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of China, Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Ancient Rome, Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the South Caucasus provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe, thereby assimilating a sizeable portion of the associated Alans. Upon the Huns, Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal kingdoms first within the Iberian Peninsula, and then in the western Mediterranean islands, and North Africa. Archaeologists associate the early Vandals with the Przeworsk culture, which has led to some authors equating them to the Lugii, who were another group of Germanic peoples associated with that same archaeological culture and region. Expanding into Dacia during the Marcomannic Wars and to Pannonia during the Crisis of the Third Century, the Vandals were confined to Pannonia by the Goths around 330 AD, where they received permission to settle from Constantine the Great. Around 400, raids by the Huns from the east forced many Germanic tribes to migrate west into the territory of the Roman Empire and, fearing that they might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by fixed laws. Kings are Hereditary monarchy, hereditary monarchs when they inherit power by birthright and Elective monarchy, elective monarchs when chosen to ascend the throne. *In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the title may refer to tribal kingship. Germanic kingship is cognate with Indo-European languages, Indo-European traditions of tribal rulership (cf. Indic ''rājan'', Gothic ''reiks'', and Old Irish ''rí'', etc.). *In the context of classical antiquity, king may translate in Latin as ''rex (king), rex'' and in Greek as ''archon'' or ''basileus''. *In classical European feudalism, the title of ''king'' as the ruler of a ''kingdom'' is und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelimer
Gelimer (original form possibly Geilamir, 480–553), was a Germanic king who ruled the Vandal Kingdom in antique North Africa from 530 to 534. He became ruler on 15 June 530 after deposing his first cousin twice removed, Hilderic, who had angered the Vandal nobility by converting to Chalcedonian Christianity; most Vandals at the time were fierce Arian Christians. The Eastern Roman Emperor Justinian I, who had supported Hilderic, soon declared war on the Vandals, ostensibly to restore Hilderic. In June 533, Justinian sent an expeditionary force commanded by Belisarius which finally reached Africa in the beginning of September. Meanwhile, in Sardinia, which formed part of the Vandal domain, the governor Godas, a Goth, revolted against Gelimer and began to treat with Justinian as an independent sovereign. Gelimer, ignorant or contemptuous of Justinian's plans, sent a large army consisting of most of the available army in Africa under his brother Tzazo to crush the rebell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilderic
Hilderic (460s – 533) was the penultimate king of the Vandals and Alans in North Africa in Late Antiquity (523–530). Although dead by the time the Vandal Kingdom was overthrown in 534, he nevertheless played a key role in that event. Life Hilderic was the grandson of king Genseric, founder of the Vandal kingdom in Africa. His father was Genseric's son Huneric, and his mother was Eudocia, the daughter of the Roman Emperor Valentinian III and Licinia Eudoxia. Most of the Vandals were Arians and had persecuted Chalcedonians, but Hilderic favored Chalcedonianism as the religion of his mother, making his accession to the throne controversial. Soon after becoming king, Hilderic had his predecessor's widow, Amalafrida, imprisoned; he escaped war with her brother, the Gothic king Theoderic the Great, only by virtue of the latter's death in 526. Hilderic's reign was noteworthy for the kingdom's excellent relations with the Eastern Roman Empire. Procopius writes that he was " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |