|
Vanadyl Compounds
The vanadyl or oxovanadium(IV) ion, cation, VO2+, is a functional group that is common in the coordination chemistry of vanadium. Complexes containing this functional group are characteristically blue and paramagnetic. A triple bond is proposed to exist between the V4+ and O2− centers. The description of the bonding in the vanadyl ion was central to the development of modern Ligand field theory, ligand-field theory. Natural occurrence Minerals Cavansite and pentagonite are vanadyl-containing minerals. Water VO2+, often in an ionic pairing with sodium (NaH2VO4), is the second most abundant transition metal in seawater, with its concentration only being exceeded by molybdenum. In the ocean the average concentration is 30 Molar concentration#Units, nM. Some mineral water Spring (hydrology), springs also contain the ion in high concentrations. For example, springs near Mount Fuji often contain as much as 54 Microgram, μg per liter. Vanadyl containing compounds Oxovan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pervanadyl
Pervanadyl is jargon that has two meanings. *Pervanadyl can refer to aquo complexes containing (). This pale yellow oxycation of vanadium(V) is the predominant vanadium(V) species in acidic solutions with pH between 0 and 2. Like permanganate, pervanadate features the metal in its highest oxidation state. *Pervanadyl also can refer to peroxo derivatives of vanadium(V) which are often abbreviated . Several vanadium(V) peroxides have been characterized. The former are formed by protonation of vanadium(V) oxide in such solutions: : (''Equilibrium constant, K'' = ) The ion can form a complex with a single aminopolycarboxylate ligand, or with tridentate Schiff base ligands. The / redox couple is used at the cathode of the vanadium redox battery. The standard reduction potential of this couple is +1.00 V. See also * Vanadate References {{Vanadium compounds Vanadyl compounds Vanadium(V) compounds Oxycations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
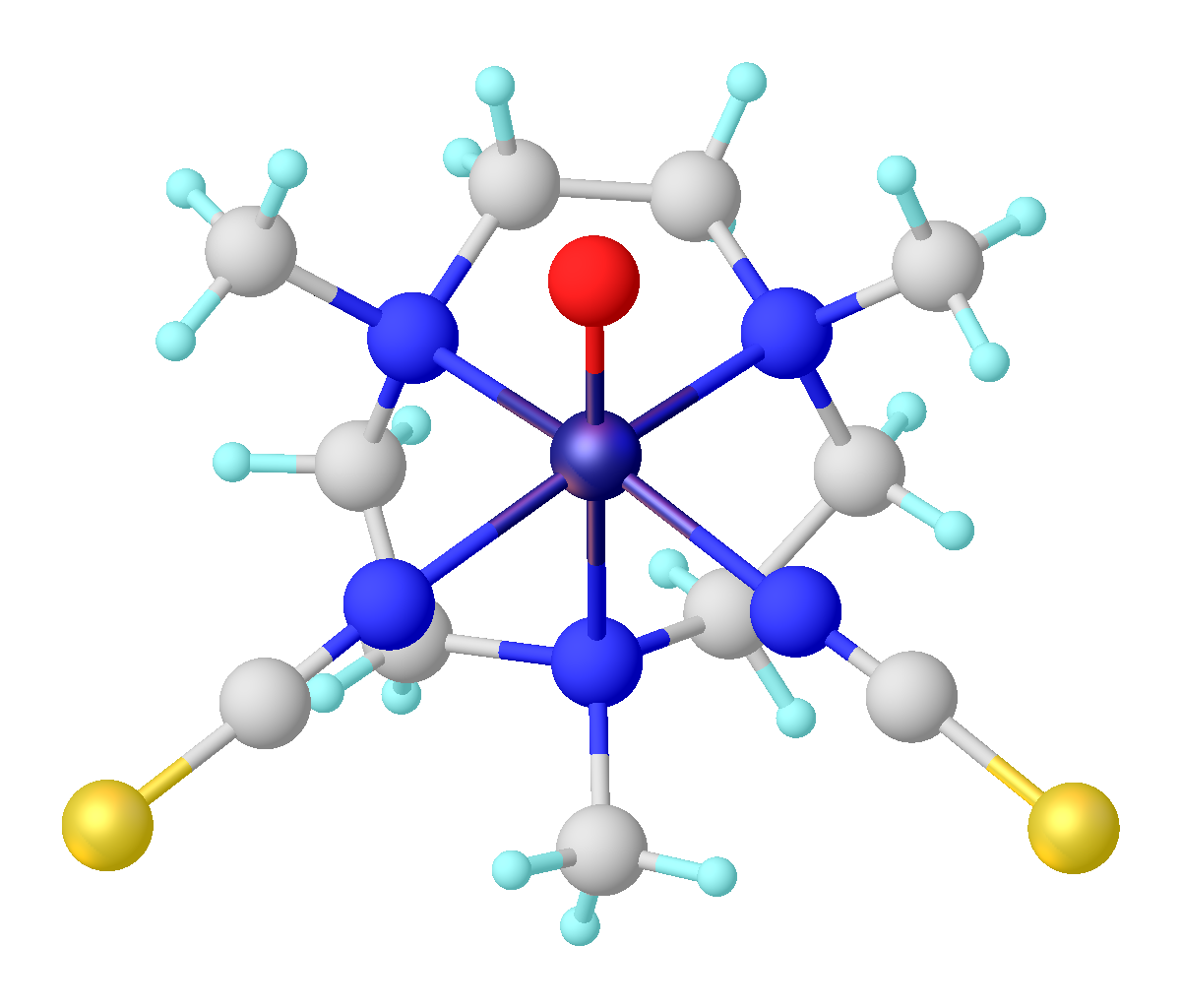
Vanadyl Acetylacetonate
Vanadyl acetylacetonate is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula VO(acac)2, where acac– is the conjugate base of acetylacetone. It is a blue-green solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents. The complex (chemistry), coordination complex consists of the vanadyl ion, vanadyl group, VO2+, bound to two acac– ligands via the two oxygen atoms on each. Like other charge-neutral acetylacetonate complexes, it is not soluble in water. Synthesis The complex is generally prepared from vanadium(IV), e.g. vanadyl sulfate: :VOSO4 + 2 Hacac → VO(acac)2 + H2SO4 It can also be prepared by a redox reaction starting with vanadium pentoxide. In this reaction, some acetylacetone is oxidized to 2,3,4-Pentanetrione. Structure and properties The complex has a square pyramidal structure with a short V=O bond. This d1 compound is paramagnetic. Its optical spectrum exhibits two transitions. It is a weak Lewis acid, forming adducts with pyridine and methylamine. Applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanyl
In inorganic chemistry, titanyl refers to the functional group TiIVO, sometimes written TiO2+. The term titanyl is used loosely to describe many titanium(IV) oxide compounds and complexes. For example, titanyl sulfate and potassium titanyl phosphate contain TiIVO centers with the connectivity O-Ti-O-Ti. In heterogeneous catalysis Heterogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the Phase (matter), phase of catalysts differs from that of the reagents or product (chemistry), products. The process contrasts with homogeneous catalysis where the reagents, products and catalyst exis ..., titanyl refers to a terminal oxo ligand on a surface titanium(IV) center.{{cite journal, title=The Role of Synchrotron-Based Studies in the Elucidation and Design of Active Sites in Titanium−Silica Epoxidation Catalysts, author=John Meurig Thomas , author2=Gopinathan Sankar , journal=Accounts of Chemical Research, year=2001, volume=34, pages=571–581, doi=10.1021/ar010003w There are a few molecular ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthovanadate
In chemistry, a vanadate is an anionic coordination complex of vanadium. Often vanadate refers to oxoanions of vanadium, most of which exist in its highest oxidation state of +5. The complexes and are referred to as hexacyanovanadate(III) and nonachlorodivanadate(III), respectively. A simple vanadate ion is the tetrahedral orthovanadate anion, (which is also called vanadate(V)), which is present in e.g. sodium orthovanadate and in solutions of in strong base ( pH > 13). Conventionally this ion is represented with a single double bond, however this is a resonance form as the ion is a regular tetrahedron with four equivalent oxygen atoms. Additionally a range of polyoxovanadate ions exist which include discrete ions and "infinite" polymeric ions. There are also vanadates, such as rhodium vanadate, , which has a statistical rutile structure where the and ions randomly occupy the positions in the rutile lattice, that do not contain a lattice of cations and balancin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Chloride
Vanadium oxytrichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula VOCl3. This yellow distillable liquid hydrolyzes readily in air. It is an oxidizing agent. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis. Samples often appear red or orange owing to an impurity of vanadium tetrachloride. Properties VOCl3 is a vanadium compound with vanadium in the +5 oxidation state and as such is diamagnetic. It is tetrahedral with O-V-Cl bond angles of 111° and Cl-V-Cl bond angles of 108°. The V-O and V-Cl bond lengths are 157 and 214 pm, respectively. VOCl3 is highly reactive toward water and evolves HCl upon standing. It is soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene, CH2Cl2, and hexane. In some aspects, the chemical properties of VOCl3 and POCl3 are similar. One distinction is that VOCl3 is a strong oxidizing agent, whereas the phosphorus compound is not. Neat VOCl3 is the usual chemical shift standard for 51V NMR spectroscopy. Preparation VOCl3 arises by the chlorination of V2O5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Fluoride
Vanadium(V) oxytrifluoride is a chemical compound with the formula V O F3. It is one of several vanadium(V) oxyhalides. VOF3 is a yellowish orange powder that is sensitive to moisture. Characteristic of early metal fluorides, the structure is polymeric in the solid state. The solid adopts a layered structure but upon evaporation, the species becomes dimeric. In contrast VOCl3 and VOBr3 remain tetrahedral in all states, being volatile liquids at room temperature. Reactions In organic synthesis, VOF3 is used for the oxidative coupling of phenols, for example in the syntheses of vancomycin and its analogues. For these applications VOF3 is typically dissolved in trifluoroacetic acid. Vanadium(V) oxytrifluoride reacts with hexamethyldisiloxane Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO or MM) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O i(CH3)3. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Perchlorate
Vanadyl perchlorate or vanadyl triperchlorate is a golden yellow coloured liquid or crystalline compound of vanadium, oxygen and perchlorate group. The substance consists of molecules covalently bound and is quite volatile; it ignites organic solvents on contact and explodes at temperatures above 80 °C. Formation Vanadyl perchlorate can be made by reacting vanadium pentoxide with dichlorine heptoxide at 5 °C. It is purified by distillation under a vacuum and recrystallisation at 21 °C. A solution of vanadium(V) perchlorate can be made by dissolving vanadium pentoxide in perchloric acid. The reaction of vanadium pentoxide and dichlorine hexoxide Dichlorine hexoxide is the chemical compound with the molecular formula or , which is correct for its gaseous state. However, in liquid or solid form, this chlorine oxide ionizes into the dark red ionic compound chloryl perchlorate or dioxochlor ... could produce VO(ClO4)3: : 2 V2O5 + 12 Cl2O6 → 4 VO(ClO4)3 + 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadyl Nitrate
Vanadyl nitrate, also called vanadium oxytrinitrate or vanadium oxynitrate is an inorganic compound of vanadium in the +5 oxidation state with nitrate ligands and oxygen. The formula is VO(NO3)3. It is a pale yellow viscous liquid. Production It is made by soaking vanadium pentoxide in liquid dinitrogen pentoxide for durations around two days at room temperature. The yield for this method is about 85%. :V2O5 + 3 N2O5 → 2 VO(NO3)3. Purification can be achieved by vacuum distillation. Mononitratodioxovanadium (VO2NO3) is an intermediate in this synthesis. It is a brick red solid. Vanadyl nitrate can also be made from vanadyl trichloride VOCl3 and dinitrogen pentoxide. Structure VO(NO3)3 has a distorted pentagonal bipyramid shape with idealized Cs (mirror) symmetry. The vanadium oxygen bond (157.2 pm) is typical for vanadyl(V). Two nitrate groups in the pentagonal plane are bidentate (V-O distances range from 199 to 206 pm). The third nitrate spans the pentagonal plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropyl
In organic chemistry, a propyl group is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr (not to be confused with the element praseodymium). An isomeric form of propyl is obtained by moving the point of attachment from a terminal carbon atom to the central carbon atom, named isopropyl or 1-methylethyl. To maintain four substituents on each carbon atom, one hydrogen atom has to be moved from the middle carbon atom to the carbon atom which served as attachment point in the ''n''-propyl variant, written as . Linear propyl is sometimes termed normal and hence written with a prefix ''n''- (i.e., ''n-''propyl), as the absence of the prefix ''n''- does not indicate which attachment point is chosen, i.e. absence of prefix does not automatically exclude the possibility of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |