|
Tryptamines
Substituted tryptamines, or simply tryptamines, also known as serotonin analogues (i.e., 5-hydroxytryptamine analogues), are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino group, amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) side chain, sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and dimethyltryptamine, DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine Rests General Formula V
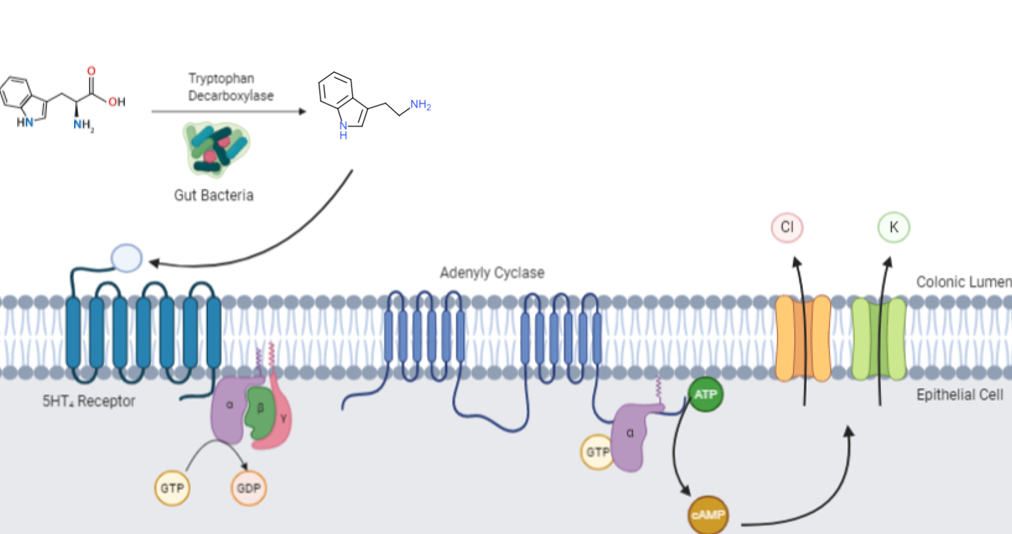
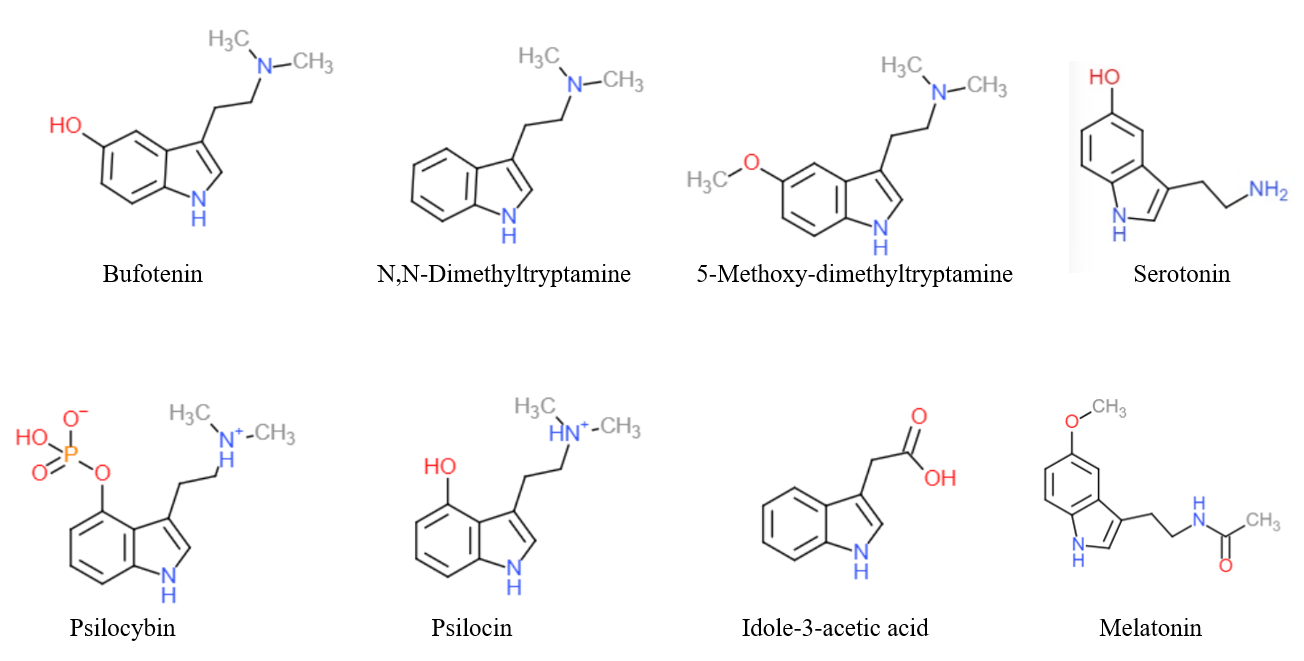
Tryptamine is an Indolamines, indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic Neuromodulation, neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and List of naturally occurring tryptamines, others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate serotonin receptors and trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of Dopaminergic pathways, dopaminergic, Serotonin pathway, serotonergic and Glutamic acid, glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptor, 5-HT4 receptors and reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine Structure
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate serotonin receptors and trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic Drug
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary mental states (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips") and a perceived "expansion of consciousness". Also referred to as classic hallucinogens or serotonergic hallucinogens, the term ''psychedelic'' is sometimes used more broadly to include various other types of hallucinogens as well, such as those which are atypical or adjacent to psychedelia like salvia and MDMA, respectively. Classic psychedelics generally cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and oftentimes a substantially altered state of consciousness. They have had the largest influence on science and culture, and include mescaline, LSD, psilocybin, and DMT. There are a large number of both naturally occurring and synthetic serotonergic psychedelics. Most psychedelic drugs fall into one of the three families of chemical compounds: tryptamines, phenethylamines, or lysergamides. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate serotonin receptors and trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyltryptamine
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT), also known as ''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (''N'',''N''-DMT), is a Psychedelic drug, serotonergic hallucinogen and Investigational New Drug, investigational drug of the substituted tryptamine, tryptamine family that natural product, occurs naturally in many plants and animals, including humans. DMT is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen. DMT has a rapid onset of action, onset, intense effects, and a relatively short duration of action. For those reasons, DMT was known as the "businessman's trip" during the 1960s in the United States, as a user could access the full depth of a psychedelic experience in considerably less time than with other substances such as Lysergic acid diethylamide, LSD or psilocybin mushrooms. DMT can be inhaled or injected and its effects depend on the dose, as well as the mode of administration. When inhaled or injected, the effects last about five to fifteen minutes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin Mushroom
Psilocybin mushrooms, or psilocybin-containing mushrooms, commonly known as magic mushrooms or as shrooms, are a type of hallucinogenic mushroom and a polyphyletic informal group of fungi that contain the prodrug psilocybin, which turns into the psychedelic psilocin upon ingestion. The most potent species are members of genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from approximately a dozen other genera, including '' Panaeolus'' (including '' Copelandia''), '' Inocybe'', '' Pluteus'', ''Gymnopilus'', and '' Pholiotina''. Amongst other cultural applications, psilocybin mushrooms are used as recreational drugs. They may be depicted in Stone Age rock art in Africa and Europe, but are more certainly represented in sculptures and glyphs seen throughout the Americas. Indoor cultivation '' Psilocybe cubensis'' grows naturally in tropical and subtropical conditions, often near ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin
Psilocybin, also known as 4-phosphoryloxy-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine (4-PO-DMT), is a natural product, naturally occurring tryptamine alkaloid and Investigational New Drug, investigational drug found in more than List of psilocybin mushroom species, 200 species of mushrooms, with Hallucinogen, hallucinogenic and Serotonin, serotonergic effects. Effects include euphoria, changes in perception, a distorted sense of time (via brain desynchronization), and perceived spiritual experiences. It can also cause adverse reactions such as nausea and panic attacks. Its effects depend on set and setting and one's subject-expectancy effect, expectations. Psilocybin is a prodrug of psilocin. That is, the compound itself is biologically inactive but quickly converted by the body to psilocin. Psilocybin is transformed into psilocin by dephosphorylation mediated via phosphatase enzymes. Psilocin is structural analog, chemically related to the neurotransmitter serotonin and acts as a binding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Shulgin
Alexander Theodore "Sasha" Shulgin (June 17, 1925 – June 2, 2014) was an American biochemist, broad researcher of synthetic psychoactive compounds, and author of works regarding these, who independently explored the organic chemistry and pharmacology of such agents—in his mid-life and later, many through preparation in his home laboratory, and testing on himself. He is acknowledged to have introduced to broader use, in the late 1970s, the previously-synthesized compound MDMA ("ecstasy"), in research psychopharmacology and in combination with conventional therapy, the latter through presentations and academic publications, including to psychologists; and for the rediscovery, occasional discovery, and regular synthesis and personal use and distribution, of possibly hundreds of Psychoactive drug, psychoactive compounds (for their Psychedelic drug, psychedelic and MDMA-like empathogenic bioactivity, bioactivities). As such, Shulgin is seen both as a pioneering and a controversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yohimbine
Yohimbine, also known as quebrachine, is an indole alkaloid derived from the bark of the African tree '' Pausinystalia johimbe'' (yohimbe); also from the bark of the unrelated South American tree '' Aspidosperma quebracho-blanco''. Yohimbine is an α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist, and has been used in a variety of research projects. It is a veterinary drug used to reverse sedation in dogs and deer. While yohimbine behaves as an aphrodisiac in some mammals, it does not do so in humans. It has been prescribed as a treatment for erectile dysfunction, although its reported clinical benefits were modest and it has largely been superseded by the PDE5 inhibitor class of drugs. Substances that have purported to be extracts from the yohimbe tree have been marketed as dietary supplements for various purposes, but they contain highly variable amounts of yohimbine, if any; no published scientific evidence supports their efficacy. Uses Sexual dysfunction and aphrodisiac Yohimbe extracts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
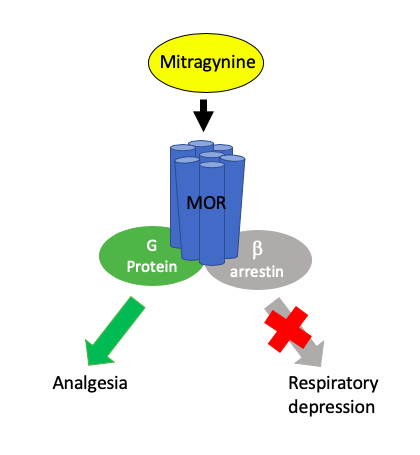
Mitragynine
Mitragynine is an indole-based alkaloid and is one of the main Psychoactive drug, psychoactive constituents in the Southeast Asian plant ''Mitragyna speciosa'', commonly known as kratom. It is an atypical opioid that is typically consumed as a part of kratom for its Analgesic, pain-relieving and Euphoria, euphoric effects. It has also been researched for its use to potentially manage symptoms of opioid withdrawal. Mitragynine is the most abundant active alkaloid in kratom. In Thai varieties of kratom, mitragynine is the most abundant component (up to 66% of total alkaloids), while 7-Hydroxymitragynine, 7-hydroxymitragynine (7-OH) is a minor constituent (up to 2% of total alkaloid content). In Malaysian kratom varieties, mitragynine is present at lower concentration (12% of total alkaloids). Total alkaloid concentration in dried leaves ranges from 0.5 to 1.5%. Such preparations are Oral administration, orally consumed and typically involve dried kratom leaves which are brewed into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibogaine
Ibogaine is a psychoactive indole alkaloid derived from plants such as '' Tabernanthe iboga'', characterized by hallucinogenic and oneirogenic effects. Traditionally used by Central African foragers, it has undergone controversial research for the treatment of substance use disorders. Ibogaine exhibits complex pharmacology by interacting with multiple neurotransmitter systems, notably affecting opioid, serotonin, sigma, and NMDA receptors, while its metabolite noribogaine primarily acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and κ-opioid receptor agonist. The psychoactivity of the root bark of the iboga tree, ''T. iboga'', one of the plants from which ibogaine is extracted, was first discovered by forager tribes in Central Africa, who passed the knowledge to the Bwiti tribe of Gabon. It was first documented in the 19th century for its spiritual use, later isolated and synthesized for its psychoactive properties, briefly marketed in Europe as a stimulant, and ultimately rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |