|
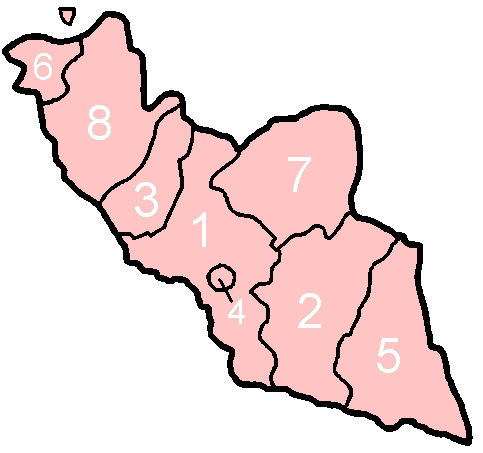
Tovuz District
Tovuz District () is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the north-west of the country and belongs to the Gazakh-Tovuz Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Gadabay, Shamkir, Samukh, Agstafa, as well as the Tavush Province of Armenia and Kakheti region of Georgia. Its capital and largest city is Tovuz. As of 2020, the district had a population of 177,200. A major train line runs through the center, stopping at Tovuz Station. In July 2020, Tovuz became the main site for the clashes with Armenia. Geography Tovuz covers 412 km2. The rayon is mountainous in the south, where it is crossed by the Lesser Caucasus mountains.Azerbaijan Development Gateway concerning both the District and the town The region includes rich deposits of ores and precious meta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 67 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these districts and cities, 7 districts and 1 city are located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into Municipalities of Azerbaijan, municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic regions of Azerbaijan, Economic Regions (). On 7 July 2021, President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed a decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The list below represents the districts of contiguous Azerbaijan. For those of the Nakhchivan exclave, see further below. Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic The seven districts and one municipality of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic are listed below. Economic regions Nagorno-Karabakh The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakheti
Kakheti (; ) is a region of Georgia. Telavi is its administrative center. The region comprises eight administrative districts: Telavi, Gurjaani, Qvareli, Sagarejo, Dedoplistsqaro, Signagi, Lagodekhi and Akhmeta. Kakhetians speak the Kakhetian dialect of Georgian. Kakheti is one of the most significant wine producing regions of Georgia, home to a number of Georgian wines. The region is bordered to the west by the Georgian regions of Mtskheta-Mtianeti and Kvemo Kartli, to the north and east by the Russian Federation, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. Popular tourist attractions in Kakheti include Tusheti, Gremi, Signagi, Kvetera, Bodbe, Lagodekhi Protected Areas and Alaverdi Monastery. The Georgian David Gareji monastery complex is partially located in this province and is subject to a border dispute between Georgian and Azerbaijani authorities. Geography Beyond the modern-day administrative subdivision into the districts, Kakheti has traditionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijani Armed Forces
The Azerbaijani Armed Forces () is the military of the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. It was re-established according to the country's Law of the Armed Forces on 9 October 1991. The original Azerbaijan Democratic Republic's armed forces were dissolved after Azerbaijan was absorbed into the Soviet Union as the Azerbaijan Soviet Socialist Republic from 28 April 1920. After the Soviet Union dissolved in 1991–92, Azerbaijan's armed forces were reformed based on the Soviet bases and equipment left on Azerbaijani soil. The armed forces have three branches: the Azerbaijani Land Forces, the Azerbaijani Air Forces and the Azerbaijani Navy. Associated forces include the Azerbaijani National Guard, the Internal Troops of Azerbaijan, and the State Border Service of Azerbaijan, State Border Service, which can be involved in state defense under certain circumstances. According to the Azerbaijani media sources, the military expenditure of Azerbaijan for 2009 was set at US$2.46 billi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijani Ministry Of Defense
The Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Azerbaijan () or MN is an Azerbaijani government agency that is associated with the Azerbaijani military. The ministry is responsible for keeping Azerbaijan defended against external threats, preserving its territorial integrity, waging war on behalf of Azerbaijan (for example, Azerbaijan's contribution to the War on Terror), and the surveillance of the Azerbaijani sector of the Caspian Sea sea and airspace. The Minister of Defence is appointed and removed from the post by the Commander-in-chief of the Azerbaijani Armed Forces, the President of Azerbaijan. The ministry building is located in Baku, at 3 Parliament Avenue. History The first defence minister of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic was General Khosrov bey Sultanov, who was appointed on 28 May 1918. In accordance with the Action Plan approved by Parliament on formation of the army, important structures and divisions were to be established by 1 November 1919. Within the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuqbulaq, Agstafa
Soyuqbulaq (also, Soyuq Bulaq) is a village in the Agstafa Rayon of Azerbaijan. It forms part of the municipality of Köçvəlili. In 2006, a French–Azerbaijani team discovered nine kurgans at the cemetery of Soyuqbulaq. They were dated to the beginning of the fourth millennium BC, which makes it the oldest kurgan cemetery in Transcaucasia. Similar kurgans have been found at Kavtiskhevi, Kaspi Municipality, in central Georgia. Several other archaeological sites seem to belong to the same ancient cultural tradition as Soyuq Bulaq. They include Berikldeebi, Kavtiskhevi, Leilatepe, Boyuk Kesik, and Poylu, Agstafa, and are characterized by pottery assemblages "mainly or totally in the North Mesopotamian tradition". Discoveries The numerous artifacts discovered at these sites have shed light on the material and spiritual culture of this ancient people during the late Eneolithic period. Amongst the finds are stone and bone tools, metal objects, and a huge cache of clay vessels. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shomu Tepe
Shomu-tepe (Şomutəpə) is an ancient settlement in the Agstafa District of Azerbaijan. The Neolithic Shulaveri-Shomu culture that formed in the Southern Caucasus is connected with the name of this monument. The settlement is located in the northern suburb of the modern city of Agstafa. Research During the 1960s, I. G. Narimanov, was the first to recognize a new culture that he named 'Shomu', after he excavated this site on the outskirts of Agstafa. This is now known as Shulaveri-Shomu culture. In 1961–1964, he carried out research in the area of 400 square meters in the residential area of Agstafa. Settlement The thickness of the cultural level at the settlement varies from 1 to 2.5 m. The inhabitants of Shomutape lived in small round houses built of unbaked plano-convex bricks. The ceiling of the house was supported by a pole buried in the floor. Houses had one and sometimes two entrances. The maximum diameter of these residential buildings was 3.7 m. Later, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kura (Caspian Sea)
The Kura, also known in Georgian as Mtkvari ( ), is an east-flowing transboundary river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus, while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, the Kura flows through to Georgia, then into Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and finally enters the Caspian Sea. The total length of the river is . People have inhabited the Caucasus region for thousands of years and first established agriculture in the Kura Valley over 4,500 years ago. Large, complex civilizations eventually grew on the river, but by 1200 CE most were reduced to ruin by natural disasters and foreign invaders. The increasing human use, and eventual damage, of the watershed's forests and grasslands, contributed to a rising intensity of floods through the 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aşağı Quşçu
Aşağı Quşçu (also, Ashaghy Gushchu) is a village and municipality in the Tovuz District of Azerbaijan Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by .... It has a population of 8,702. References * Populated places in Tovuz District {{Tovuz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Caucasus
The Lesser Caucasus or Lesser Caucasus Mountains, also called Caucasus Minor, is the second of the two main ranges of the Caucasus Mountains, of length about . The western portion of the Lesser Caucasus overlaps and converges with east Turkey and northwest Iran. It runs parallel to the Greater Caucasus, at a distance averaging about south from the Likhi Range (Georgia), and limits east Turkey from the north and north-east. It is connected with the Pontic range and separated from it by the Kolkhida Lowland (Georgia) in the west and Kura-Aras Lowland (Azerbaijan) (by the Kura River) in the east. Description The highest peak is Aragats in Armenia, . The borders between Georgia, Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Iran run through the range, although its crest does not usually define the border. The range was historically called ''Anticaucasus'' or ''Anti-Caucasus'' (Greek: Αντι-Καύκασος, Russian: Антикавка́з, Анти-Кавка́з). This usage is comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |