|
Thirteen Classics
The Thirteen Classics () is a term for the group of thirteen classics of Confucian tradition that became the basis for the Imperial Examinations during the Song dynasty and have shaped much of East Asian culture and thought. It includes all of the Four Books and Five Classics but organizes them differently and includes the '' Classic of Filial Piety'' and '' Erya''. List The classics are: * '' Classic of Changes'' or ''I Ching'' (易經 ''Yìjīng'') * ''Book of Documents'' (書經 ''Shūjīng'') * ''Classic of Poetry'' (詩經 ''Shījīng'') * The Three Ritual Classics (三禮 ''Sānlǐ'') ** ''Rites of Zhou'' (周禮 ''Zhōulǐ'') ** '' Ceremonies and Rites'' (儀禮 ''Yílǐ'') ** ''Book of Rites'' (禮記 ''Lǐjì'') * The Three Commentaries on the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'' ** '' The Commentary of Zuo'' (左傳 ''Zuǒzhuàn'') ** '' The Commentary of Gongyang'' (公羊傳 ''Gōngyáng Zhuàn'') ** '' The Commentary of Guliang'' (穀梁傳 ''Gǔliáng Zhuàn'') * '' The A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Classics
The Chinese classics or canonical texts are the works of Chinese literature authored prior to the establishment of the imperial Qin dynasty in 221 BC. Prominent examples include the Four Books and Five Classics in the Neo-Confucian tradition, themselves an abridgment of the Thirteen Classics. The Chinese classics used a form of written Chinese consciously imitated by later authors, now known as Classical Chinese. A common Chinese word for "classic" () literally means 'warp (weaving), warp thread', in reference to the techniques by which works of this period were bound into volumes. Texts may include ''shi'' (, 'Chinese historiography, histories') ''zi'' ( 'master texts'), Chinese philosophy, philosophical treatises usually associated with an individual and later systematized into schools of thought but also including works on agriculture, Traditional Chinese medicine, medicine, mathematics, Chinese astronomy, astronomy, divination, art criticism, and other miscellaneous wri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuo Zhuan
The ''Zuo Zhuan'' ( zh, t=左傳, w=Tso Chuan; ), often translated as ''The Zuo Tradition'' or as ''The Commentary of Zuo'', is an ancient Chinese narrative history traditionally regarded as a commentary on the ancient Chinese chronicle the '' Spring and Autumn Annals''. It comprises 30 chapters covering the period from 722 to 468BC, and focuses mainly on political, diplomatic, and military affairs from that era. For many centuries, the ''Zuo Zhuan'' was the primary text through which educated Chinese learned their ancient history. The ''Zuo Zhuan'' does not simply explain the wording of the ''Spring and Autumn Annals'', but rather expounds upon its historical background with rich and lively accounts of the history and culture of the Spring and Autumn period (771476 BC). The ''Zuo Zhuan'' is the source of more Chinese sayings and idioms than any other classical work, and its concise, flowing style served as a paragon of elegant Classical Chinese. Its tendency toward thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Classics
The Four Books and Five Classics are authoritative and important books associated with Confucianism, written before 300 BC. They are traditionally believed to have been either written, edited or commented by Confucius or one of his disciples. Starting in the Han dynasty, they became the core of the Chinese classics on which students were tested in the Imperial examination system. Four Books The Four Books () are Chinese classic texts illustrating the core value and belief systems in Confucianism. They were selected by intellectual Zhu Xi in the Song dynasty to serve as general introduction to Confucian thought, and they were, in the Ming and Qing dynasties, made the core of the official curriculum for the civil service examinations. More information of them are as follows: List ; ''Great Learning'' : Originally one chapter in the ''Book of Rites''. It consists of a short main text attributed to Confucius and nine commentary chapters by Zengzi, one of the disciples of Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng engaged in a Qin's wars of unification, series of wars conquering each of the rival states that had previously pledged fealty to the Zhou. This culminated in 221 BC with the successful unification of China under Qin, which then assumed an imperial prerogativewith Ying Zheng declaring himself to be Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China, and bringing an end to the Warring States period (221 BC). This state of affairs lasted until 206 BC, when the dynasty collapsed in the years following Qin Shi Huang's death. The Qin dynasty's 14-year existence was the shortest of any major dynasty in Chinese history, with only two emperors. However, the succeeding Han dynasty (202 BC220 AD) largely continued the military and administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Of Music
The ''Classic of Music'' () was a Confucian classic text lost by the time of the Han dynasty. It is sometimes referred to as the "Sixth Classic" (for example, by Sima Qian) and is thought to have been important in the traditional interpretations of the ''Classic of Poetry''. Qing dynasty scholar Shao Yichen ( 邵懿辰, 18101861) proposed that the book never existed, but more usually it is thought that all copies were destroyed during the burning of books and burying of scholars. A few traces remain in other surviving works, including the '' Zuo Zhuan'', the '' Rites of Zhou'', and the extremely redacted, poor-quality Record of Music contained in the '' Classic of Rites''. As accounted in the '' Book of Han'', Dou Gong 竇公 (5-4 cc. BC), a musician of the state of Wei possessed a copy of the ''Classic of Music'' which was presented to the Emperor Han Wen-di. However, the text is associated with the ''Dàsīyuè zhī zhí'' (大司樂之職) section of the ''Rites of Zhou,'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laozi
Laozi (), also romanized as Lao Tzu #Name, among other ways, was a semi-legendary Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher and author of the ''Tao Te Ching'' (''Laozi''), one of the foundational texts of Taoism alongside the ''Zhuangzi (book), Zhuangzi''. The name, literally meaning 'Old Master', was likely intended to portray an archaic anonymity that could converse with Confucianism. Modern scholarship generally regards his biographical details as later inventions, and his opus a collaboration. Traditional accounts addend him as , born in the 6th-centuryBC state of Chu during China's Spring and Autumn period (). Serving as the royal archivist for the Zhou dynasty, Zhou court at Wangcheng (Zhou dynasty), Wangcheng (modern Luoyang), he met and impressed Confucius () on one occasion, composing the ''Tao Te Ching'' in a single session before retiring into the western wilderness. A central figure in Chinese culture, Laozi is generally considered the founder of Taoism. He was cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
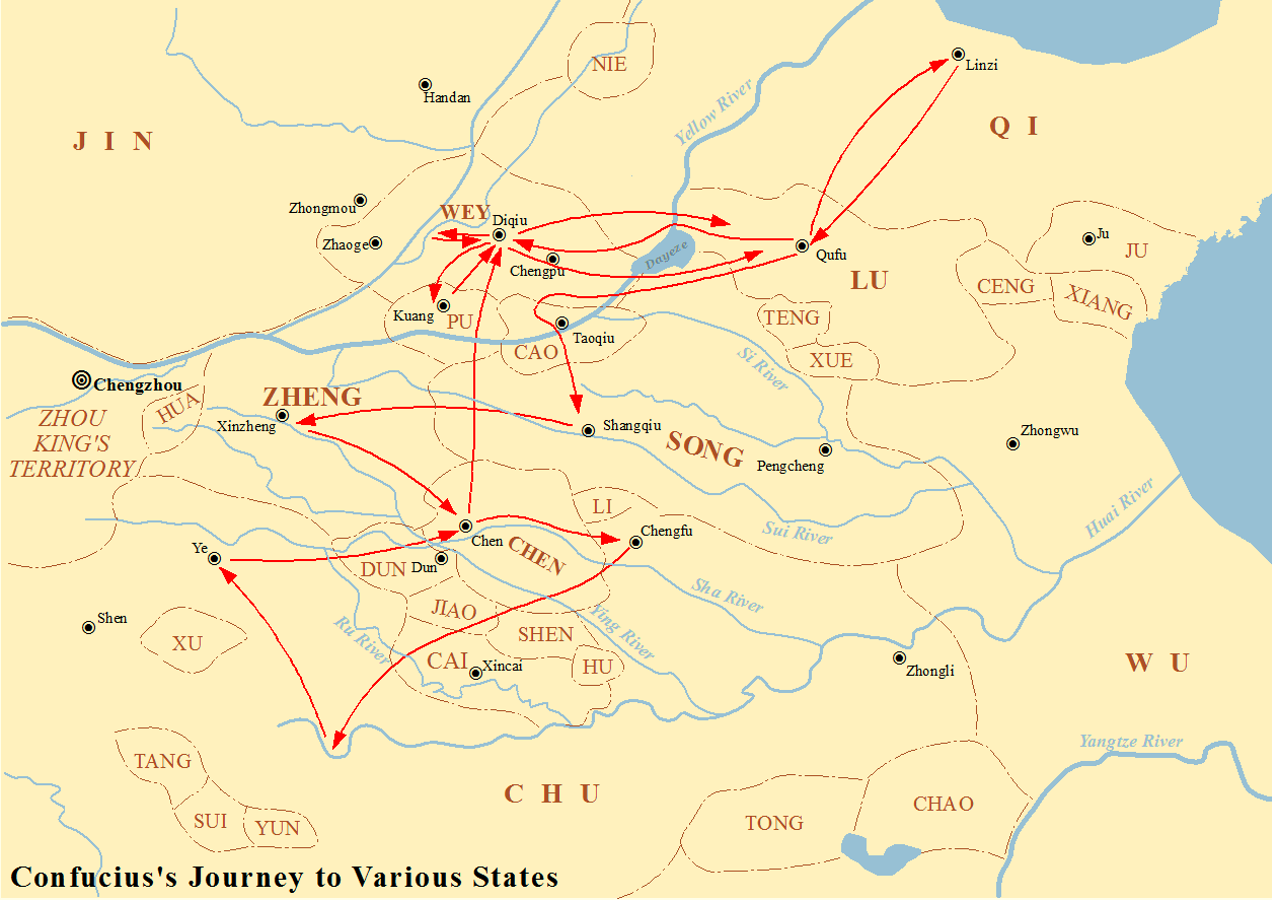
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuangzi (book)
The ''Zhuangzi'' (historically romanized ) is an ancient Chinese text that is one of the two foundational texts of Taoism, alongside the ''Tao Te Ching''. It was written during the late Warring States period (476–221 BC) and is named for its traditional author, Zhuang Zhou, who is customarily known as "Zhuangzi" ("Master Zhuang"). The ''Zhuangzi'' consists of stories and maxims that exemplify the nature of the ideal Taoist sage. It recounts many anecdotes, allegories, parables, and fables, often expressed with irreverence or humor. Recurring themes include embracing spontaneity and achieving freedom from the human world and its conventions. The text aims to illustrate the arbitrariness and false dichotomy, ultimate falsity of dichotomies normally embraced by human societies, such as those between good and bad, large and small, life and death, or human and nature. In contrast with the focus on good morals and personal duty expressed by many Chinese philosophers of the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and struggles for greater hegemonic influence among the ancient Chinese states, various autonomous feudal states of the Eastern Zhou dynasty. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the eventual unification of China by the western state of Qin (state), Qin under Qin Shi Huang, who Qin's wars of unification, conquered all other contender states by 221 BC and found the Qin dynasty, the first history of China#Imperial China, imperial dynasty in East Asian history. While scholars have identified several different dates as marking the beginning of the Warring States period, Sima Qian's choice of 475 BC, the first year of King Yuan of Zhou's reign, is the most often cited due to the paucity of preceding annals after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mencius (book)
The ''Mencius'' is an anthology of conversations and anecdotes attributed to the Confucian philosopher Mencius (). The book is one of the Chinese Thirteen Classics, and explores Mencius's views on the topics of moral and political philosophy, often as a dialogue with the ideas presented by Confucianism. The interviews and conversations are depicted as being either between Mencius and the various rulers of the Warring States period (221 BC), or with his students and other contemporaries. The book documents Mencius's travel across the states, and his philosophical conversations and debates with those he meets on his journey. A number of scholars suggest that the text was not written by Mencius himself, but rather by his disciples. The text is believed to have been written during the late 4th century BC. History Mencius's core ideas on education and human nature were largely shaped during the Warring States period. When the Zhou dynasty was ended by the Qin, Mencius and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiao Jing
The ''Classic of Filial Piety'', also known by its Chinese name as the ''Xiaojing'', is a Confucian classic treatise giving advice on filial piety: that is, how to behave towards a senior such as a father, an elder brother, or a ruler. The text was most likely written during the late Warring States period and early Han dynasty and claims to be a conversation between Confucius and his student Zengzi. The text was widely used during the Han and later dynasties to teach young children basic moral messages as they learned to read. Authorship The text dates from the 4th century BC to 3rd century BC. It is not known who actually wrote the document. It is attributed to a conversation between Confucius and his disciple Zengzi. A 12th-century author named He Yin claimed: "The ''Classic of Filial Piety'' was not made by Zengzi himself. When he retired from his conversation (or conversations) with Kung-ne on the subject of Filial Piety, he repeated to the disciples of his own school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |