|
Thermoproteota
The Thermoproteota are prokaryotes that have been classified as a phylum (biology), phylum of the domain Archaea. Initially, the Thermoproteota were thought to be sulfur-dependent extremophiles but recent studies have identified characteristic Thermoproteota environmental rRNA indicating the organisms may be the most abundant archaea in the marine environment. Originally, they were separated from the other archaea based on rRNA sequences; other physiological features, such as lack of histones, have supported this division, although some crenarchaea were found to have histones. Until 2005 all cultured Thermoproteota had been thermophilic or hyperthermophilic organisms, some of which have the ability to grow at up to 113 °C. These organisms stain Gram negative and are morphologically diverse, having rod, cocci, Filamentation, filamentous and oddly-shaped cells. Recent evidence shows that some members of the Thermoproteota are methanogens. Thermoproteota were initially classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even though the domain Archaea Cladistics, cladistically includes eukaryotes, the term "archaea" (: archaeon , from the Greek "ἀρχαῖον", which means ancient) in English still generally refers specifically to prokaryotic members of Archaea. Archaea were initially Taxonomy (biology), classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (, in the Archaebacteria Kingdom (biology), kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from Bacteria and Eukaryote, Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phylum, phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been Isolation (microbiology), isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their Gene, gene s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
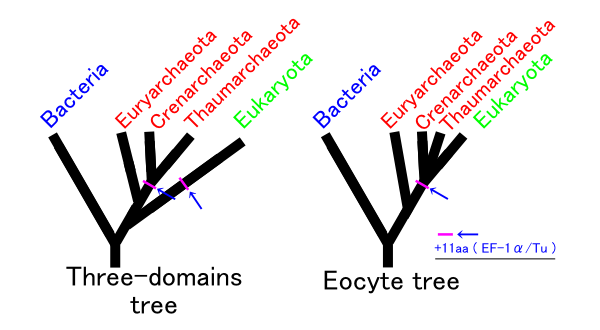
Eocyta
Thermoproteati is a kingdom of archaea. Its synonym, "TACK", is an acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic thermophiles to mesophiles and psychrophiles and with different types of metabolism, predominantly anaerobic and chemosynthetic. Thermoproteati is a kingdom that is sister to the Asgard branch that gave rise to the eukaryotes. It has been proposed that the Thermoproteati kingdom be classified as "Crenarchaeota" and that the traditional "Crenarchaeota" (Thermoproteota) be classified as a class called "Sulfolobia", along with the other phyla with class rank or order. After including the kingdom category into ICNP, the only validly published name of this group is kingdom Thermoproteati (Guy and Ettema 2024). Classification * Thermoproteota (formerly "Crenarchaeota"). It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfolobus Solfataricus
''Saccharolobus solfataricus'' is a species of thermophilic archaeon. It was transferred from the genus ''Sulfolobus'' to the new genus ''Saccharolobus'' with the description of ''Saccharolobus caldissimus'' in 2018. It was first discovered and isolated from the Solfatara volcano (Pisciarelli-Campania, Italy) in 1980 by two German microbiologists Karl Setter and Wolfram Zillig. However, these organisms are not isolated to volcanoes, but are found all over the world in places such as hot springs. The species grows best in temperatures around 80 °C, a pH level between 2 and 4, and with enough sulfur for ''S.'' ''solfataricus'' to metabolize in order to gain energy. These conditions qualify it as an extremophile, and it is specifically known as a thermoacidophile because of its preference for high temperatures and low pH levels. It is also aerobic and heterotropic due to its metabolic system. Being an autotroph, it receives energy by growing on sulfur or even a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fervidicoccales
''Fervidicoccus fontis'' is an extremophilic, coccus-shaped archaeaon known for thriving in high-temperature environments. It was discovered in Russia's Uzon Caldera and exhibits anaerobic, organotrophic metabolism, primarily fermenting organic compounds such as peptides and yeast extract. ''F. fontis'' is genetically distinct, sharing no more than 89% of its genetic material with its closest relatives. It is the sole species within the order Fervidicoccales and genus ''Fervidicoccus'', although ongoing research suggests potential new species. It plays a significant role in biotechnological applications due to its lipid- hydrolyzing capabilities, contributing to industries ranging from wastewater treatment to pharmaceuticals. Scientific Classification Taxonomy ''F. fontis'' belongs to the Archaea domain and falls within the Crenarchaeota phylum. Organisms within this phylum are known for their extremophilic nature, enabling them to survive in severe environments such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoprotei
The Thermoprotei is a class of the Thermoproteota. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However, in the List provided bel ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * * * Scientific books * * External links Archaea classes Thermoproteota {{Archaea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrososphaerota
The Nitrososphaerota (syn. Thaumarchaeota) are a phylum of the Archaea proposed in 2008 after the genome of '' Cenarchaeum symbiosum'' was sequenced and found to differ significantly from other members of the hyperthermophilic phylum Thermoproteota (formerly Crenarchaeota). Three described species in addition to ''C. symbiosum'' are '' Nitrosopumilus maritimus'', '' Nitrososphaera viennensis'', and '' Nitrososphaera gargensis''. The phylum was proposed in 2008 based on phylogenetic data, such as the sequences of these organisms' ribosomal RNA genes, and the presence of a form of type I topoisomerase that was previously thought to be unique to the eukaryotes. This assignment was confirmed by further analysis published in 2010 that examined the genomes of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea '' Nitrosopumilus maritimus'' and '' Nitrososphaera gargensis'', concluding that these species form a distinct lineage that includes ''Cenarchaeum symbiosum''. The lipid crenarchaeol has been fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The All-Species Living Tree Project
The All-Species Living Tree' Project is a collaboration between various academic groups/institutes, such as ARB, SILVA rRNA database project, and LPSN, with the aim of assembling a database of 16S rRNA sequences of all validly published species of ''Bacteria'' and ''Archaea''. At one stage, 23S sequences were also collected, but this has since stopped. Currently there are over 10,950 species in the aligned dataset and several more are being added either as new species are discovered or species that are not represented in the database are sequenced. Initially the latter group consisted of 7% of species. Similar (and more recent) projects include the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea (GEBA), which focused on whole genome sequencing of bacteria and archaea. Tree The tree was created by maximum likelihood analysis without bootstrap: consequently accuracy is traded off for size and many phylum level clades are not correctly resolved (such as the Firmicutes). (Eukaryote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfolobus
''Sulfolobus'' is a genus of microorganism in the family Sulfolobaceae. It belongs to the kingdom Thermoproteati of the Archaea domain. ''Sulfolobus'' species grow in volcanic springs with optimal growth occurring at pH 2–3 and temperatures of 75–80 °C, making them acidophiles and thermophiles respectively. ''Sulfolobus'' cells are irregularly shaped and flagellar. Species of ''Sulfolobus'' are generally named after the location from which they were first isolated, e.g. ''Sulfolobus solfataricus'' (now recombined as ''Saccharolobus solfataricus)'' was first isolated in the Solfatara volcano. Other species can be found throughout the world in areas of volcanic or geothermal activity, such as geological formations called mud pots, which are also known as ''solfatare'' (plural of solfatara). ''Sulfolobus'' as a model to study the molecular mechanisms of DNA replication When the first Archaeal genome, '' Methanococcus jannaschii'', had been sequenced completely i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desulfurococcales
The Desulfurococcales is an order of the Thermoprotei, part of the kingdom Archaea. The order encompasses some genera which are all thermophilic, autotrophs which utilise chemical energy, typically by reducing sulfur compounds using hydrogen. Desulfurococcales cells are either regular or irregular coccus in shape, with forms of either discs or dishes. These cells can be single, in pairs, in short chains, or in aciniform formation. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However, in the List provided bel ... References Further reading Scientific journals * * Scientific books * * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoproteales
Thermoproteales are an order of archaeans in the class Thermoprotei. They are the only organisms known to lack the SSB proteins, instead possessing the protein ThermoDBP that has displaced them. The rRNA genes of these organisms contain multiple introns, which can be homing endonuclease encoding genes, and their presence can impact the binding of "universal" 16S rRNA primers often used in environmental sequencing surveys. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) See also * List of Archaea genera This article lists the genera of the Archaea. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However, in the List provided bel ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * Archaea taxonomic orders Thermoprote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |