|
Thermoplastics
A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling. Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped, and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling. Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) (chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' ) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point. ABS is a terpolymer made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. The proportions can vary from 15% to 35% acrylonitrile, 5% to 30% butadiene and 40% to 60% styrene. The result is a long chain of polybutadiene crisscrossed with shorter chains of poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile). The nitrile groups from neighboring chains, being polar, attract each other and bind the chains together, making ABS stronger than pure polystyrene. The acrylonitrile also contributes chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, hardness, and rigidity, while increasing the heat deflection temperature. The styrene gives the plastic a shiny, impervious surface, as well as hardness, rigidity, and improved processing ease. The polybutad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection Moulding
Injection moulding (U.S. spelling: injection molding) is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polylactic Acid
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a plastic material. As a thermoplastic polyester (or polyhydroxyalkanoate) it has the backbone formula or . PLA is formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of lactide , the cyclic dimer of the basic repeating unit. Often PLA is blended with other polymers. PLA can be biodegradable or long-lasting, depending on the manufacturing process, additives and copolymers. PLA has become a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resources and the possibility to use it for compostable products. In 2022, PLA had the highest consumption volume of any bioplastic of the world, with a share of ca. 26 % of total bioplastic demand. Although its production is growing, PLA is still not as important as traditional commodity polymers like PET or PVC. Its widespread application has been hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds. Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made through step-growth polymerization or solid-phase synthesis yielding materials such as nylons, aramids, and sodium polyaspartate. Synthetic polyamides are commonly used in textiles, automotive industry, carpets, kitchen utensils and sportswear due to their high durability and strength. The transportation manufacturing industry is the major consumer, accounting for 35% of polyamide (PA) consumption. Classification Polymers of amino acids are known as polypeptides or proteins. According to the composition of their main chain, synthetic polyamides are classified as follows: All polyamides are made by the formation of an amide function to link two molecules of monomer together. The monomers can be amides themselves (usually in the form of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybutadiene
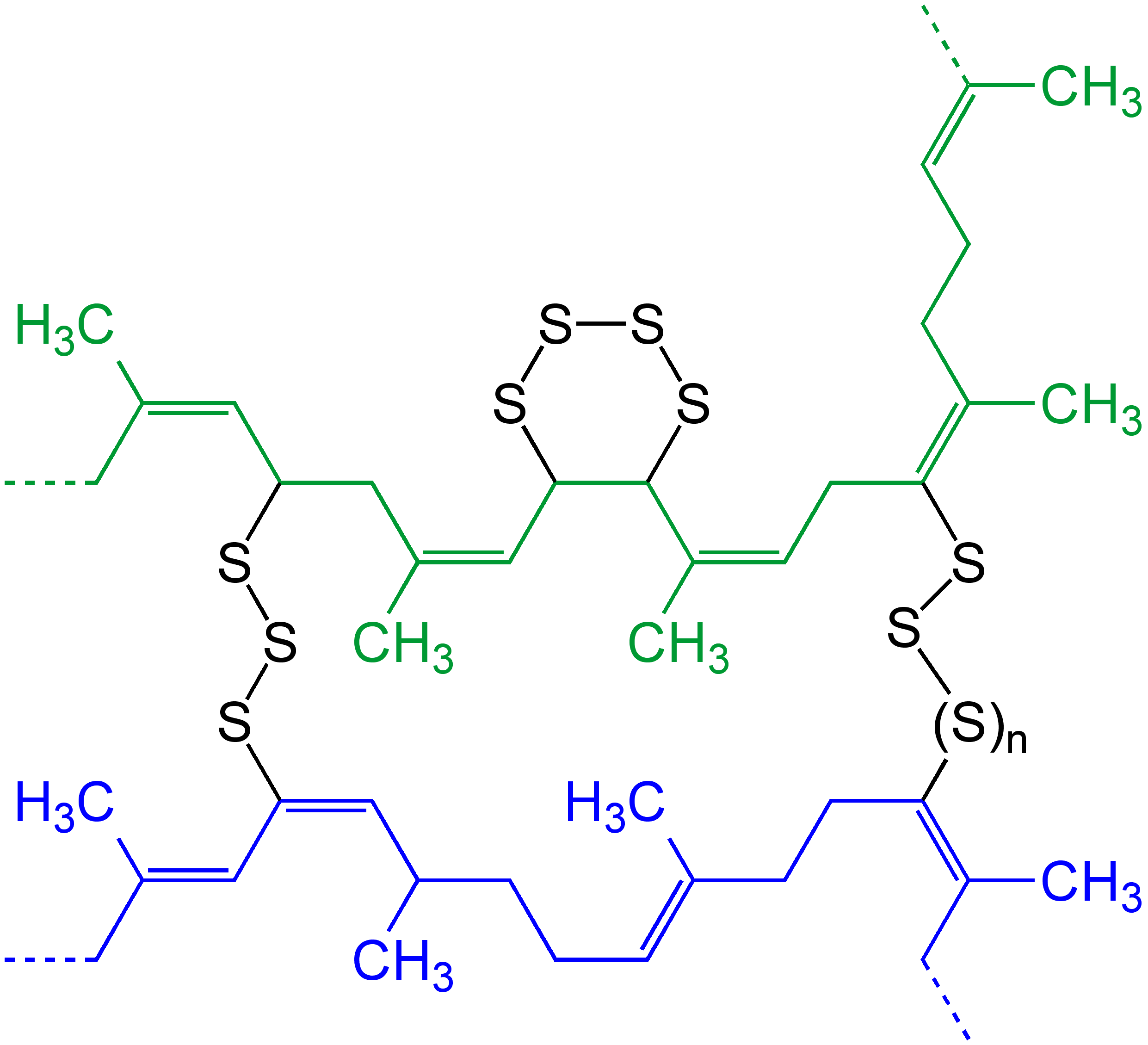
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber, BRis a synthetic rubber. It offers high elasticity, high resistance to wear, good strength even without fillers, and excellent abrasion resistance when filled and vulcanized. "Polybutadiene" is a collective name for homopolymers formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. The IUPAC refers to polybutadiene as "poly(buta-1,3-diene)". Historically, an early generation of synthetic polybutadiene rubber produced in Germany by Bayer using sodium as a catalyst was known as "Buna rubber". Polybutadiene is typically crosslinked with sulphur, however, it has also been shown that it can be UV cured when bis-benzophenone additives are incorporated into the formulation. Polybutadiene rubber (BR) accounted for about 28% of total global consumption of synthetic rubbers in 2020, whereas styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) was by far the most important grade (S-SBR 12%, E-SBR 27% of the entire synthetic rubber market). It is mainly used in the manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poly(methyl Methacrylate)
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) is a synthetic polymer derived from methyl methacrylate. It is a transparent thermoplastic, used as an engineering plastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Walcast, Hesalite, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Lucite, PerClax, and Perspex, among several others ( see below). This plastic is often used in sheet form as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It can also be used as a casting resin, in inks and coatings, and for many other purposes. It is often technically classified as a type of glass, in that it is a non-crystalline vitreous substance—hence its occasional historic designation as ''acrylic glass''. History The first acrylic acid was created in 1843. Methacrylic acid, derived from acrylic acid, was formulated in 1865. The reaction between methacrylic acid and methanol results in the ester methyl methacrylate. It was developed in 1928 in several different la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Stress Cracking
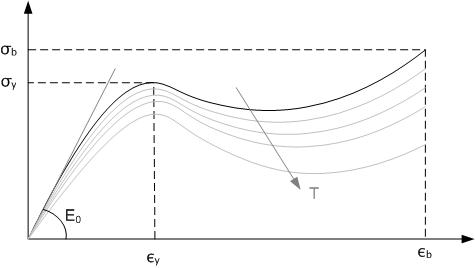
Environmental Stress Cracking (ESC) is one of the most common causes of unexpected brittle failure of thermoplastic (especially amorphous) polymers known at present. According to ASTM D883, stress cracking is defined as "an external or internal crack in a plastic caused by tensile stresses less than its short-term mechanical strength". This type of cracking typically involves brittle cracking, with little or no ductile drawing of the material from its adjacent failure surfaces. Environmental stress cracking may account for around 15-30% of all plastic component failures in service.H. F. Mark (2004). Encyclopedia of Polymers Science and Technology – 3rd Ed. Vol 12. John Miley & Sons Inc. This behavior is especially prevalent in glassy, amorphous thermoplastics. Amorphous polymers exhibit ESC because of their loose structure which makes it easier for the fluid to permeate into the polymer. Amorphous polymers are more prone to ESC at temperature higher than their glass tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Link
In chemistry and biology, a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. Synthetic polymers : 260px, left, Chemical reactions associated with crosslinking of drying oils, the process that produces curing'' refers to the crosslinking of thermosetting">linoleum. Cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylic Acid
Poly(acrylic acid) (PAA; trade name Carbomer) is a polymer with the formula (CH2−CHCO2H)''n''. It is a derivative of acrylic acid (CH2=CHCO2H). In addition to the homopolymers, a variety of copolymers and crosslinked polymers, and partially deprotonated derivatives thereof, are known and of commercial value. In a water solution at neutral pH, PAA is an anionic polymer, i.e., many of the side chains of PAA lose their protons and acquire a negative charge. Partially or wholly deprotonated PAAs are polyelectrolytes, with the ability to absorb and retain water and swell to many times their original volume. These properties acid–base and water-attracting are the basis of many applications. Synthesis PAA, like any acrylate polymer, is usually synthesized through a process known as free radical polymerization, though graft polymerization may also be used. Free radical polymerization involves the conversion of monomers, in this case, acrylic acid (CH2=CHCO2H), into a polymer cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mass
The molecular mass () is the mass of a given molecule, often expressed in units of daltons (Da). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The derived quantity relative molecular mass is the unitless ratio of the mass of a molecule to the atomic mass constant (which is equal to one dalton). The molecular mass and relative molecular mass are distinct from but related to the ''molar mass''. The molar mass is defined as the mass of a given substance divided by the amount of the substance, and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). That makes the molar mass an ''average'' of many particles or molecules (weighted by abundance of the isotopes), and the molecular mass the mass of one specific particle or molecule. The molar mass is usually the more appropriate quantity when dealing with macroscopic (weigh-able) quantities of a substance. The definition of molecular weight is most authoritat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |