|
Thelema
Thelema () is a Western esotericism, Western esoteric and occult social or spiritual philosophy and a new religious movement founded in the early 1900s by Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), an English writer, mystic, occultist, and ceremonial magician. Central to Thelema is the concept of discovering and following one's True Will, a divine and individual purpose that transcends ordinary desires. Crowley's system begins with ''The Book of the Law'', a text he maintained was dictated to him by a non-corporeal entity named Aiwass. This work outlines key principles, including the axioms "Do what thou wilt shall be the whole of the Law" and "love is the law, love under will", emphasizing personal freedom and the pursuit of one's true path. The Thelemic cosmology features deities inspired by ancient Egyptian religion. The highest deity is Nuit, the night sky symbolized as a naked woman covered in stars, representing the ultimate source of possibilities. Hadit, the infinitely small poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleister Crowley, Magus
Aleister Crowley ( ; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, novelist, mountaineer, and painter. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the prophet entrusted with guiding humanity into the Aeon of Horus, Æon of Horus in the early 20th century. A prolific writer, he published widely over the course of his life. Born to a wealthy family in Royal Leamington Spa, Warwickshire, Crowley rejected his parents' fundamentalist Christian Plymouth Brethren faith to pursue an interest in Western esotericism. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, Trinity College at the University of Cambridge, where he focused his attention upon mountaineering and poetry, resulting in several publications. Some biographers allege that here he was recruited into a British intelligence agency, further suggesting that he remained a spy throughout his life. In 1898, he joined the esoteric Hermetic Order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Parsons
John Whiteside Parsons (born Marvel Whiteside Parsons; October 2, 1914 – June 17, 1952) was an American Aerospace engineering, rocket engineer, chemist, and Thelemite, Thelemite occultist. Parsons was one of the principal founders of both the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Aerojet. He invented the first rocket engine to use a Castability, castable, Composite material, composite rocket propellant, and pioneered the advancement of both Liquid-fuel rocket, liquid-fuel and Solid-fuel rocket, solid-fuel rockets. Parsons was raised in Pasadena, California. He began Amateur rocketry, amateur rocket experiments with school friend Edward Forman in 1928. Parsons was admitted to Stanford University but left before graduating due to financial hardship during the Great Depression. In 1934, Parsons, Forman, and Frank Malina formed the Caltech-affiliated Guggenheim Aeronautical Laboratory (GALCIT) Rocket Research Group, with support by GALCIT chairman Theodore von Kármán. The group w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Work (Thelema)
Within Thelema, the Great Work is the spiritual endeavor aimed at realizing one's True Will and achieving a profound mystical union with Nuit, the Thelemic personification of the infinite and boundless expanse of the universe. This path, crafted by Aleister Crowley, draws inspiration from Hermetic alchemy and the Hermetic Qabalah. The cornerstone of Thelema is the ''Book of the Law'', received by Crowley in 1904 through a communication with the entity Aiwass. This text became the central scripture, heralding a new Aeon for humanity and outlining the principles of Thelema. The core purpose of Thelema is twofold: to discover one's unique True Will, or life's purpose, and to attain mystical union with the universal consciousness. Crowley described the Great Work as the unification of opposing forces, be it the individual with the universal or the ego with the non-ego. The techniques to achieve these goals are collectively termed "Magick", encompassing Western ceremonial magic, med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
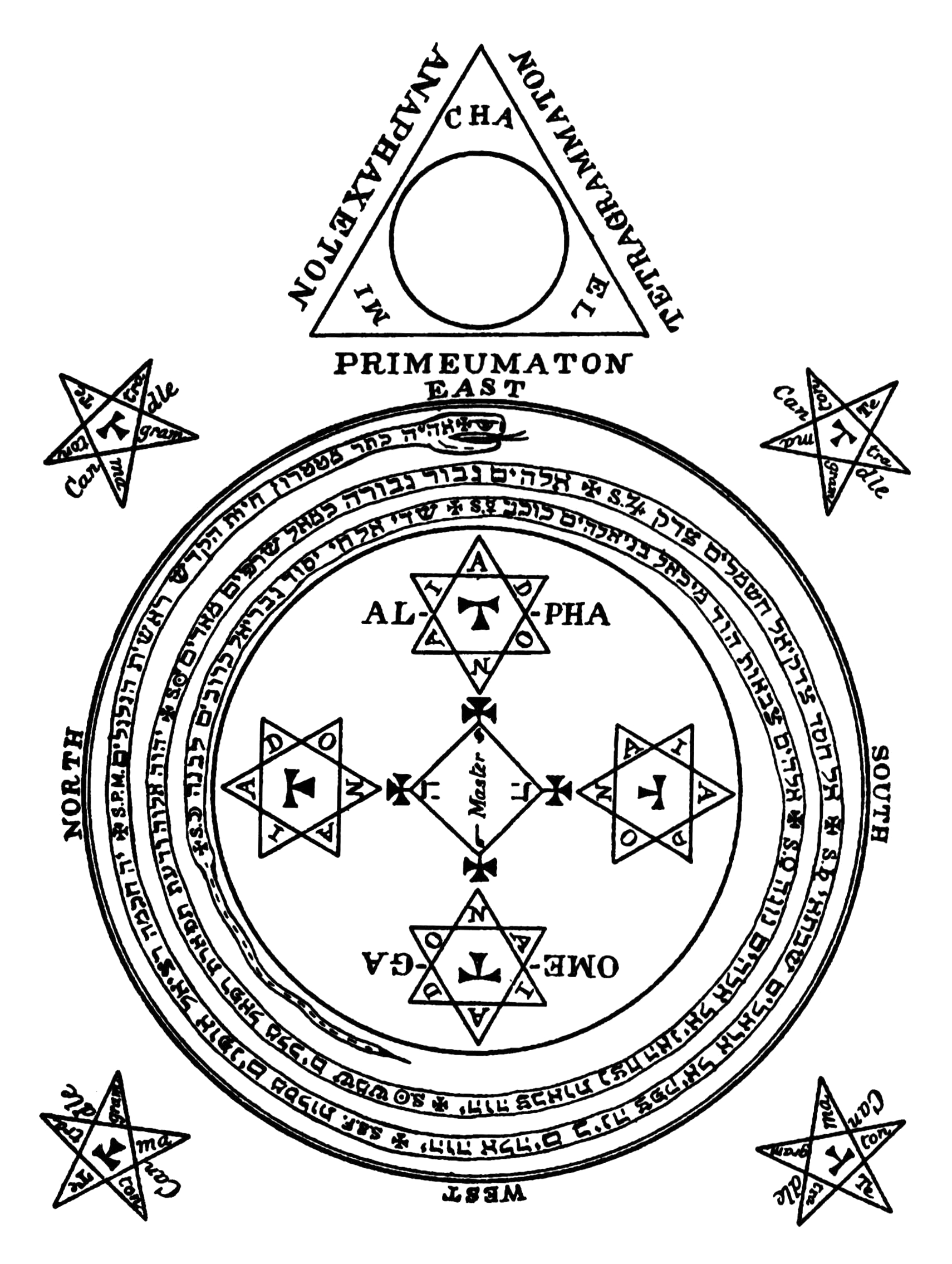
James Lees (English Magician)
Ceremonial magic (also known as magick, ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah, Enochian magic, Thelema, and the magic of various grimoires. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism and Western esotericism. The synonym ''magick'' is an archaic spelling of 'magic' used during the Renaissance, which was revived by Aleister Crowley to differentiate occult magic from stage magic. He defined it as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", including ordinary acts of will as well as ritual magic. Crowley wrote that "it is theoretically possible to cause in any object any ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magick
Ceremonial magic (also known as magick, ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of Magic (supernatural), magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah, Enochian magic, Thelema, and the magic of various grimoires. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism and Western esotericism. The synonym ''magick'' is an archaic spelling of 'magic' used during the Renaissance, which was revived by Aleister Crowley to differentiate occult magic from magic (illusion), stage magic. He defined it as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", including ordinary acts of will as well as ritual magic. Crowley wrote that "it is theoretically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Book Of The Law
''Liber AL vel Legis'' (), commonly known as ''The Book of the Law'', is the central sacred text of Thelema. The book is often referred to simply as ''Liber AL'', ''Liber Legis'' or just ''AL'', though technically the latter two refer only to the manuscript. Aleister Crowley wrote the ''Liber AL vel Legis'' in 1904, saying that the book was dictated to him by a beyond-human being, Aiwass, who he later referred to as his own Holy Guardian Angel. Following positive reception of the Book, Crowley proclaimed the arrival of a new stage in the spiritual evolution of humanity, to be known as the " Æon of Horus". The primary precept of this new aeon is the charge, "Do what thou wilt shall be the whole of the Law." The book contains three chapters, each of which Crowley said had been dictated and written down in one hour, beginning at noon, on 8 April, 9 April, and 10 April in Cairo, Egypt, in the year 1904. The three chapters of the book are attributed to the deities Nuit, Hadit, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Thelemites
Thelema is a philosophical and mystical system founded by Aleister Crowley early in the 20th century. This is a list of Thelemites, self-professed adherents of Thelema (including those who identified as Thelemites during part of their lives but subsequently left the faith) who have Wikipedia articles. These individuals come from diverse backgrounds, including artists, writers, occultists, scientists, musicians, and more, hailing from countries such as the United States, England, Canada, Germany, Australia, and Brazil. A * Kenneth Anger (1927–2023), American underground experimental filmmaker, actor, and writer. B * Frank Bennett (1868–1930), Australian chemist. * William Breeze (b. 1955), American writer and musician. * Mary Butts (1890–1937), English modernist writer. C * Marjorie Cameron (1922–1995), American artist, poet, actress and occultist. * Barbara Canright (1919–1997), American human computer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, member of Agape L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babalon
Babalon (also known as the Scarlet Woman, Great Mother or Mother of Abominations) is a goddess found in the occult system of Thelema, which was established in 1904 with the writing of ''The Book of the Law'' by English author and occultist Aleister Crowley. The spelling of the name as "Babalon" was revealed to Crowley in '' The Vision and the Voice''. Her name and imagery feature prominently in Crowley's "Liber Cheth vel Vallum Abiegni". In her most abstract form, Babalon represents the female sexual impulse and the liberated woman. In the creed of the Gnostic Mass she is also identified with Mother Earth, in her most fertile sense. Along with her status as an archetype or goddess, Crowley believed that Babalon had an earthly aspect or avatar; a living woman who occupied the spiritual office of the "Scarlet Woman". This office, first identified in ''The Book of the Law'', is usually described as a counterpart to his own identification as " To Mega Therion" (The Great Beast) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aiwass
Aiwass is the name given to a voice that the English occultist and ceremonial magician Aleister Crowley reported to have heard on April 8, 9, and 10 in 1904. Crowley reported that this voice, which he considered originated with a non-corporeal being, dictated a text known as ''The Book of the Law'' or ''Liber AL vel Legis'' to him during his honeymoon in Cairo. Dictation According to Crowley, Aiwass first appeared during the Three Days of the writing of ''Liber al vel Legis''. His first and only identification as such is in Chapter I: "Behold! it is revealed by Aiwass the minister of Hoor-paar-kraat" (AL I:7). Hoor-paar-kraat (Egyptian: Har-pa-khered) is more commonly referred to by the Greek transliteration Harpocrates, meaning "Horus the Child", whom Crowley considered to be the central deity within the Thelemic cosmology (see Æon of Horus). However, Harpocrates also represents the Higher Self, the Holy Guardian Angel. Crowley described the encounter in detail in his 1936 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Qaballa
English Qaballa (EQ) is a Hermetic Qabalah, based on a system of arithmancy that interprets the letters of the English alphabet via an assigned set of values. It was created by James Lees in 1976, through his efforts to understand, interpret, and elaborate on Aleister Crowley's ''Book of the Law''. This system has also been referred to as the ALW cipher and the New Aeon English Qabalah (NAEQ) by other writers. Background In 1904, Aleister Crowley wrote out in English the text of the foundational document of his world-view, known as ''Liber AL vel Legis'', ''The Book of the Law''. In this text was the injunction found at verse 2:55; "Thou shalt obtain the order & value of the English Alphabet, thou shalt find new symbols to attribute them unto" which was understood by Crowley as referring to an English Qabalah yet to be developed or revealed. Order and value The "order & value" proposed by James Lees lays the letters out on the grid superimposed on the page of manuscript of ''Lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |