|
The Holocaust In Russia
The Holocaust in Russia is the Nazi crimes during the occupation of Russia (Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic) by Nazi Germany. On the Eve of the Holocaust The Soviet Union did grant official "equality of all citizens regardless of status, sex, race, religion, and nationality." The years before the Holocaust were an era of rapid change for Soviet Jews, leaving behind the dreadful poverty of the Pale of Settlement. 40% of the population in the former Pale left for large cities within the Soviet Union. Emphasis on education and movement from countryside ''shtetls'' to newly industrialized cities allowed many Soviet Jews to enjoy overall advances under Joseph Stalin and to become one of the most educated population groups in the world. Due to Stalinist emphasis on its urban population, interwar migration inadvertently rescued countless Soviet Jews—Nazi Germany penetrated the entire former Jewish Pale, but were kilometers short of Leningrad and Moscow. World War II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
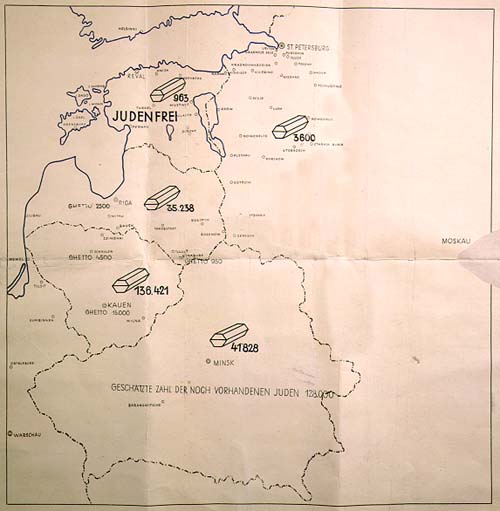
Map Used To Illustrate Stahlecker's Report To Heydrich On January 31, 1942
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the List of European cities by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the List of cities and towns around the Baltic Sea, most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's List of northernmost items#Cities and settlements, northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a Ports of the Baltic Sea, historically strategic port, it is governed as a Federal cities of Russia, federal city. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavropol
Stavropol (; rus, Ставрополь, p=ˈstavrəpəlʲ) is a city and the administrative centre of Stavropol Krai, Russia. As of the 2021 Census, its population was 547,820, making it one of Russia's fastest growing cities. It was known as ''Voroshilovsk'' until January 12, 1943.Decree of January 12, 1943 Etymology The name ''Stavropol'' ( rus, Ста́врополь) is a Russian rendering of the Greek name, ( grc-gre, Σταυρούπολις 'City of the Cross'). According to legend, soldiers found a stone cross there while building the fortress in the city's future location. It is unrelated to Byzantine Stauroupolis (ancient Aphrodisias) in Asia Minor, nor to the city of Stavropol-on-Volga (now called Tolyatti). History It was founded on October 22, 1777Charter of Stavropol, Article 2 following the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 as a military encampment, and was granted city status in 1785. Prince Grigory Potemkin, who founded Stavropol as on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kislovodsk
Kislovodsk (russian: Кислово́дск, lit. ''sour waters''; ; krc, Ачысуу) is a spa town, spa types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Stavropol Krai, Russia, in the North Caucasus region of Russia which is located between the Black Sea, Black and Caspian Seas. Population: History In 1803 Tsar Alexander I of Russia ordered the construction of the military station which became Kislovodsk. The site took its name from the many mineral springs around the city. The settlement gained town status in 1903. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Kislovodsk as a fashionable spa attracted many musicians, artists, and members of the Russian aristocracy. Several of the events in Mikhail Lermontov's 1840 novel ''A Hero of Our Time'' take place in Kislovodsk. Archaeology Numerous ancient settlements of the Koban culture (ca. 1100 to 400 BC) are found in the Kislovodsk city and its surroundings. They include the sites of Industria I, Sultan-gora I, Berezovka I, Berez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yessentuki
Yessentuki ( rus, Ессентуки́, p=jɪsɪntʊˈkʲiˑ) is a city in Stavropol Krai, Russia, located in the shadow of Mount Elbrus at the base of the Caucasus Mountains. The city serves as a railway station in the Mineralnye Vody—Kislovodsk branch, and is located southwest of Mineralnye Vody and west of Pyatigorsk. It is considered the cultural capital of Russia's Greek population and even today close to ten percent of its population is of Greek descent. Population: History Research by the Soviet archaeologist M.E. Masson and excavations of eight mausoleums showed that there was a large Golden Horde settlement near the present-day Essentuki in the 13th-15th centuries. Masson believed that the name Essentuki came from the name of a certain Khan Essentug from the names "Yesan Forest" and "Yesan Field" that have survived to this day. In 1798, the Russian military and border redoubt of Yessentuksky was laid on the right bank of the Bolshoy Yessentuchok River, near its c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostov-on-Don
Rostov-on-Don ( rus, Ростов-на-Дону, r=Rostov-na-Donu, p=rɐˈstof nə dɐˈnu) is a port city and the administrative centre of Rostov Oblast and the Southern Federal District of Russia. It lies in the southeastern part of the East European Plain on the Don River, from the Sea of Azov, directly north of the North Caucasus. The southwestern suburbs of the city lie above the Don river delta. Rostov-on-Don has a population of over one million people, and is an important cultural centre of Southern Russia. History Early history From ancient times, the area around the mouth of the Don River has held cultural and commercial importance. Ancient indigenous inhabitants included the Scythian and Sarmatian tribes. It was the site of Tanais, an ancient Greek colony, Fort Tana under the Genoese, and Fort Azak in the time of the Ottoman Empire. In 1749, a custom house was established on the Temernik River, a tributary of the Don, by edict of the Empress Elizabeth, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest cities in Russia. Population: The city has been destroyed several times throughout its long history because it was on the invasion routes of various empires. Smolensk is known for its electronics, textiles, food processing, and diamond faceting industries. Etymology The name of the city is derived from the name of the Smolnya River. Smolnya river flows through Karelian and Murmansk areas of north-western Russia. The origin of the river's name is less clear. One possibility is the old Slavic word () for black soil, which might have colored the waters of the Smolnya. An alternative origin could be the Russian word (), which means resin, tar, or pitch. Pine trees grow in the area, and the city was once a center of resin processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Black Book Of Soviet Jewry
''The Black Book of Soviet Jewry'' or simply ''The Black Book'' ( rus, Чёрная Кни́га, r=Chyórnaya Kníga, p=ˈt͡ɕɵrnəjə ˈknʲiɡə; yi, דאָס שוואַרצע בוך, ''Dos shvartse bukh''), also known as ''The Complete Black Book of Russian Jewry'', is a 500-page document compiled for publication by Ilya Ehrenburg and Vasily Grossman originally in late 1944 in the Russian language. It was a result of the collaborative effort by the Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee (JAC) and members of the American Jewish community to document the anti-Jewish crimes of the Holocaust and the participation of Jews in the resistance movement against the Nazis during World War II. The 1991 Kyiv edition of ''The Black Book'' was subtitled ''The Ruthless Murder of Jews by German-Fascist Invaders Throughout the Temporarily-Occupied Regions of the Soviet Union and in the German Nazi Death Camps established on occupied Polish soil during the War 1941–1945''. The book was not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Berenbaum
Michael Berenbaum (born July 31, 1945, in Newark, New Jersey) is an American scholar, professor, rabbi, writer, and filmmaker, who specializes in the study of the Holocaust. He served as deputy director of the President's Commission on the Holocaust (1979–1980), Project Director of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum (USHMM) (1988–1993), and Director of the USHMM's Holocaust Research Institute (1993–1997). Berenbaum played a leading role in the creation of the USHMM and the content of its permanent exhibition. From 1997 to 1999, he served as president and CEO of the Survivors of the Shoah Visual History Foundation, and subsequently (and currently) as Director of the Sigi Ziering Institute: Exploring the Ethical and Religious Implications of the Holocaust, located at the American Jewish University (formerly known as the University of Judaism), in Los Angeles, California. Professional career Berenbaum, who is Jewish, graduated from Queens College with a Bachelor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raul Hilberg
Raul Hilberg (June 2, 1926 – August 4, 2007) was a Jewish Austrian-born American political scientist and historian. He was widely considered to be the preeminent scholar on the Holocaust. Christopher R. Browning has called him the founding father of Holocaust Studies and his three-volume, 1,273-page ''magnum opus'' '' The Destruction of the European Jews'' is regarded as seminal for research into the Nazi Final Solution. Life and career Hilberg was born in Vienna, Austria, to a Polish-speaking Jewish family. His father, a small-goods salesman, was born in a Galician village, moved to Vienna in his teens, was decorated for bravery on the Russian front, and married Hilberg's mother who was from Buczacz, now in Ukraine. The young Hilberg was a loner, pursuing solitary hobbies such as geography, music and train spotting. Though his parents attended synagogue on occasion, he personally found the irrationality of religion repellent and developed an allergy to it. He did however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhard Heydrich
Reinhard Tristan Eugen Heydrich ( ; ; 7 March 1904 – 4 June 1942) was a high-ranking German SS and police official during the Nazi era and a principal architect of the Holocaust. He was chief of the Reich Security Main Office (including the Gestapo, Kripo, and SD). He was also ''Stellvertretender Reichsprotektor'' (Deputy/Acting Reich-Protector) of Bohemia and Moravia. He served as president of the International Criminal Police Commission (ICPC, now known as Interpol) and chaired the January 1942 Wannsee Conference which formalised plans for the "Final Solution to the Jewish question"—the deportation and genocide of all Jews in German-occupied Europe. Many historians regard Heydrich as the darkest figure within the Nazi regime; Adolf Hitler described him as "the man with the iron heart". He was the founding head of the '' Sicherheitsdienst'' (Security Service, SD), an intelligence organisation charged with seeking out and neutralising resistance to the Nazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the implementation of the so-called "Final Solution to the Jewish question" () in territories conquered by Nazi Germany, and were involved in the murder of much of the intelligentsia and cultural elite of Poland, including members of the Catholic priesthood. Almost all of the people they murdered were civilians, beginning with the intelligentsia and swiftly progressing to Soviet political commissars, Jews, and Romani people, as well as actual or alleged partisans throughout Eastern Europe. Under the direction of Heinrich Himmler and the supervision of SS- Reinhard Heydrich, the operated in territories occupied by the Wehrmacht (German armed forces) following the invasion of Poland in September 1939 and the invasion of the Soviet Union in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2.jpg)

.jpg)
