|
Thaliacea
Thaliacea is a class of marine chordates within the subphylum Tunicate, Tunicata, comprising the salps, pyrosomes and doliolids. Unlike their benthic relatives the Ascidiacea, ascidians, from which they are believed to have emerged, thaliaceans are free-floating (pelagic) for their entire lifespan. The group includes species with complex life cycles, with both solitary and Colony (biology), colonial forms. Anatomy The three orders of thaliaceans are filter feeders. Pyrosoma, Pyrosomes are colonial animals, with multiple tiny ascidian-like zooids arranged in a cylinder closed at one end. All of the atrial siphons point inwards, emptying into a single, common cloaca in the centre of the cylinder. As the water exhaled by the zooids exits through a common opening, the water movement slowly propels the pyrosome through the sea. Salps and doliolids have a transparent barrel-shaped body through which they pump water, propelling them through the sea, and from which they extract food. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urochordates
Tunicates are marine invertebrates belonging to the subphylum Tunicata ( ). This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. Despite their simple appearance and very different adult form, their close relationship to the vertebrates is certain. Both groups are chordates, as evidenced by the fact that during their mobile larval stage, tunicates possess a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail, and an endostyle. They resemble a tadpole. Tunicates are the only chordates that have lost their Myomere, myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the seriation of the gill slits. However, Doliolida, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals, but others replicate by budding and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
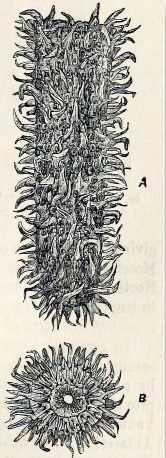
Ascidiacea
Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians or sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer test or "tunic" made of the polysaccharide cellulose. Ascidians are found all over the world, usually in shallow water with salinities over 2.5%. While members of the Thaliacea (salps, doliolids and pyrosomes) and Appendicularia (larvaceans) swim freely like plankton, sea squirts are sessile animals after their larval phase: they then remain firmly attached to their substratum, such as rocks and shells. There are 2,300 species of ascidians and three main types: solitary ascidians, social ascidians that form clumped communities by attaching at their bases, and compound ascidians that consist of many small individuals (each individual is called a zooid) forming large colonies. Sea squirts feed by taking in water through a tube, the oral siphon. The water enters the mouth and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunicate
Tunicates are marine invertebrates belonging to the subphylum Tunicata ( ). This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. Despite their simple appearance and very different adult form, their close relationship to the vertebrates is certain. Both groups are chordates, as evidenced by the fact that during their mobile larval stage, tunicates possess a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail, and an endostyle. They resemble a tadpole. Tunicates are the only chordates that have lost their Myomere, myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the seriation of the gill slits. However, Doliolida, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals, but others replicate by budding and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrosoma Atlanticum
''Pyrosoma atlanticum'' is a pelagic species of marine colonial tunicate in the class Thaliacea found in temperate waters worldwide. The name of the genus comes from the Greek words ''pyros'' meaning 'fire' and ''soma'' meaning 'body', referring to the bright bioluminescence sometimes emitted.''Pyrosoma atlanticum'' (Peron, 1804) : Pyrosome The JelliesZone. Retrieved 2011-11-10. The ''atlanticum'' refers to the , from where the first specimen of the species was collected for scientific description; it was desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrosome
Pyrosomes are free-floating colonial tunicates in family Pyrosomatidae. Pyrosomes consist of colonies of small Zooids. There are three genera, '' Pyrosoma'', '' Pyrosomella'' and '' Pyrostremma'', and eight species. They usually live in the upper layers of the open ocean in warm seas, although some may be found at greater depths. Pyrosomes exhibit bioluminescence, and the name ''Pyrosoma'' derives from the Greek words ''pyro'', meaning "fire", and ''soma'', meaning "body". Pyrosomes are hermaphroditic and reproduce via a two-part process. They have the ability to create massive blooms that may affect pelagic food webs. Description Pyrosomes are commonly called "sea pickles", due to their tube-like gelatinous structure. Other nicknames include "sea worms", "sea squirts", "fire bodies", and "cockroaches of the sea". Each zooid opens both to the inside and outside of the "tube". The zooids draw in ocean water from the outside into their internal filtering mesh called the branchia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordate
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics ( synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post- anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochords are replaced by a cartilaginous/ bony axia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salp
A salp (: salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (: salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, Plankton, planktonic tunicate in the family Salpidae. The salp moves by contracting its gelatinous body in order to pump water through it; it is one of the most efficient examples of jet propulsion in the animal kingdom. The salp feeds on phytoplankton, which it collects by straining water through its internal feeding filters. Distribution Salps are common in equatorial, temperate, and cold seas, where they can be seen at the surface, singly or in long, stringy colony (biology), colonies. The most abundant concentrations of salps are in the Southern Ocean (near Antarctica), where they sometimes form enormous swarms, often in deep water, and are sometimes even more abundant than krill. Since 1910, while krill populations in the Southern Ocean have declined, salp populations appear to be increasing. Salps have been seen in increasing numbers along the coast of Washingto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doliolida
The Doliolida are an order of small marine chordates of the subphylum Tunicata. They are in the class Thaliacea, which also includes the salps and pyrosomes. The doliolid body is small, typically 1–2 mm long, and barrel-shaped; it features two wide siphons, one at the front and the other at the back end, and eight or nine circular muscle strands reminiscent of barrel bands. Like all tunicates, except for the predatory tunicate, they are filter feeders. Unlike the related class Ascidiacea, which are sessile, but like the class Appendicularia, they are free-swimming plankton; cilia pump water through the body which drives them forward. As the water passes through, small particles and plankton on which the animal feeds are strained from the water by the gill slits. Doliolids can also move by contracting the muscular bands around the body creating a temporary water jet that thrusts them forward or backward quite quickly. The Doliolida have a complicated life cycle tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salpida
A salp (: salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (: salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, planktonic tunicate in the family Salpidae. The salp moves by contracting its gelatinous body in order to pump water through it; it is one of the most efficient examples of jet propulsion in the animal kingdom. The salp feeds on phytoplankton, which it collects by straining water through its internal feeding filters. Distribution Salps are common in equatorial, temperate, and cold seas, where they can be seen at the surface, singly or in long, stringy colonies. The most abundant concentrations of salps are in the Southern Ocean (near Antarctica), where they sometimes form enormous swarms, often in deep water, and are sometimes even more abundant than krill. Since 1910, while krill populations in the Southern Ocean have declined, salp populations appear to be increasing. Salps have been seen in increasing numbers along the coast of Washington, United States. Life cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrosoma
''Pyrosoma'' is a genus of pyrosomes, marine colonial tunicates in the class Thaliacea. It contains four pelagic species found in temperate waters worldwide. Pyrosomes are filter feeders that uniquely use a type of continuous jet propulsion, generated by individual zooids A zooid or zoöid is an animal that is part of a colonial animal. This lifestyle has been adopted by animals from separate unrelated taxa. Zooids are multicellular; their structure is similar to that of other solitary animals. The zooids can ..., to slowly move forward while grazing; the species ''P. atlanticum'' has the highest known food clearance rate among zooplankton grazers. Colonies can reach lengths of up to . Species The genus contains four recognized species: References Pyrosomatidae Tunicate genera Taxa described in 1804 Taxa named by François Péron {{Tunicata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doliolid
The Doliolida are an order of small marine chordates of the subphylum Tunicata. They are in the class Thaliacea, which also includes the salps and pyrosomes. The doliolid body is small, typically 1–2 mm long, and barrel-shaped; it features two wide siphons, one at the front and the other at the back end, and eight or nine circular muscle strands reminiscent of barrel bands. Like all tunicates, except for the predatory tunicate, they are filter feeders. Unlike the related class Ascidiacea, which are sessile, but like the class Appendicularia, they are free-swimming plankton; cilia pump water through the body which drives them forward. As the water passes through, small particles and plankton on which the animal feeds are strained from the water by the gill slits. Doliolids can also move by contracting the muscular bands around the body creating a temporary water jet that thrusts them forward or backward quite quickly. The Doliolida have a complicated life cycle that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |