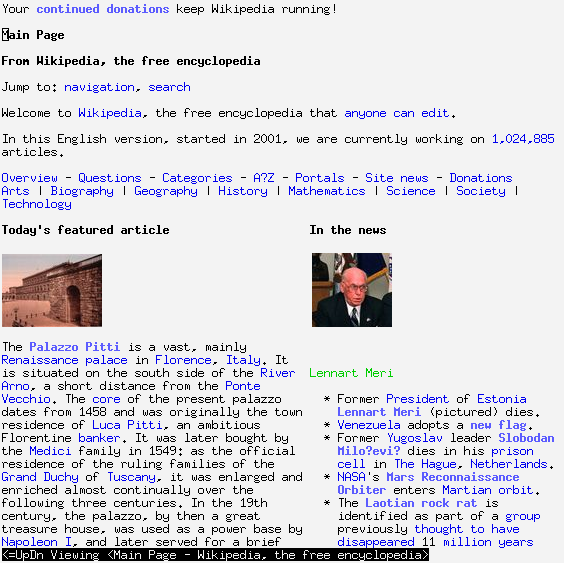
|
Text-based Web Browsers
A text-based web browser is a web browser that renders only the text of web pages, and ignores most graphic content. Under small bandwidth connections, usually, they render pages faster than graphical web browsers due to lowered bandwidth demands. Additionally, the greater CSS, JavaScript and typography functionality of graphical browsers require more CPU resources. They also can be heavily modified to display certain content differently Text-based browsers are often very useful for users with visual impairment or partial blindness. They are especially useful with speech synthesis or text-to-speech software, which reads content to users. Progressive enhancement allows a site to be compatible with text-based web browsers without compromising functionality to more sophisticated browsers, as the content is readable through pure HTML without CSS or JavaScript. List of notable text-based web browsers * browsh *Charlotte Web Browser (for VM/CMS) * Emacs/W3 & EWW for GNU Emacs * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emacs/W3
GNU Emacs is a text editor and suite of free software tools. Its development began in 1984 by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement. The program's tagline is "the extensible self-documenting text editor." Most functionality in GNU Emacs is implemented in user-accessible Emacs Lisp, allowing deep extensibility directly by users and through community-contributed packages. Its built-in features include a file browser and editor (Dired), an advanced calculator (Calc), an email client and news reader ( Gnus), a Language Server Protocol integration, and the productivity system Org-mode. A large community of users have contributed extensions such as the Git interface Magit, the Vim emulation layer Evil, several search frameworks, the window manager EXWM, and tools for working with a wide range of programming l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text-based Email Client
A text-based email client is an email client with its user interface being text-based, occupying a whole terminal screen. Other kind of email clients are GUI-based (cf. email client) or Web-based, see Webmail. Text-based email clients may be useful for users with visual impairment or partial blindness allowing speech synthesis or text-to-speech software to read content to users. Text-based email clients also allow to manage communication via simple remote sessions, e. g. per SSH, for instance when it is not possible to install a local GUI-client and/or access mail via Web interface. Also users may prefer text-based user interfaces in general. Typical features include: * Editing various emails via tab support * Configurable rendering of various MIME types, for instance OpenPGP encryption or HTML email * Vim-style keybindings * Support for multiple accounts and protocols, e. g. IMAP, Maildir, SMTP, and sendmail * UTF-8 support List of text-based email clients Notable clie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gopher (protocol)
The Gopher protocol () is a communication protocol designed for distributing, searching, and retrieving documents in Internet Protocol networks. The design of the Gopher protocol and user interface is menu-driven, and presented an alternative to the World Wide Web in its early stages, but ultimately fell into disfavor, yielding to Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The Gopher ecosystem is often regarded as the effective predecessor of the World Wide Web. Usage The Gopher protocol was invented by a team led by Mark P. McCahill at the University of Minnesota. It offers some features not natively supported by the Web and imposes a much stronger hierarchy on the documents it stores. Its text menu interface is well-suited to computing environments that rely heavily on remote text-oriented computer terminals, which were still common at the time of its creation in 1991, and the simplicity of its protocol facilitated a wide variety of client implementations. File:Gopher in Firefox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini (protocol)
Gemini is an application-layer internet communication protocol for accessing remote documents, similar to HTTP and Gopher (protocol), Gopher. It comes with a special document format, commonly referred to as "gemtext", which allows linking to other documents. Started by a pseudonymous person known as Solderpunk, the protocol is being finalized collaboratively and , has not been submitted to the IETF organization for standardization. History The Gemini project was started in June 2019 by Solderpunk. Additional work has been done by an informal community of users. According to Solderpunk's FAQ, Gemini is not intended to replace Gopher (protocol), Gopher or HTTP, but to co-exist with them. Much of the development happened on the Gemini mailing list until the list disappeared at the end of 2021 due to a hardware issue. The creation of the Usenet newsgroup ''comp.infosystems.gemini'' in October 2021 was the first new newsgroup in the Big 8 (Usenet), Big Eight hierarchy in eight year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparison Of Lightweight Web Browsers
A lightweight web browser is a web browser that sacrifices some of the features of a mainstream web browser in order to reduce the consumption of system resources, and especially to minimize the memory footprint. The tables below compare notable lightweight web browsers. Several of them use a common layout engine, but each has a unique combination of features and a potential niche. The minimal user interface in surf, for example, does not have tabs, whereas xombrero can be driven with vi-like keyboard commands. Four of the browsers compared—Lynx, w3m, Links, and ELinks—are designed for text mode, and can function in a terminal emulator. Eww is limited to working within Emacs. Links 2 has both a text-based user interface and a graphical user interface. w3m is, in addition to being a web browser, also a terminal pager. Overview Operating system support ;Notes Features Test scores reflect the version of the browser engine in use. Generally, a lower score indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx (web Browser)
Lynx is a customizable text-based web browser for use on cursor-addressable character cell terminals. , it is the oldest web browser still being maintained, having started in 1992. History Lynx was a product of the Distributed Computing Group within Academic Computing Services of the University of Kansas. It was initially developed in 1992 by a team of students and staff at the university ( Lou Montulli, Michael Grobe and Charles Rezac) as a hypertext browser used solely to distribute campus information as part of a ''Campus-Wide Information System'' and for browsing the Gopher space. Beta availability was announced to Usenet on 22 July 1992. In 1993, Montulli added an Internet interface and released a new version (2.0) of the browser. , the support of communication protocols in Lynx is implemented using a version of libwww, forked from the library's code base in 1996. The supported protocols include Gopher, HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, NNTP and WAIS. Support for NNTP was added to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELinks
ELinks is a free text-based web browser for Linux, DOS, and Windows operating systems. It began in late 2001 as an experimental fork by Petr Baudiš of the Links Web browser, hence the E in the name. Since then, the E has come to stand for Enhanced or Extended. On 1 September 2004, Baudiš handed maintainership of the project over to Danish developer Jonas Fonseca, citing a lack of time and interest and a desire to spend more time coding rather than reviewing and organising releases. On 17 March 2017, OpenBSD removed ELinks from its ports tree, citing concerns with security issues and lack of responsiveness from the developers. On , ELinks was forked into another program called felinks, meaning ''forked elinks''. On , the felinks repository on GitHub was renamed to elinks, with permission from Baudiš, as the old ELinks was no longer being actively maintained. elinks is being actively maintained: preview version 0.18.0rc1 was released , while stable version 0.18.0 was relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
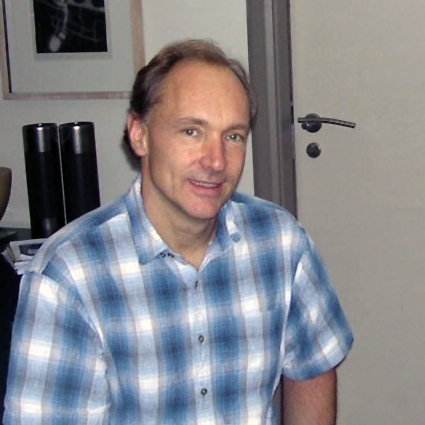
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee (born 8 June 1955), also known as TimBL, is an English computer scientist best known as the inventor of the World Wide Web, the HTML markup language, the URL system, and HTTP. He is a professorial research fellow at the University of Oxford and a professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Berners-Lee proposed an information management system on 12 March 1989 and implemented the first successful communication between a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) client and Server (computing), server via the Internet in mid-November. He devised and implemented the first Web browser and Web server and helped foster the Web's subsequent development. He is the founder and emeritus director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which oversees the continued development of the Web. He co-founded (with Rosemary Leith) the World Wide Web Foundation. In April 2009, he was elected as Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Mode Browser
The Line Mode Browser (also known as LMB, WWWLib, or just www) is the second web browser ever created. The browser was the first demonstrated to be portable to several different operating systems. Operated from a simple command-line interface, it could be widely used on many computers and computer terminals throughout the Internet. The browser was developed starting in 1990, and then supported by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) as an example and test application for the libwww library. History One of the fundamental concepts of the "World Wide Web" projects at CERN was " universal readership". In 1990, Tim Berners-Lee had already written the first browser, WorldWideWeb (later renamed to ''Nexus''), but that program only worked on the proprietary software of NeXT computers, which were in limited use. Berners-Lee and his team could not port the WorldWideWeb application with its features—including the graphical WYSIWYG editor— to the more widely deployed X Window Sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eww (web Browser)
Emacs Web Wowser (a backronym of "eww") is a lightweight web browser within the GNU Emacs text editor. Eww can only do basic rendering of HTML; there is no capability for executing JavaScript JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language and core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior. Web browsers have ... or handling the intricacies of CSS. It was developed by Lars Magne Ingebrigtsen, who also created the underlying HTML rendering library. See also * w3m used with emacs-w3m interface * Emacs/W3 References External links GNU Emacs manualSource code Free web browsers Emacs Cross-platform free software Free software programmed in Lisp Software using the GNU General Public License Emacs modes {{web-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |