|
Statistical Tests
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data provide sufficient evidence to reject a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic. Then a decision is made, either by comparing the test statistic to a critical value or equivalently by evaluating a ''p''-value computed from the test statistic. Roughly 100 specialized statistical tests are in use and noteworthy. History While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Choice of null hypothesis Paul Meehl has argued that the epistemological importance of the choice of null hypothesis has gone largely unacknowledged. When the null hypothesis is predicted by theory, a more precise experiment will be a more severe test of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
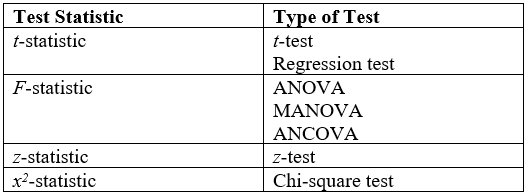
Common Test Statistics Chart
Common may refer to: As an Irish surname, it is anglicised from Irish language, Irish Gaelic surname Ó Comáin. Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Battle Green, Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District (Salem, Massachusetts), Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (1841–1903), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (1889–1953), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (1850–1919), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher (17 February 1890 – 29 July 1962) was a British polymath who was active as a mathematician, statistician, biologist, geneticist, and academic. For his work in statistics, he has been described as "a genius who almost single-handedly created the foundations for modern statistical science" and "the single most important figure in 20th century statistics". In genetics, Fisher was the one to most comprehensively combine the ideas of Gregor Mendel and Charles Darwin, as his work used mathematics to combine Mendelian genetics and natural selection; this contributed to the revival of Darwinism in the early 20th-century revision of the theory of evolution known as the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis. For his contributions to biology, Richard Dawkins declared Fisher to be the greatest of Darwin's successors. He is also considered one of the founding fathers of Neo-Darwinism. According to statistician Jeffrey T. Leek, Fisher is the most in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'' is a fortnightly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society. It publishes original research and review content in a wide range of physical scientific disciplines. Articles can be accessed online a few months prior to the printed journal. All articles become freely accessible two years after their publication date. The current editor-in-chief is John Dainton. Overview ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A'' publishes themed journal issues on topics of current scientific importance and general interest within the physical, mathematical and engineering sciences, edited by leading authorities and comprising original research, reviews and opinions from prominent researchers. Past issue titles include "Supercritical fluids - green solvents for green chemistry?", "Tsunamis: Bridging science, engineering and society", "Spatial transformations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductive Inference
Inductive reasoning refers to a variety of methods of reasoning in which the conclusion of an argument is supported not with deductive certainty, but with some degree of probability. Unlike ''deductive'' reasoning (such as mathematical induction), where the conclusion is ''certain'', given the premises are correct, inductive reasoning produces conclusions that are at best ''probable'', given the evidence provided. Types The types of inductive reasoning include generalization, prediction, statistical syllogism, argument from analogy, and causal inference. There are also differences in how their results are regarded. Inductive generalization A generalization (more accurately, an ''inductive generalization'') proceeds from premises about a sample to a conclusion about the population. The observation obtained from this sample is projected onto the broader population. : The proportion Q of the sample has attribute A. : Therefore, the proportion Q of the population has attrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiducial Inference
Fiducial inference is one of a number of different types of statistical inference. These are rules, intended for general application, by which conclusions can be drawn from samples of data. In modern statistical practice, attempts to work with fiducial inference have fallen out of fashion in favour of frequentist inference, Bayesian inference and decision theory. However, fiducial inference is important in the history of statistics since its development led to the parallel development of concepts and tools in theoretical statistics that are widely used. Some current research in statistical methodology is either explicitly linked to fiducial inference or is closely connected to it. Background The general approach of fiducial inference was proposed by Ronald Fisher. Here "fiducial" comes from the Latin for faith. Fiducial inference can be interpreted as an attempt to perform inverse probability without calling on prior probability distributions. Fiducial inference quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type II Error
Type I error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. A type II error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. Type I errors can be thought of as errors of commission, in which the status quo is erroneously rejected in favour of new, misleading information. Type II errors can be thought of as errors of omission, in which a misleading status quo is allowed to remain due to failures in identifying it as such. For example, if the assumption that people are ''innocent until proven guilty'' were taken as a null hypothesis, then proving an innocent person as guilty would constitute a Type I error, while failing to prove a guilty person as guilty would constitute a Type II error. If the null hypothesis were inverted, such that people were by default presumed to be ''guilty until proven innocent'', then proving a guilty person's innocence would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real number, real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is f(x) = \frac e^\,. The parameter is the Mean#Mean of a probability distribution, mean or expected value, expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode (statistics), mode), while the parameter \sigma^2 is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural science, natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egon Pearson
Egon Sharpe Pearson (11 August 1895 – 12 June 1980) was one of three children of Karl Pearson and Maria, née Sharpe, and, like his father, a British statistician. Career Pearson was educated at Winchester College and Trinity College, Cambridge, and succeeded his father as professor of statistics at University College London and as editor of the journal '' Biometrika''. He is best known for development of the Neyman–Pearson lemma of statistical hypothesis testing. He was elected a Fellow of the Econometric Society in 1948. Pearson was President of the Royal Statistical Society in 1955–56, and was awarded its Guy Medal in gold in 1955. He was appointed a CBE in 1946. Pearson was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the Fellows of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerzy Neyman
Jerzy Spława-Neyman (April 16, 1894 – August 5, 1981; ) was a Polish mathematician and statistician who first introduced the modern concept of a confidence interval into statistical hypothesis testing and, with Egon Pearson, revised Ronald Fisher's null hypothesis testing. Neyman allocation, an optimal strategy for choosing sample sizes in stratified sampling, is named for him. Spława-Neyman spent the first part of his professional career at various institutions in Warsaw, Poland, and then at University College London; and the second part, at the University of California, Berkeley. Life and career He was born into a Polish people, Polish family in Bendery, in the Bessarabia Governorate of the Russian Empire, the fourth of four children of Czesław Spława-Neyman and Kazimiera Lutosławska. His family was Roman Catholic, and Neyman served as an Altar server, altar boy during his early childhood. Later, Neyman would become an agnostic. Neyman's family descended from a long line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when a result at least as "extreme" would be very infrequent if the null hypothesis were true. More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the p-value, ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is said to be ''statistically significant'', by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or Observational study, observation that involves drawing a Sampling (statistics), sample from a Statistical population, population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a family of statistical methods used to compare the Mean, means of two or more groups by analyzing variance. Specifically, ANOVA compares the amount of variation ''between'' the group means to the amount of variation ''within'' each group. If the between-group variation is substantially larger than the within-group variation, it suggests that the group means are likely different. This comparison is done using an F-test. The underlying principle of ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, which states that the total variance in a dataset can be broken down into components attributable to different sources. In the case of ANOVA, these sources are the variation between groups and the variation within groups. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. In its simplest form, it provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the Student's t-test#Independent two-sample t-test, ''t''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis (often denoted ''H''0) is the claim in scientific research that the effect being studied does not exist. The null hypothesis can also be described as the hypothesis in which no relationship exists between two sets of data or variables being analyzed. If the null hypothesis is true, any experimentally observed effect is due to chance alone, hence the term "null". In contrast with the null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis (often denoted ''H''A or ''H''1) is developed, which claims that a relationship does exist between two variables. Basic definitions The null hypothesis and the ''alternative hypothesis'' are types of conjectures used in statistical tests to make statistical inferences, which are formal methods of reaching conclusions and separating scientific claims from statistical noise. The statement being tested in a test of statistical significance is called the null hypothesis. The test of significance is designed to assess the strength of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |