|
Soma (drink)
In the Vedic tradition, ''soma'' () is a ritual drink of importance among the early Vedic Indo-Aryans. The Rigveda mentions it, particularly in the Soma Mandala. Gita mentions the drink in chapter 9. It is equivalent to the Iranian haoma. The texts describe the preparation of soma by means of extracting the juice from a plant, the identity of which is now unknown and debated among scholars. Both in the ancient religions of Historical Vedic religion and Zoroastrianism, the name of the drink and the plant are not exactly the same.Victor Sarianidi, Viktor Sarianidi in The PBS Documentary The Story of India There has been much speculation about the most likely identity of the original plant. Traditional Indian accounts, such as those from practitioners of Ayurveda, Siddha medicine, and Somayajna called Somayajis, identify the plant as "Somalata" ('' Cynanchum acidum''). Non-Indian researchers have proposed candidates including ''Amanita muscaria'', ''Psilocybin'' mushroo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''. The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. There are four Vedas: the Rigveda, the Yajurveda, the Samaveda and the Atharvaveda. Each Veda has four subdivisions – the Samhitas ( mantras and benedictions), the Brahmanas (commentaries on and explanation of rituals, ceremonies and sacrifices – Yajñas), the Aranyakas (text on rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices and symbolic-sacrifices), and the Upanishads (texts discussing meditation, philosophy and spiritual knowledge).Gavin Flood (1996), ''An Introduction to Hinduism'', Cambridge University Press, , pp. 35–39A Bhattacharya (2006), ''Hindu Dharma: Introduction to Scriptures and Theology'', , pp. 8–14; George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocybin Mushrooms
Psilocybin mushrooms, or psilocybin-containing mushrooms, commonly known as magic mushrooms or as shrooms, are a type of hallucinogenic mushroom and a polyphyletic informal group of fungi that contain the prodrug psilocybin, which turns into the psychedelic psilocin upon ingestion. The most potent species are members of genus ''Psilocybe'', such as '' P. azurescens'', '' P. semilanceata'', and '' P. cyanescens'', but psilocybin has also been isolated from approximately a dozen other genera, including '' Panaeolus'' (including '' Copelandia''), '' Inocybe'', '' Pluteus'', ''Gymnopilus'', and '' Pholiotina''. Amongst other cultural applications, psilocybin mushrooms are used as recreational drugs. They may be depicted in Stone Age rock art in Africa and Europe, but are more certainly represented in sculptures and glyphs seen throughout the Americas. Indoor cultivation '' Psilocybe cubensis'' grows naturally in tropical and subtropical conditions, often near ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan" (meaning ) in both respective native languages and most other languages. The region is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the southwest, European Russia to the northwest, China and Mongolia to the east, Afghanistan and Iran to the south, and Siberia to the north. Together, the five Central Asian countries have a total population of around million. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians, and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. As the result of Turkic migration, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Kyrgyzs, Volga Tatars, Tatars, Turkmens, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
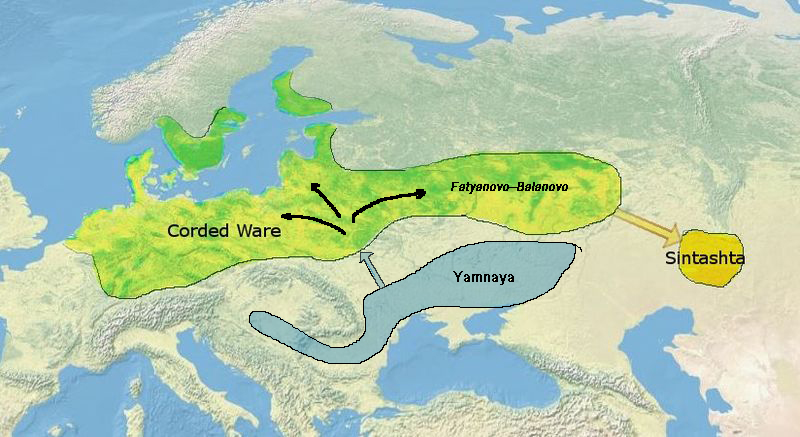
Kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus (burial mound) constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons, and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asia and Eastern, Southeast, Western, and Northern Europe during the third millennium BC. The earliest kurgans date to the fourth millennium BC in the Caucasus, and some researchers associate these with the Indo-Europeans. Kurgans were built in the Eneolithic, Bronze, Iron, Antiquity, and Middle Ages, with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia. Etymology According to the Etymological dictionary of the Ukrainian language the word "kurhan" is borrowed directly from the Kipchak, part of the Turkic languages, and means: fortress, embankment, high grave. The word has two possible etymologies, either from the Old Turkic root ''qori-'' "to close, to block, to guard, to protect", or ''qur-'' " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronovo Culture
The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1150 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.3: "...By Andronovo cultures we may understand only Fyodorovka and Alakul cultures..."Parpola, Asko, (2020)"Royal 'Chariot' Burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological Correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian Languages" in Studia Orientalia Electronica, Vol. 8, No. 1, Oct 23, 2020, p.188: "...the Alakul’ culture (c.2000–1700 BCE) in the west and the Fëdorovo culture (c.1850–1450 BCE) in the east..." spanning from the southern Urals to the upper Yenisei River in central Siberia and western Xinjiang in the east. In the south, the Andronovo sites reached Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It is agreed among scholars that the Andronovo culture was Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian.: "Archaeologists are now generally agreed that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintashta Culture
The Sintashta culture is a Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Southern Urals, dated to the period 2200–1900 BCE. It is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka complex, –1750 BCE. The culture is named after the Sintashta archaeological site, in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, and spreads through Orenburg Oblast, Bashkortostan, and Northern Kazakhstan. Widely regarded as the origin of the Indo-Iranian languages, whose speakers originally referred to themselves as the ''Aryan''s'','' the Sintashta culture is thought to represent an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture. The earliest known chariots have been found in Sintashta burials, and the culture is considered a strong candidate for the origin of the technology, which spread throughout the Old World and played an important role in ancient warfare. Sintashta settlements are also remarkable for the intensity of copper mining and bronze metallurgy carried out there, which is unusual f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e.g., Tajikistan and Afghanistan), Armenia, and areas of southern India. Historically, Indo-European languages were also spoken in Anatolia. Some European languages of this family— English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Spanish, and Dutch—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, including Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic, all of which contain present-day living languages, as well as many more extinct branches. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Spanish, Portuguese, Russian, Hindustani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of peoples predominantly found in South Asia, who (traditionally) speak Indo-Aryan languages. Historically, Aryans were the Indo-Iranian speaking pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and introduced the Proto-Indo-Aryan language. The early Indo-Aryan peoples were known to be closely related to the Indo-Iranian group that have resided north of the Indus River; an evident connection in cultural, linguistic, and historical ties. Today, Indo-Aryan speakers are found south of the Indus, across the modern-day regions of Bangladesh, Nepal, eastern-Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and northern-India. History Proto-Indo-Iranians The introduction of the Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent was the outcome of a migration of Indo-Aryan people from Central Asia into the northern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka). These migrations started appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE and its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from approximately 4500 BCE to 2500 BCE during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manfred Mayrhofer
Manfred Mayrhofer (26 September 1926 – 31 October 2011) was an Austrian Indo-Europeanist who specialized in Indo-Iranian languages. Mayrhofer served as professor emeritus at the University of Vienna. He is noted for his etymological dictionary of Sanskrit. Mayrhofer was born in Linz and studied Indo-European and Semitic linguistics and philosophy at the University of Graz, where he received his Ph.D. in 1949. From 1953 to 1963 he taught at the University of Würzburg, and from 1963 to 1966 he was a professor at Saarland University. In 1966 he returned to Austria, serving as professor at the University of Vienna until his retirement in 1990. He died in Vienna at the age of 85. Works *1953 – ''Sanskrit-Grammatik''. ** English translation: ''A Sanskrit Grammar'' (2003), . *1956–80 – ''Kurzgefasstes etymologisches Wörterbuch des Altindischen''. 4 vols. Heidelberg: Carl Winter. . ** 1956 – vol. 1: A–Th ** 1963 – vol. 2: D–M ** 1976 – vol. 3: Y–H ** 1980 – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
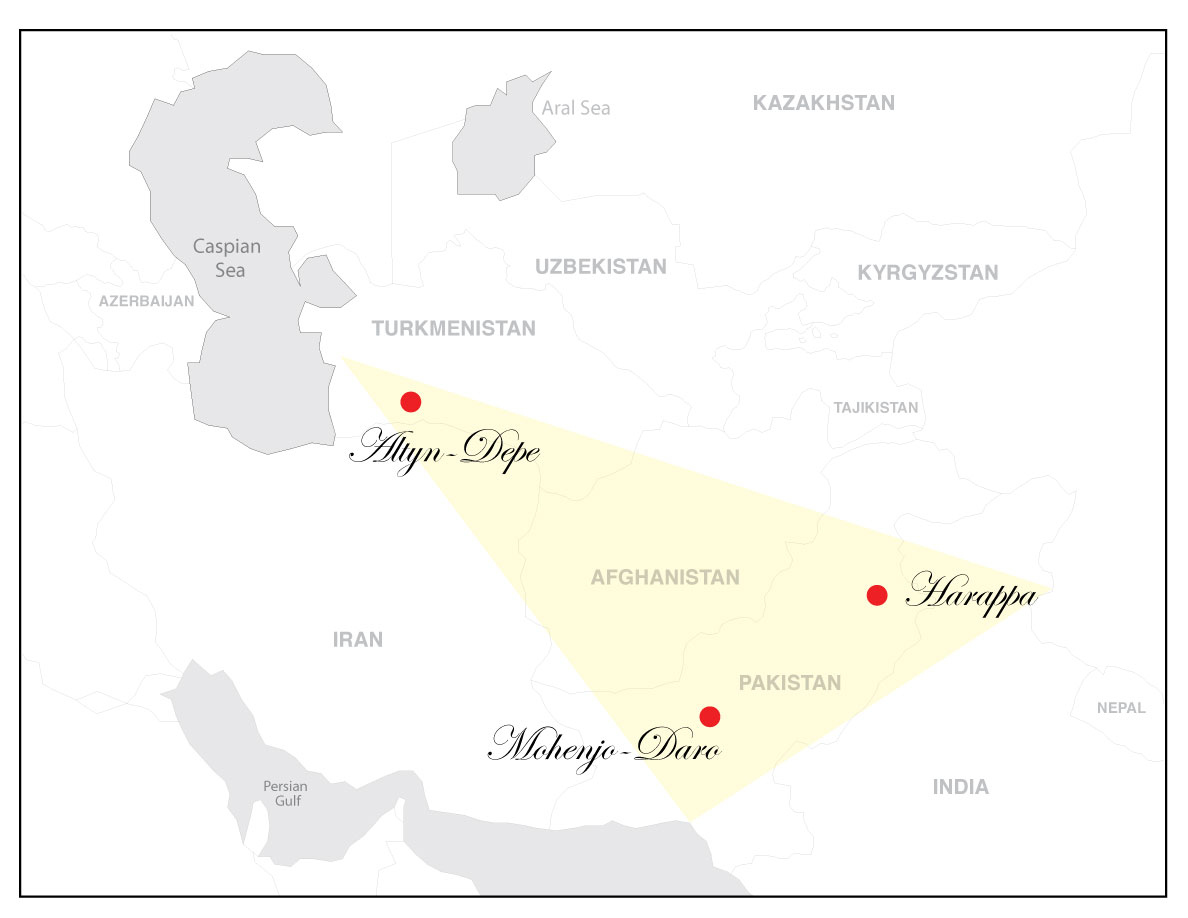
Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to –1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, –1700 BC.Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC): an overview" in Bertille Lyonnet and Nadezhda A. Dubova (eds.), ''The World of the Oxus Civilization'', Routledge, London and New York, p. 32.: "...Salvatori has often dated its beginning very early (ca. 2400 BC), to make it match with Shahdad where a large amount of material similar to that of the BMAC has been discovered. With the start of international cooperation and the multiplication of analyses, the dates now admitted by all place the Oxus Civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avestan
Avestan ( ) is the liturgical language of Zoroastrianism. It belongs to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family and was First language, originally spoken during the Avestan period, Old Iranian period ( – 400 BCE) by the Arya (Iran), Iranians living in the Avestan geography, eastern portion of Greater Iran. After Avestan Language death, became extinct, its religious texts were first transmitted Oral literature, orally until being collected and Sasanian Avesta, put into writing during the Sasanian empire, Sasanian period ( – 500 CE). The Avesta, extant material falls into two Variety (linguistics), groups: Old Avestan ( – 900 BCE) and Younger Avestan ( – 400 BCE). The immediate ancestor of Old Avestan was the Proto-Iranian language, a sister language to the Proto-Indo-Aryan language, with both having developed from the earlier Proto-Indo-Iranian language. As such, Old Avestan is quite close in both grammar and lexi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |