|
Sign Languages Of The United States
The most commonly used language in the United States is English language, English (specifically American English), which is the national language. A March 2025 executive order declared English the official language of the United States; despite some previous attempts, no legislation has been passed by the U.S. Congress to make English the official language. In addition, 32 U.S. states out of 50 and all five U.S. territories have declared English as an official language, with three states and most territories having adopted English plus one or more other official languages. Accommodations for non-English-language speakers are sometimes made under various federal, state, and local laws. The majority of the U.S. population (78%) speaks only English at home as of 2023, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) of the U.S. Census Bureau. The remainder of the population speaks many other languages at home, most notably Spanish language, Spanish (13.4% of the population), Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Order 14224
Executive Order 14224, titled Designating English as the Official Language of the United States, is an executive order signed by Donald Trump on March 1, 2025 to designate English language, English as the official language of the United States. It does not attach any specific rights to the designation. Changes to federal guidance on non-English accommodations EO 14224 repeals Executive Order 13166, issued by President Bill Clinton on August 11, 2000. The Clinton order required agencies of the federal government to make plans to implement Department of Justice guidance ensuring people with limited English proficiency would have improved access to federal services on a non-discriminatory basis, to the degree needed and without an undue burden on the agencies. The Trump order instructed agency heads to make accommodations as they "deem necessary to fulfill their respective agencies' mission". Legal authority The United States Congress, U.S. Congress has never passed legislation d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyak Language
Eyak is an extinct Na-Dené language, historically spoken by the Eyak people, indigenous to south-central Alaska, near the mouth of the Copper River. The name Eyak comes from a Chugach Sugpiaq name () for an Eyak village at the mouth of the Eyak River.Michael E. Krauss 200A history of Eyak language documentation and study: Fredericæ de Laguna in Memoriam. ''Arctic Anthropology'' 43 (2): 172-217 The closest relatives of Eyak are the Athabaskan languages. The Eyak–Athabaskan group forms a basic division of the Na-Dené language family, the other being Tlingit. Numerous Tlingit place names along the Gulf Coast are derived from names in Eyak; they have obscure or even nonsensical meanings in Tlingit, but oral tradition has maintained many Eyak etymologies. The existence of Eyak-derived Tlingit names along most of the coast towards southeast Alaska is strong evidence that the prehistoric range of Eyak was once far greater than it was at the time of European contact. This co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsimshian Languages
The Tsimshianic languages are a family of languages spoken in northwestern British Columbia and in Southeast Alaska on Annette Island and Ketchikan. All Tsimshianic languages are endangered, some with only around 400 speakers. Only around 2,170 people of the ethnic Tsimshian population in Canada still speak a Tsimshian language; about 50 of the 1,300 Tsimshian people living in Alaska still speak Coast Tsimshian.Alaska Native Language Center. (2001-12-07)"Tsimshian." University of Alaska Fairbanks. Retrieved on 2007-04-11.Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.). (2005)"Tsimshian." Dallas, TX: SIL International Retrieved on 2007-04-11. Tsimshianic languages are considered by most linguists to be an independent language family, with four main languages: Coast Tsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlingit Language
The Tlingit language ( ; ' ) is an Indigenous language of the northwestern coast of North America, which is spoken by the Tlingit people of Southeast Alaska and Western Canada and is a branch of the Na-Dene language family. Extensive effort is being put into revitalization programs in Southeast Alaska to revive and preserve the Tlingit language and culture. Missionaries of the Russian Orthodox Church were the first to develop a written version of Tlingit by using the Cyrillic script to record and translate it when the Russian Empire had contact with Alaska and the coast of North America down to Sonoma County, California. After the Alaska Purchase, English-speaking missionaries from the United States developed a written version of the language with the Latin alphabet. History The history of Tlingit is poorly known, mostly because there is no written record until the first contact with Europeans around the 1790s. Documentation was sparse and irregular until the early 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanana Language
Lower Tanana (also Tanana and/or Middle Tanana) is an endangered language spoken in Interior Alaska in the lower Tanana River villages of Minto and Nenana. Of about 380 Tanana people in the two villages, about 30 still speak the language. As of 2010, “Speakers who grew up with Lower Tanana as their first language can be found only in the 250-person village of Minto.” It is one of the large family of Athabaskan languages, also known as Dené. The Athabaskan Athabaskan ( ; also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large branch of the Na-Dene language family of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, ... (or Dené) bands who formerly occupied a territory between the Salcha and the Goodpaster rivers spoke a distinct language that linguists term the Middle Tanana language. Dialects *Toklat area dialect (') *Minto Flats-Nenana River dialect: Minto (') and Nenana (') *Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanacross Language
Tanacross (also Transitional Tanana) is an endangered language, endangered Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan language spoken by fewer than 60 people in eastern Alaska Interior, Interior Alaska. Overview The word Tanacross (from "Tanana Athabaskans, Tanana Crossing") has been used to refer both to a village in eastern Alaska and to an ethnolinguistic group. The modern village of Tanacross, Alaska, Tanacross is accessible by a short access road from the Alaska Highway, and some speakers now reside in the regional center of Tok, Alaska, Tok, located approximately ten miles east of the village on the highway. In addition several speakers now reside in the nearest commercial center of Fairbanks, Alaska, Fairbanks, located two hundred miles downstream from Tanacross village and accessible by all-weather highway. Tanacross is the ancestral language of the Mansfield-Kechumstuk and Healy Lake, Alaska, Healy Lake-Joseph Village bands of Tanana Athabaskans, Tanana Athabaskan people, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
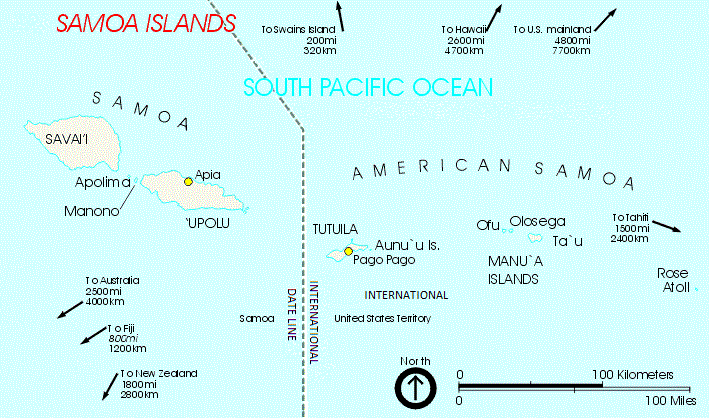
Samoan Language
Samoan ( or , ) is a Polynesian languages, Polynesian language spoken by Samoans of the Samoan Islands. Administratively, the islands are split between the sovereign country of Samoa and the Unincorporated territories of the United States, United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language, alongside English language, English, in both jurisdictions. It is widely spoken across the Pacific region, heavily so in New Zealand and in Australia and the United States. Among the Polynesian languages, Samoan is the most widely spoken by number of native speakers. Samoan is spoken by approximately 260,000 people in the archipelago and with many Samoans living in diaspora in a number of countries, the total number of speakers worldwide was estimated at 510,000 in 2015. It is the third-most widely spoken language in New Zealand, where 2.2% of the population, 101,900 people, were able to speak it as of 2018. The language is notable for the phonology, phonological differenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koyukon Language
Koyukon (also called ''Denaakk'e'') is the geographically most widespread Athabascan language spoken in Alaska. The Athabaskan language is spoken along the Koyukuk and the middle Yukon Rivers in western interior Alaska. In 2007, the language had approximately 300 speakers, who were generally older adults and bilingual in English. The total Koyukon ethnic population was 2,300. History Jules Jetté, a French Canadian Jesuit missionary, began recording the language and culture of the Koyukon people in 1898. Considered a fluent Koyukon speaker after spending years in the region, Jetté died in 1927. He had made a significant quantity of notes on the Koyukon people, their culture and beliefs, and their language. Eliza Jones, a Koyukon, came across these manuscripts while studying, and later working, at the University of Alaska in the early 1970s. Working from Jetté's notes and in consultation with Koyukon tribal elders, Jones wrote the ''Koyukon Athabaskan Dictionary.'' It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holikachuk Language
Holikachuk (own name: ) is a recently extinct Athabaskan language formerly spoken at the village of Holikachuk () on the Innoko River in central Alaska. In 1962, residents of Holikachuk relocated to Grayling on the lower Yukon River. Holikachuk is intermediate between the Deg Xinag and Koyukon languages, linguistically closer to Koyukon but socially much closer to Deg Xinag, which has influenced it. Though it was recognized by scholars as a distinct language as early as the 1840s, it was only definitively identified in the 1970s. Of about 180 Holikachuk people, only about 5 spoke the language in 2007. In March 2012, the last living fluent speaker of Holikachuk died in Alaska.ICTMN Staff. "Alaska Native Language Loses Last Fluent Speaker." Indian Country Today Media Network. 18 Apr. 2012. Web. 19 Apr. 2012 James Kari compiled a short dictionary of Holikachuk in 1978, but Holikachuk remains one of the least documented Alaska Native languages.Kari, James. 1978Holikachuk Noun Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Language
Hawaiian (', ) is a critically endangered Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family, originating in and native to the Hawaiian Islands. It is the native language of the Hawaiian people. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the U.S. state of Hawaii. King Kamehameha III established the first Hawaiian-language constitution in 1839 and 1840. In 1896, the Republic of Hawaii passed Act 57, an English-only law which subsequently banned Hawaiian language as the medium of instruction in publicly funded schools and promoted strict physical punishment for children caught speaking the Hawaiian language in schools. The Hawaiian language was not again allowed to be used as a medium of instruction in Hawaii's public schools until 1987, a span of 91 years. The number of native speakers of Hawaiian gradually decreased during the period from the 1830s to the 1950s. English essentially displaced Hawaiian on six of seven inhabited islands. In 2001, native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hän Language
The Hän language (alternatively spelled as Haen) (also known as Dawson, Han-Kutchin, Moosehide) is a Northern Athabaskan language spoken by the Hän Hwëch'in (translated to ''people who live along the river'', sometimes anglicized as ''Hankutchin''). Athabascan refers to the interrelated complexity of languages spoken in Canada and Alaska each with its own dialect: the village of Eagle, Alaska in the United States and the town of Dawson City, Yukon Territory in Canada, though there are also Hän speakers in the nearby city of Fairbanks, Alaska. Furthermore, there was a decline in speakers in Dawson City as a result of the influx of gold miners in the mid-19th century. Hän is in the Northern Athabaskan subgrouping of the Na-Dené language family. It is most closely related to Gwich'in and Upper Tanana. Phonology Consonants The consonants of Hän are listed below with IPA notation on the left, the standard orthography in : Vowels Nasal vowels are marked orthographi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |