|
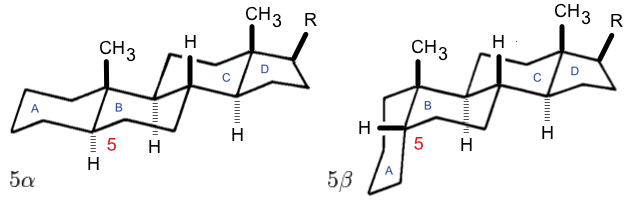
Secosteroids
A secosteroid () is a type of steroid with a "broken" ring. The word ''secosteroid ''derives from the Latin verb ''secare'' meaning "to cut", and 'steroid'. Secosteroids are described as a subclass of steroids under the IUPAC nomenclature. Some sources instead describe them as compounds derived from steroids. Types or subclasses of secosteroids are defined by the carbon atoms of the parent steroid skeleton where the ring cleavage has taken place. For example, 9,10-secosteroids are derived from cleavage of the bond between carbon atoms C9 and C10 of the steroid B-ring (similarly 5,6-secosteroids, 13,14-secosteroids, etc.). The prototypical secosteroid is cholecalciferol Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3, colecalciferol or calciol, is a type of vitamin D that is produced by the skin when exposed to UV light, UVB light; it is found in certain foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement. Cholecalcife ... (vitamin D3). Its IUPAC systematic is "(5''Z'',7''E'')-(3'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3, colecalciferol or calciol, is a type of vitamin D that is produced by the skin when exposed to UV light, UVB light; it is found in certain foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement. Cholecalciferol is synthesised in the skin following sunlight exposure. It is then converted in the liver to calcifediol (25-hydroxycholecalciferol D), which is further converted in the kidney to calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol D). One of calcitriol's most important functions is to promote calcium uptake by the intestines. Cholecalciferol is present in food such as fatty fish, beef liver, eggs, and cheese. In some countries, cholecalciferol is also added to products like plants, cow milk, fruit juice, yogurt, and margarine. Cholecalciferol can be taken orally as a dietary supplement to prevent vitamin D deficiency or as a medication to treat associated diseases, including rickets. It is also used in the management of familial hypophosphatem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signal transduction, signaling molecules. Examples include the lipid cholesterol, sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, anabolic steroids, and the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid drug dexamethasone. Hundreds of steroids are found in Fungus, fungi, plants, and animals. All steroids are manufactured in cells from a sterols, sterol: Cholesterol, cholesterol (animals), lanosterol (opisthokonts), or cycloartenol (plants). All three of these molecules are produced via Cyclic compound, cyclization of the triterpene squalene. Structure The steroid nucleus (parent structure, core structure) is called gonane (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene). It is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pure And Applied Chemistry
''Pure and Applied Chemistry'' is the official journal for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published monthly by Walter de Gruyter Walter de Gruyter GmbH, known as De Gruyter (), is a German scholarly publishing house specializing in academic literature. History The roots of the company go back to 1749 when Frederick the Great granted the Königliche Realschule in Be ... and contains recommendations and reports, and lectures from symposia. References Chemistry journals Academic journals established in 1960 De Gruyter academic journals {{Chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national List of chemistry societies, chemistry societies, national Academy of Sciences, academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Cleavage
In chemistry, bond cleavage, or bond fission, is the splitting of chemical bonds. This can be generally referred to as dissociation when a molecule is cleaved into two or more fragments. In general, there are two classifications for bond cleavage: ''homo''lytic and ''hetero''lytic, depending on the nature of the process. The triplet and singlet excitation energies of a sigma bond can be used to determine if a bond will follow the homolytic or heterolytic pathway. A metal−metal sigma bond is an exception because the bond's excitation energy is extremely high, thus cannot be used for observation purposes. In some cases, bond cleavage requires catalysts. Due to the high bond-dissociation energy of C−H bonds, around , a large amount of energy is required to cleave the hydrogen atom from the carbon and bond a different atom to the carbon. Homolytic cleavage In homolytic cleavage, or homolysis, the two electrons in a cleaved covalent bond are divided equally betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Estrogen
A nonsteroidal estrogen is an estrogen with a nonsteroidal chemical structure. The most well-known example is the stilbestrol estrogen diethylstilbestrol (DES). Although nonsteroidal estrogens formerly had an important place in medicine, they have gradually fallen out of favor following the discovery of toxicities associated with high-dose DES starting in the early 1970s, and are now almost never used. On the other hand, virtually all selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are nonsteroidal, with triphenylethylenes like tamoxifen and clomifene having been derived from DES, and these drugs remain widely used in medicine for the treatment of breast cancer among other indications. In addition to pharmaceutical drugs, many xenoestrogens, including phytoestrogens, mycoestrogens, and synthetic endocrine disruptors like bisphenol A, are nonsteroidal substances with estrogenic activity. Pharmacology Nonsteroidal estrogens act as agonists of the estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doisynolic Acid
Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, orally active, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, whose levorotatory isomer is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone. Doisynolic acid is the parent compound of a group of synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogens with high oral activity. The synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogens methallenestril, fenestre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secoergoline
Secoergoline is an structural analog, analogue of ergoline with one or more bonds removed and may refer to: * 3,5-Secoergoline (also known as RU-27251) * 8,10-Secoergoline (e.g., 8,10-seco-LSD also known as NDTDI) * 10,11-Secoergoline (e.g., 10,11-seco-LSD, CT-5252) Other secoergolines include partial clavines like chanoclavine and paliclavine. See also * Seco-LSD * Partial ergoline * Ergoline * Secosteroid {{Chemistry index Partial ergolines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |