|
Science Diplomacy
Science diplomacy describes how scientific exchanges and the cross-border collaboration of scientists or scientific organizations can perform diplomatic functions in the context of international relations. Most often this diplomacy happens as part of scientific cooperation as a means of building relationships between states and within international organizations. Science diplomacy is a set of activities in which scientific, diplomatic, and other interests overlap and in which states, international organizations and non-state actors represent themselves and their interests. It is a global phenomenon. Science diplomacy can include formal, informal, research-based, academic or engineering exchanges. It typically involves interactions between scientists and officials involved in diplomacy. Science diplomacy’s advocates note that science diplomacy aims to address common problems. However, science diplomacy can at times reify or accentuate asymmetrical power relations, and, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Relations
International relations (IR, and also referred to as international studies, international politics, or international affairs) is an academic discipline. In a broader sense, the study of IR, in addition to multilateral relations, concerns all activities among states—such as war, diplomacy, trade, and foreign policy—as well as relations with and among other international actors, such as intergovernmental organizations (IGOs), international nongovernmental organizations (INGOs), international legal bodies, and multinational corporations (MNCs). International relations is generally classified as a major multidiscipline of political science, along with comparative politics, political methodology, political theory, and public administration. It often draws heavily from other fields, including anthropology, economics, geography, history, law, philosophy, and sociology. There are several schools of thought within IR, of which the most prominent are realism, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
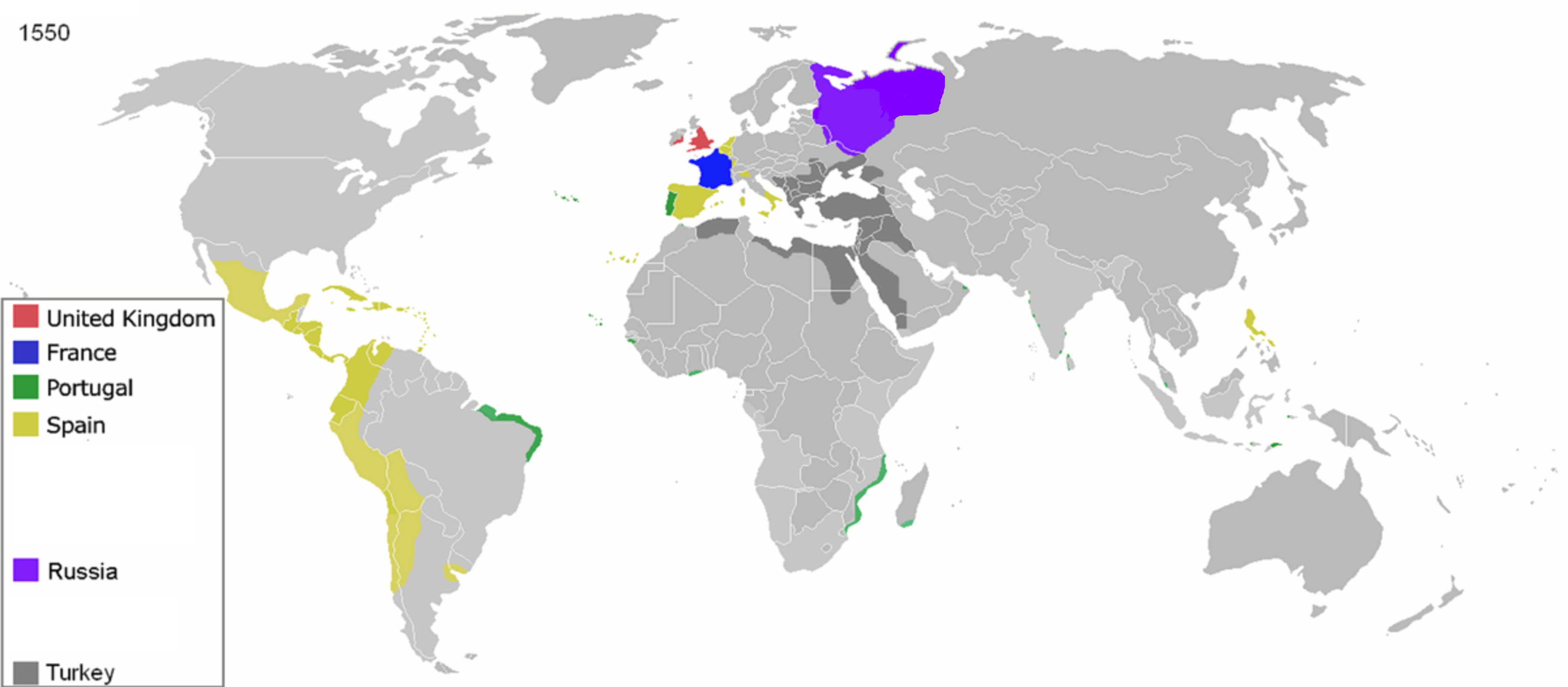
Colonization
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence. Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples for the purpose of cultivation, exploitation, trade and possibly settlement, setting up coloniality and often colonies. Colonization is commonly pursued and maintained by, but distinct from, imperialism, mercantilism, or colonialism. The term "colonization" is sometimes used synonymously with the word "settling", as with colonisation in biology. Settler colonialism is a type of colonization structured and enforced by the settlers directly, while their or their ancestors' metropolitan country ('' metropole'') maintains a connection or control through the settler's activities. In settler colonization, a minority group rules either through the assimilation or oppression of the existing inhabitants, or by establishing itself as the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Foreign Affairs (Japan)
The is an Ministry of Japan, executive department of the Government of Japan, and is responsible for the country's foreign policy of Japan, foreign policy and international relations. The ministry was established by the second term of the third article of the National Government Organization Act, and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Establishment Act. According to the law, the mission of the ministry is "to aim at improvement of the profits of Japan and Japanese nationals, while contributing to maintenance of peaceful and safe international society, and, through an active and eager measure, both to implement good international environment and to keep and develop harmonic foreign relationships". Policy formulation Under the Constitution of Japan, 1947 constitution, the Cabinet of Japan, cabinet exercises primary responsibility for the conduct of foreign affairs, subject to the overall supervision of the National Diet. The Prime Minister of Japan, prime minister is required to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
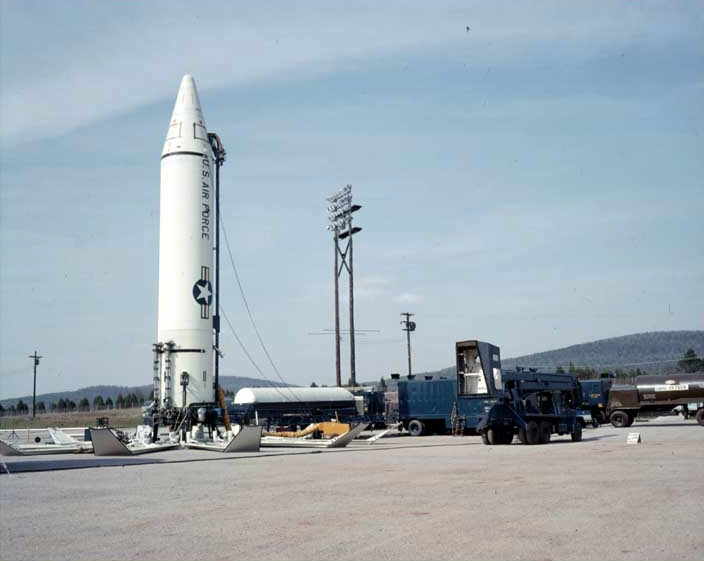
Castle Bravo
Castle Bravo was the first in a series of high-yield thermonuclear weapon design tests conducted by the United States at Bikini Atoll, Marshall Islands, as part of ''Operation Castle''. Detonated on 1 March 1954, the device remains the most powerful nuclear weapon, nuclear device ever detonated by the United States and the first lithium deuteride-fueled thermonuclear weapon tested using the Teller–Ulam design. Castle Bravo's Nuclear weapon yield, yield was , 2.5 times the predicted , due to unforeseen additional reactions involving Isotopes of lithium, lithium-7, which led to radioactive contamination in the surrounding area. Radioactive nuclear fallout, the heaviest of which was in the form of pulverized surface coral from the detonation, fell on residents of Rongelap Atoll, Rongelap and Utirik Atoll, Utirik atolls, while the more particulate and gaseous fallout spread around the world. The inhabitants of the islands were evacuated three days later and suffered radiation sickn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 as an autonomous international organization; though governed by its own founding treaty, the IAEA Statute, the organization reports to both the General Assembly and the Security Council of the United Nations, and is headquartered at the UN Office at Vienna, Austria. The IAEA was created in response to growing international concern toward nuclear weapons, especially amid rising tensions between the foremost nuclear powers, the United States and the Soviet Union. U.S. president Dwight D. Eisenhower's " Atoms for Peace" speech, which called for the creation of an international organization to monitor the global proliferation of nuclear resources and technology, is credited with catalyzing the formation of the IAEA, whose Statute came into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Office At Geneva
The United Nations Office at Geneva (UNOG, ) in Geneva, Switzerland, is one of the four major offices of the United Nations where numerous different UN agencies have a joint presence. The main UNOG administrative offices are located inside the Palace of Nations, Palais des Nations complex, which was originally constructed for the League of Nations between 1929 and 1938. Besides United Nations administration, the Palais des Nations also hosts the offices for a number of programmes and funds such as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the United Nations Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) and the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (ECE). The United Nations System, United Nations and its specialized agencies, programmes and funds may have other offices or functions hosted outside the Palais des Nations, normally in office spaces provided by the Swiss Federal Council, Swiss Government. UN specialised agencies and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Arms Race
The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War. During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuclear stockpiles, other countries developed nuclear weapons, though no other country engaged in Nuclear weapon design, warhead production on nearly the same scale as the two superpowers. The race began during World War II, dominated by the Western Allies' Manhattan Project and Soviet atomic spies. Following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, the Soviet Union accelerated Soviet atomic bomb project, its atomic bomb project, resulting in the RDS-1 test in 1949. Both sides then pursued an all-out effort, realizing deployable thermonuclear weapons by the mid-1950s. The arms race in Nuclear weapons testing, nuclear testing culminated with the 1961 Tsar Bomba. Atmospheric testing was ended in the 1963 Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Atomic Energy Commission
The United Nations Atomic Energy Commission (UNAEC) was founded on 24 January 1946 by the very first resolution of the United Nations General Assembly "to deal with the problems raised by the discovery of atomic energy." The General Assembly asked the Commission to make specific proposals: (a) for extending between all nations the exchange of basic scientific information for peaceful ends; (b) for control of atomic energy to the extent necessary to ensure its use only for peaceful purposes; (c) for the elimination from national armaments of atomic weapons and of all other major weapons adaptable to mass destruction; (d) for effective safeguards by way of inspection and other means to protect complying States against the hazards of violations and evasions. On 14 December 1946, the General Assembly passed a follow-up resolution urging an expeditious completion of the report by the Commission as well as its consideration by the United Nations Security Council. The Security Counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoms For Peace Stamp
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. A human hair is about a million carbon atoms wide. Atoms are smaller than the shortest wavelength of visible light, which means humans cannot see atoms with conventional microscopes. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is not possible due to quantum mechanics, quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. Protons hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Council Of Scientific Unions
The International Council for Science (ICSU, after its former name, International Council of Scientific Unions) was an international non-governmental organization devoted to international cooperation in the advancement of science. Its members were national scientific bodies and international scientific unions. In 2017, the ICSU comprised 122 multi-disciplinary National Scientific Members, Associates and Observers representing 142 countries and 31 international, disciplinary Scientific Unions. ICSU also had 22 Scientific Associates. In July 2018, ICSU merged with the International Social Science Council (ISSC) to form the International Science Council (ISC) at a constituent general assembly in Paris. Mission and principles The ICSU's mission was to strengthen international science for the benefit of society. To do this, the ICSU mobilized the knowledge and resources of the international scientific community to: * Identify and address major issues of importance to science and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifesto Of The Ninety-Three
The "Manifesto of the Ninety-Three" (; originally "To the Civilized World," , by "Professors of Germany") is a 4 October 1914 proclamation by 93 prominent Germans supporting Germany in the start of World War I. The Manifesto galvanized support for the war throughout German schools and universities, but many foreign intellectuals were outraged. The astronomer Wilhelm Julius Foerster soon repented having signed the document. With the physiologist Georg Friedrich Nicolai, he drew up the '' Manifesto to the Europeans''. They argued: Whilst various people expressed sympathy with those sentiments, only the philosopher Otto Buek and Albert Einstein signed Foerster and Nicolai's counter manifesto and it remained unpublished at the time. It was subsequently brought to light by Einstein. In 1921, a report in ''The New York Times'' found that of 76 surviving signatories, 60 expressed varying degrees of regret, and some claimed not to have seen what they had signed. Purpose and reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |