|
Science And Technology In Uganda
Science and technology in Uganda refers to the growth within the technological industry in response to government efforts to develop a national innovation system, as well as any subsequent socioeconomic and cultural impacts of these endeavours. In 2013, manufacturers contributed 10% of GDP, compared to 21% for the industry as a whole and 25% for agriculture. Half of GDP (54%) came from the services sector. In 2012, Uganda's main exports were all agricultural products: unroasted coffee (30.6%), cotton (5.6%) and tobacco (5.5%). In 2010, it spent less than 5% of GDP on agriculture, despite African countries having committed to the target of 10% when the African Union adopted the Maputo Declaration in 2003. They reiterated this goal in the Malabo Declaration adopted in Equatorial Guinea in 2014. In the latter declaration, they reaffirmed their 'intention to devote 10% of their national budgets to agricultural development and agreed to target such as doubling agricultural productivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance of a country or region. Several national and international economic organizations maintain definitions of GDP, such as the OECD and the International Monetary Fund. GDP is often used as a metric for international comparisons as well as a broad measure of economic progress. It is often considered to be the world's most powerful statistical indicator of national development and progress. The GDP can be divided by the total population to obtain the average GDP per capita. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. Nominal GDP is useful when comparing national economies on the international market according to the exchange rate. To compare economies over time inflation can be adjus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Researchers (HC) In Southern Africa Per Million Inhabitants, 2013 Or Closest Year
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, economic, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
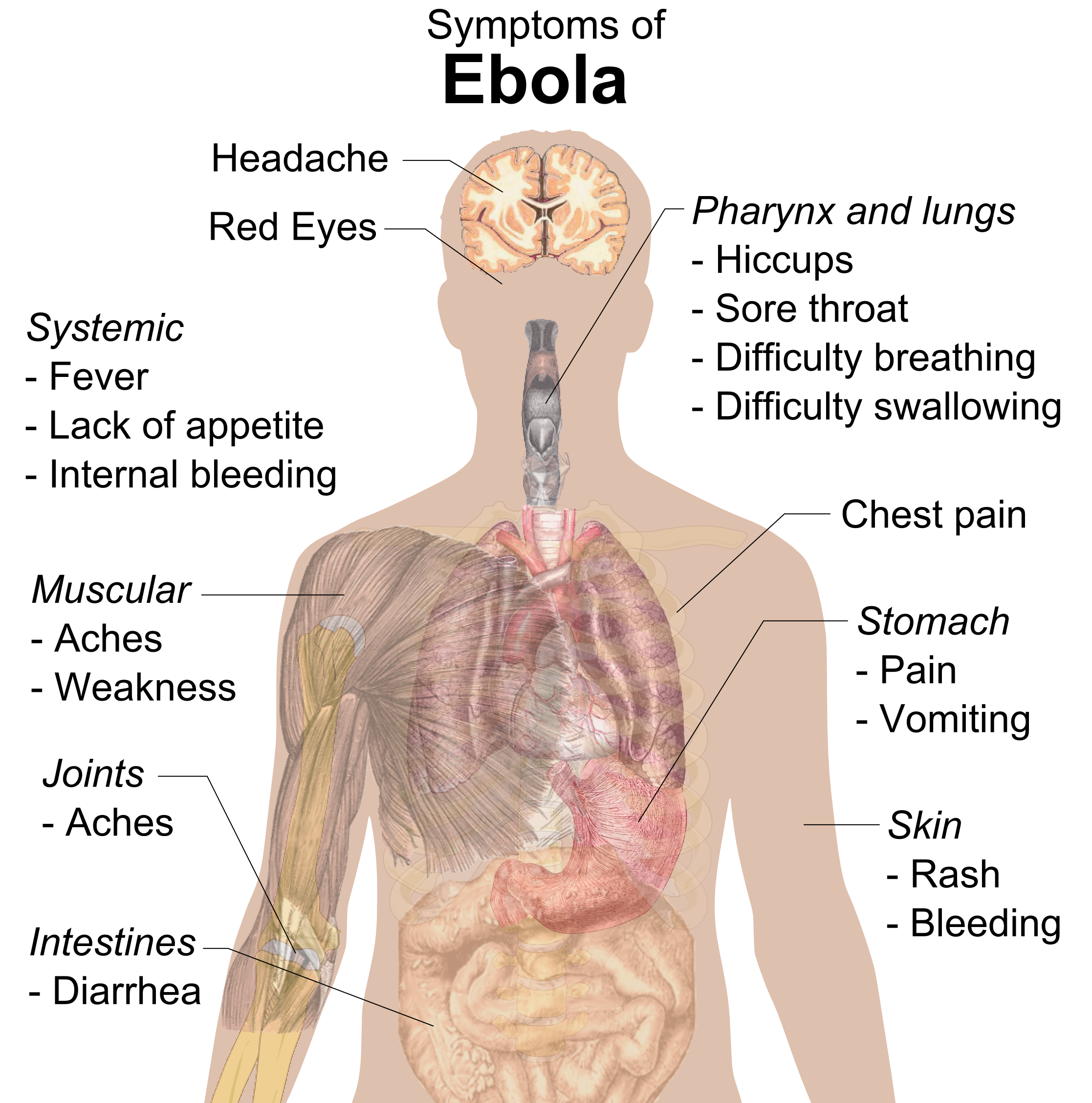
Ebola Epidemic
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. It kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between 6 and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start.Ebola in Uganda: An Ebola vaccine was approved by the US FDA in December 2019. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergovernmental Authority On Development
The Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) is an eight-country trade bloc in Africa. It includes governments from the Horn of Africa, Nile Valley and the African Great Lakes. It is headquartered in Djibouti. Formation The Intergovernmental Authority on Development was established in 1996. It succeeded the earlier Intergovernmental Authority on Drought and Development (IGADD), a multinational body founded in 1986 by Djibouti, Ethiopia, Somalia, Sudan, Uganda and Kenya, with a focus on development and environmental control. IGADD's headquarters were later moved to Djibouti, following an agreement signed in January 1986 by the member states. Eritrea joined the organization in 1993, upon achieving independence. In April 1995, the Assembly of Heads of State and Government met in Addis Ababa, where they agreed to strengthen cooperation through the organization. This was followed with the signing of a Letter of Instrument to Amend the IGADD Charter / Agreement on 21 March 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Development Bank
The African Development Bank Group (AfDB, also known as BAD in French) is a multilateral development finance institution, headquartered in Abidjan, Ivory Coast since September 2014. The AfDB is a financial provider to African governments and private companies investing in the regional member countries (RMC). The AfDB was founded in 1964 by the Organisation of African Unity, which is the predecessor of the African Union. The AfDB comprises three entities: The African Development Bank, the African Development Fund and the Nigeria Trust Fund. History Following the end of the colonial period in Africa, a growing desire for more unity within the continent led to the establishment of two draft charters: one for the establishment of the Organization of African Unity (established in 1963, later replaced by the African Union) and one for a regional development bank. A draft accord was submitted to top African officials and then to the Conference of Finance Ministers on the Estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East African Development Bank
The East African Development Bank (EADB) is a regional development finance institution located in Kampala, Uganda with the objective of promoting development in the member countries of the East African Community. The current member states of the EADB are Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, and Tanzania including other development and commercial financial institutions. The bank was initiated in 1967 and has been in operation since the development of its charter. Overview EADB plays a threefold role of lender, adviser, and development partner. The bank supports economic development in member states through short and long term lending of financially and sustainable projects. It provides a range of products and services that are tailored for the region's development requirements. The East African Development Bank also has experienced, financial backing, staff, and knowledge of the region's financial requirements. , the institution's total assets were valued at approximately US$415,998 million, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Economic Community
The African Economic Community (AEC) is an organization of African Union states establishing grounds for mutual economic development among the majority of African states. The stated goals of the organization include the creation of free trade areas, customs unions, a single market, a central bank, and a common currency (see African Monetary Union) thus establishing an economic and monetary union. Goals The AEC founded through the Abuja Treaty, signed in 1991 and entered into force in 1994 is envisioned to be created in six stages: # (completed in 1999) Creation of regional blocs in regions where such do not yet exist # (completed in 2007) Strengthening of intra-REC integration and inter-REC harmonisation # (completed in 2021) Establishing of a free trade area and customs union in each regional bloc # (to be completed in 2023) Establishing of a continent-wide customs union (and thus also a free trade area) # (to be completed in 2025) Establishing of a continent-wide African ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Market For Eastern And Southern Africa
The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is a regional economic community in Africa with twenty-one member states stretching from Tunisia to Eswatini. COMESA was formed in December 1994, replacing a Preferential Trade Area which had existed since 1981. Nine of the member states formed a free trade area in 2000 (Djibouti, Egypt, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Sudan, Zambia and Zimbabwe), with Rwanda and Burundi joining the FTA in 2004, the Comoros and Libya in 2006, Seychelles in 2009, Uganda in 2012 and Tunisia in 2018. COMESA is one of the pillars of the African Economic Community. In 2008, COMESA agreed to an expanded free-trade zone including members of two other African trade blocs, the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC). COMESA is also considering a common visa scheme to boost tourism. Membership Current members Former members Organs According to the treaties, the following organs hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East African Community
The East African Community (EAC) is an intergovernmental organisation in East Africa. The EAC's membership consists of eight states: Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Federal Republic of Somalia, the Republics of Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Uganda, and Tanzania. William Ruto, the president of Kenya, is the current EAC chairman. The organisation was founded in 1967, collapsed in 1977, and was revived on 7 July 2000. The main objective of the EAC is to foster regional economic integration. In 2008, after negotiations with the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), the EAC agreed to an expanded free trade area including the member states of all three organisations. The EAC is an integral part of the African Economic Community. The EAC is a potential precursor to the establishment of the East African Federation, a proposed federation of its members into a single sovereign state. In 2010, the EAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO Institute For Statistics
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) is the statistical office of UNESCO and is the UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and technology, culture, and communication. The UIS was established in 1999. Based in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, it was created by a collaboration between Université de Montréal, the INRS and UNESCO to provide statistics for the UN. The institute serves member states of UNESCO as well as intergovernmental and nongovernmental organisations, research institutes, universities, and citizens. All data is available for free. Its offices are based at Côte-des-Neiges on the main campus of Université de Montréal, in building 3333 Queen-Mary Road. The institute provides education data to many global reports and databases, such as the SDG global database of the UN Stats Division, the Global Education Monitoring Report, World Development Indicators and World Development Report (World Bank), Human Development Report ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The bloc was launched on 9 July 2002 in Durban, South Africa. The intention of the AU was to replace the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa by 32 signatory governments; the OAU was disbanded on 9 July 2002. The most important decisions of the AU are made by the Assembly of the African Union, a semi-annual meeting of the heads of state and government of its member states. The AU's secretariat, the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa. The largest city in the AU is Lagos, Nigeria while the list of urban areas in Africa by population, largest urban agglomeration is Cairo, Egypt. The African Union has more than 1.3 billion people and an area of around and includes world landmarks such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information And Communications Technology
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications (telephone lines and wireless signals) and computers, as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware, storage and audiovisual, that enable users to access, store, transmit, understand and manipulate information. ICT is also used to refer to the convergence (telecommunications), convergence of audiovisuals and telephone networks with computer networks through a single cabling or link system. There are large economic incentives to merge the telephone networks with the computer network system using a single unified system of cabling, signal distribution, and management. ICT is an umbrella term that includes any communication device, encompassing radio, television, cell phones, computer and network hardware, satellite systems and so on, as well as the various services and appliances with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |